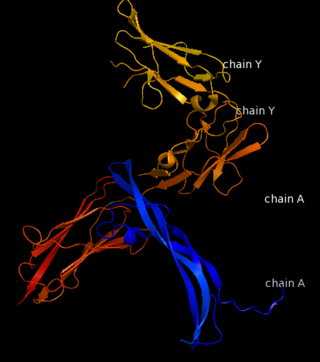
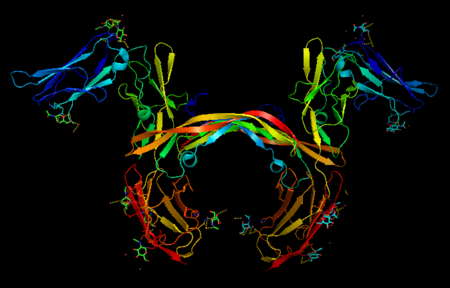
Platelet-derived growth factors and receptors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
-D. Intracellular receptors | -D. Intracellular receptors | ||
| - | { | + | {The monomeric forms of PDGF and PDGF-R are fully functional.} |
-A. TRUE. | -A. TRUE. | ||
+B. FALSE. | +B. FALSE. | ||
| - | { | + | {The dimerization of the subunits, either in the hetero- or homodimerization forms signals for cellular growth.} |
+A. TRUE. | +A. TRUE. | ||
-B. FALSE. | -B. FALSE. | ||
| - | { | + | {PDGFs are functionally important when? (may be more than one answer)} |
+A. In embryonic development | +A. In embryonic development | ||
-B. In making new neurons. | -B. In making new neurons. | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
-D. They are always important during the life cycle, especially as adults. | -D. They are always important during the life cycle, especially as adults. | ||
| - | { | + | {PDGF and PDGF-R are responsible for which of the following? (may be more than one correct answer)} |
-A. signaling cells to lyse. | -A. signaling cells to lyse. | ||
+B. regulating cell propagation, cellular differentiation, cell growth. | +B. regulating cell propagation, cellular differentiation, cell growth. | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
-D. Only propagate cell growth in smooth muscle cells. | -D. Only propagate cell growth in smooth muscle cells. | ||
| - | { | + | {PDGF is composed of how many amino acids?} |
-A. 192. | -A. 192. | ||
-B. 272. | -B. 272. | ||
| Line 66: | Line 66: | ||
+D. 172. | +D. 172. | ||
| - | { | + | {PDGF-R is composed of how many amino acids?} |
_A. 172. | _A. 172. | ||
-B. 298. | -B. 298. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
-D. 350. | -D. 350. | ||
| - | { | + | {The four units making up the PDGF-R complex are completely different proteins } |
-A. TRUE. | -A. TRUE. | ||
+B. FALSE. | +B. FALSE. | ||
| - | { | + | {When the receptors undergo a conformational change what occurs? (may be more than one answer).} |
-A. The molecule bends. | -A. The molecule bends. | ||
-B. Kinase activity hydrolyzes a critical tyrosine residue, thereby "unlocking" the kinase, leading to full enzymatic activity directed toward other tyrosine residues in the receptor molecules as well as other substrates for the kinase.. | -B. Kinase activity hydrolyzes a critical tyrosine residue, thereby "unlocking" the kinase, leading to full enzymatic activity directed toward other tyrosine residues in the receptor molecules as well as other substrates for the kinase.. | ||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
- Hydrolase activity phosphorylates a critical tyrosine residue, thereby "unlocking" the kinase, leading to full enzymatic activity directed toward other tyrosine residues in the receptor molecules as well as other substrates for the kinase. | - Hydrolase activity phosphorylates a critical tyrosine residue, thereby "unlocking" the kinase, leading to full enzymatic activity directed toward other tyrosine residues in the receptor molecules as well as other substrates for the kinase. | ||
| - | { | + | {The extracellular region of the receptor contains______ whereas the intracellular region of the receptor contains_________.} |
-A. 4 hemoglobin type domains; tyrosine kinase domain. | -A. 4 hemoglobin type domains; tyrosine kinase domain. | ||
+B. 5 hemoglobin type domains; tyrosine kinase domain. | +B. 5 hemoglobin type domains; tyrosine kinase domain. | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
-D. 3 hemoglobin type domains; cytosine kinase domain. | -D. 3 hemoglobin type domains; cytosine kinase domain. | ||
| - | { | + | {The PDGF protein contains ________ alpha helix/helices and _______ beta-pleated sheet(s).} |
+A. 1; 8. | +A. 1; 8. | ||
-B. 2, 8. | -B. 2, 8. | ||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
-D. 1; 28. | -D. 1; 28. | ||
| - | { | + | {The extracellular region of the receptor contains______ whereas the intracellular region of the receptor contains_________.} |
-A. 2;19. | -A. 2;19. | ||
-B. 1;29. | -B. 1;29. | ||
Revision as of 22:02, 19 January 2018
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Heldin CH, Ostman A, Eriksson A, Siegbahn A, Claesson-Welsh L, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: isoform-specific signalling via heterodimeric or homodimeric receptor complexes. Kidney Int. 1992 Mar;41(3):571-4. PMID:1315403
- ↑ Shim AH, Liu H, Focia PJ, Chen X, Lin PC, He X. Structures of a platelet-derived growth factor/propeptide complex and a platelet-derived growth factor/receptor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 22;107(25):11307-12. Epub 2010 Jun 2. PMID:20534510
- ↑ Heldin CH, Westermark B. Platelet-derived growth factor: three isoforms and two receptor types. Trends Genet. 1989 Apr;5(4):108-11. PMID:2543106
- ↑ Williams LT. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1564-70. PMID:2538922
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Joel L. Sussman, Lisa Tice, Michal Harel, Angel Herraez, Jaime Prilusky, Alexander Berchansky