We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1063
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
==='''Structural Overview'''=== | ==='''Structural Overview'''=== | ||
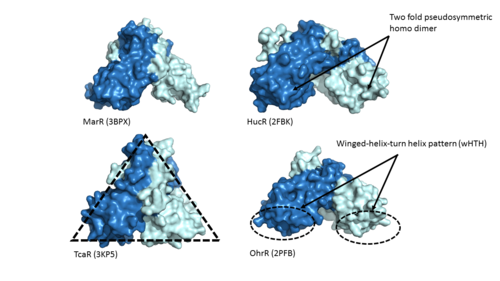
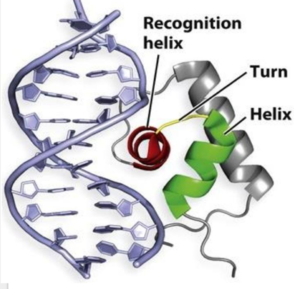
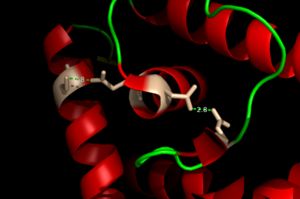
| - | One of the two functional domains of AdcR is the <scene name='69/694230/Dimerization_domain/3'> dimerization domain</scene>. This domain connects and stabilizes the two pseudosymmetric dimers and is composed of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_1/1'>α1 helix</scene>, the C-terminus of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_five/1'>α5 helix</scene> , and the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_6/1'>α6 helix</scene>. This domain is connected to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA-binding_domain DNA binding domain] by the long α5 helix. The DNA binding domain stabilizes the major and minor groove of DNA via the <scene name='69/694230/Whth_4/7'>winged helix-turn-helix (wHTH)</scene> motif. The binding of Zinc to the <scene name='69/694230/2_binding_sites/4'>Zinc binding pocket</scene> induces a conformational change that allows for a <scene name='69/694230/Hydrogen_bonding_1/4'>hydrogen bond network</scene> between 4 specific residues. This network connects multiple helices from the metal binding pockets and DNA binding domain | + | One of the two functional domains of AdcR is the <scene name='69/694230/Dimerization_domain/3'> dimerization domain</scene>. This domain connects and stabilizes the two pseudosymmetric dimers and is composed of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_1/1'>α1 helix</scene>, the C-terminus of the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_five/1'>α5 helix</scene> , and the <scene name='69/694230/Alpha_6/1'>α6 helix</scene>. This domain is connected to the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/DNA-binding_domain DNA binding domain] by the long α5 helix. The DNA binding domain stabilizes the major and minor groove of DNA via the <scene name='69/694230/Whth_4/7'>winged helix-turn-helix (wHTH)</scene> motif. The binding of Zinc to the <scene name='69/694230/2_binding_sites/4'>Zinc binding pocket</scene> induces a conformational change that allows for a <scene name='69/694230/Hydrogen_bonding_1/4'>hydrogen bond network</scene> between 4 specific residues. This network connects multiple helices from the metal binding pockets and DNA binding domain, and is believed play a critical role in the allosteric activation of AdcR, allowing the protein to bind exposed bases along the major and minor grooves of the DNA ligand <ref name="guerra">PMID:22085181</ref>. Thus, the protein is able to perform its biological function by activating transcription after binding DNA. |
Revision as of 18:50, 4 December 2017
Adhesin Competence Regulator
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Sanson M, Makthal N, Flores AR, Olsen RJ, Musser JM, Kumaraswami M. Adhesin competence repressor (AdcR) from Streptococcus pyogenes controls adaptive responses to zinc limitation and contributes to virulence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Jan;43(1):418-32. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1304. Epub 2014 Dec, 15. PMID:25510500 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1304
- ↑ Grove A. MarR family transcription factors. Curr Biol. 2013 Feb 18;23(4):R142-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.013. PMID:23428319 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.013
- ↑ Ma Z, Jacobsen FE, Giedroc DP. Coordination chemistry of bacterial metal transport and sensing. Chem Rev. 2009 Oct;109(10):4644-81. doi: 10.1021/cr900077w. PMID:19788177 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/cr900077w
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 Guerra AJ, Dann CE, Giedroc DP. Crystal Structure of the Zinc-Dependent MarR Family Transcriptional Regulator AdcR in the Zn(II)-Bound State. J Am Chem Soc. 2011 Nov 21. PMID:22085181 doi:10.1021/ja2080532
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Reyes-Caballero H, Guerra AJ, Jacobsen FE, Kazmierczak KM, Cowart D, Koppolu UM, Scott RA, Winkler ME, Giedroc DP. The metalloregulatory zinc site in Streptococcus pneumoniae AdcR, a zinc-activated MarR family repressor. J Mol Biol. 2010 Oct 22;403(2):197-216. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030. Epub 2010, Sep 8. PMID:20804771 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2010.08.030