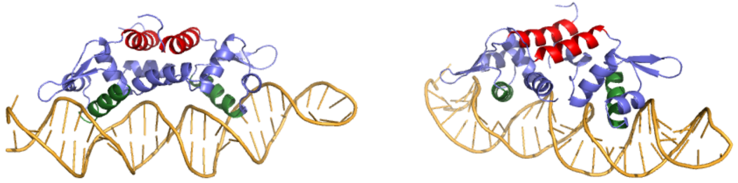is a transcriptional repressor protein responsible for the regulation of the Czr operon in prokaryotes. The best studied example to date comes from Staphylococcus aureus.
Biological Function
Operon Overview
Operons are a critical genetic component of most prokaryotic cells. There are many different operons, responsible for the production of proteins with a wide range of functions. The most well-known and studied operons are the Lac and Trp operons, responsible for producing enzymes which metabolize lactose and tryptophan respectively. Despite many differences in each operon and the proteins that they encode, operons all function in the same general manner (Figure 1). Each operon contains a regulator, an operator, and one or more structural genes. The regulator gene codes for a protein responsible for managing the expression level of the structural genes. The operator contains the binding sequence for RNA polymerase and is the site where transcription begins. Lastly, the structural genes code for proteins to be used elsewhere. The regulator protein (produced as a result of expression of the regulator gene) usually acts in a repressive manner. The regulator protein will bind to the operator gene, inhibiting the binding and/or progression of RNA polymerase to the structural genes, thus inhibiting transcription of the genes into mRNA. If the regulator protein were always active, the structural genes would never be expressed, so there must be a way to inactive the regulator protein, thus enabling expression of the structural genes. This is usually achieved through the binding of an inhibitor to the regulator protein. Since regulator proteins are DNA binding proteins, often this inhibition is allosteric rather than competitive. The inhibitor of the regulator protein binds to somewhere other than the active site of the protein, changing the conformation of the regulator protein to decrease its ability to bind DNA and repress transcription.
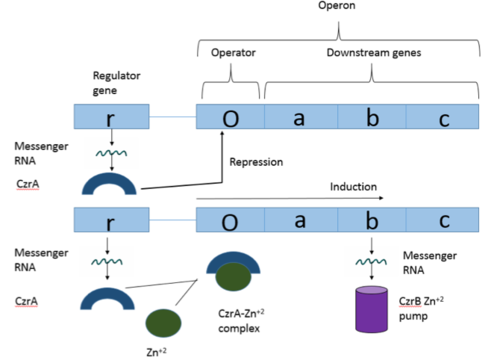
Figure 1: Overview of operon structure
The Czr Operon
The Chromosome determined zinc responsible (Czr) operon acts as described above (Figure 1), with CzrA acting as a regulator protein to the downstream structural gene CzrB[1]. The CzrB gene in turn codes for a Zn+2 pump, the CzrB protein. When relatively low amounts of zinc are present in the cell CzrA will bind to the operator on the Czr operon, preventing the progression of RNA polymerase and thus inhibiting expression of CzrB. Decreased expression of CzrB results in a buildup of Zn+2 inside the cell, as there are fewer pumps to export Zn+2. This metal sensing system serves to maintain an appropriate intracellular concentration of Zn+2.
Structure and Mechanism of Action
Czr A functions as a dimer to repress gene transcription. Each contains seen in purple and displayed in yellow. Key helices regulate the binding of DNA versus Zn+2. The (green) are the location of DNA binding and the (red) contain the Zn+2 binding sites. As Zn+2 ions bind to the alpha 5 helices, the alpha 5 helices move and push the alpha 4 helices into a conformation with low affinity for DNA (Figure 2). Two separate PDB codes exist for Czr A: Czr A with DNA bound (2KJB) and Czr A with zinc+2 bound (2KJC). Unfortunately, zinc ions are not visible in the 2KJC NMR structure that was obtained for Czr A.

Figure 2: Comparison of Czr A bound to DNA to Czr A with Zn
+2 bound with the alpha five helices shown in red and the alpha four helices shown in green
CzrA is allosterically inhibited by the binding of two Zn+2 ions. CzrA displays two different conformations; the first has a high affinity for DNA and has no Zn+2 ions bound to it (PDB code: 2KJB). In this conformation the . Binding of zinc drives a conformational change (PDB code: 2KJC) in which the , changing the overall shape of the protein and significantly lowering its affinity for DNA (Figure 2). This allows for zinc transport to be self regulated. That is, when zinc concentration in the cell is high, zinc ions bind to Czr A, causing a conformational change which releases the bound DNA. DNA without Czr A bound is free to be transcribed and Czr B is again expressed, allowing for Zn+2 transport out of the cell. At low Zn+2 concentrations, Czr A represses RNA Polymerase activity, and Zn+2 ions are maintained inside the cell.
DNA Binding
Ser 54, Ser 57, and His 58 are the primary sites of in Czr A [1]. These residues are likely to interact with the 5'-TGAA sequence found in the half-site of the DNA, where the alpha 4 helices (green) (figure 3). Binding of two Zn+2 ions . Additionally, Val 42 and Gln 53 (lime green) are involved in the . This conclusion was experimentally determined by mutagenesis of the Gln and Val residues with an Ala and measuring the mutant DNA binding capacity. The DNA bound state of Czr A was tested by using the known critical residues for DNA interactions [1]. Gln 53, Val 42 (aqua), Ser 54, Ser 57, and His 58 (lime) were individually mutated to Ala, and kinetic experiments were performed. Compared to wild type Czr A, mutating Gln53 and V42 residues resulted in an 11-fold and 160-fold decrease in Ka, respectively. Mutations to the main DNA interaction sites Ser 54, Ser 57, and His 58 result in binding similar to the inhibited non-DNA binding state, suggesting that these residues are essential to binding DNA. While the conformational change that occurs from the Zinc to DNA bound state of Czr A is small,the alpha 4 helices (shown in green in Figure 2) are slightly shifted. The loss of DNA binding in the mutagenesis experiements in combination with the lack of any other major physical changes between these two states further suggests that the alpha 4 helices are the location of DNA binding in Czr A. Experimental data can be found in table 1 from this same article.
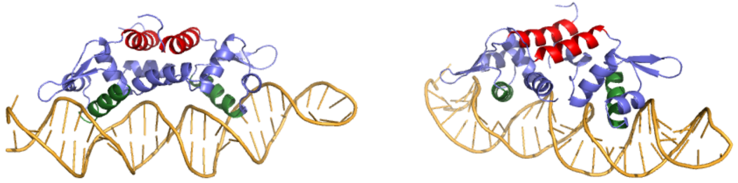
Figure 3: Two views of Czr A bound to DNA. A segment of DNA is shown in orange with the alpha 5 helices displayed in red and the alpha 4 helices shown in green
Zinc Binding
Many zinc-dependent proteins are transcriptional regulators[2]. Czr A fits into this category as an allosteric inhibitor of the czr operon. Two Zn +2 ions may bind to the dimer[1], at the location of the from each monomer. As zinc binds, the alpha 5 helices to inhibit the DNA binding residues (Figure 2). Furthermore, CzrA must be in its dimer form for zinc to bind. The are formed by two residues from each monomer, so Zn+2 cannot bind to the monomer. The is formed by Asp 84 and His 86 from one monomer, and His 97 and His 100 from the other monomer. Zinc ions were not present in the solution NMR structure, so a representation of a zinc ion in the binding pocket can be seen in figure 4. The large number of histidines used in the Czr A zinc pocket is a repetitive and commonly found feature in zinc-binding proteins [3].
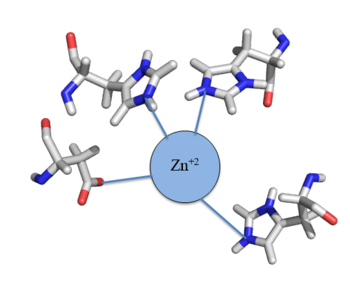
Figure 4: Zn
+2 tetrahedral binding complex
Zn+2 binding is driven by a large entropic gain [4]. Water molecules around the metal ion and Czr A protein are displaced, and gain greater freedom. This gain in entropy allows Zn+2 to bind to Czr A with reasonable affinity and speed in vivo. The zinc+2 ion forms a tetrahedral complex with the four residues (Figure 4), allowing other metal ions to also act as allosteric inhibitors to Czr A. Any metal that may form a tetrahedral complex will have some affinity for Czr A, assuming it is not too large to fit into the pocket. However, the metal binding pocket of Czr A has been optimized to bind Zn+2 with the highest affinity. As Czr A is a transcriptional repressor, binding of Zn+2 to the dimer will activate the czr operon. Zn+2 is preferred as Czr B opens a Zn+2 channel, allowing the excess zinc ions to export the cell.