We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Poly(A) binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
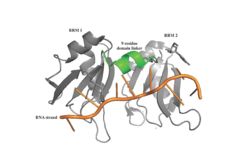
A primary function of PABP is recognizing and interacting with the 3'poly (A) tail created in mRNA processing. As found by EMSA competition experiments, there is a minimum of 11-12 adenosines necessary in the poly (A) tail for the adenosine chain to bind to PABP with high affinity. However, for one biological assembly, a chain containing 9 adenosines sufficiently binds the assembly for crystallization and is shown in the biological assembly structure. The 4 RRM domains that are the primary interacting sites for the adenosine recognition exist as globular domains, each having four antiparallel β-strands and two α-helices. With the N-terminal to C-terminal motifs labeled as S1 to S4 for the β-strands and H1 to H2 for the α-helices, the strands are spatially arranged as S2-S3-S1-S4. Furthermore, there are two conserved sequences in each RRM, called RNP1 and 2. RNP 1 consists of a conserved sequence of 8 residues, while RNP2 consists of a conserved sequence of 6 residues. Much of the weak intermolecular interactions with adenosine from the RRMs occur from the <scene name='78/781946/Rnp1_rnp2_primary_a_binding/1'>RNP1 and RNP2</scene> conserved sequences, which correspond to the two central β-strands, with specific interactions shown in Figure 2.The support for adenosine recognition by the RRMs occurs as a type of binding trough with the sheets, primarily <scene name='78/781946/Rnp1_rnp2_primary_a_binding/1'>RNP1 and RNP2 forming the Primary Binding Trough</scene>, and the interstrand loop between β-strands 2 and 3 as well as the domain linker forming the <scene name='78/781946/Adenosine_binding_wall/1'> Adenosine Binding Wall</scene>. Additionally, the primary binding trough is stabilized by <scene name='78/781946/Rrm1_2_packing_intxn/2'>Stabilizing Packing Interactions of RRM1 RRM2 Binding Trough</scene>. | A primary function of PABP is recognizing and interacting with the 3'poly (A) tail created in mRNA processing. As found by EMSA competition experiments, there is a minimum of 11-12 adenosines necessary in the poly (A) tail for the adenosine chain to bind to PABP with high affinity. However, for one biological assembly, a chain containing 9 adenosines sufficiently binds the assembly for crystallization and is shown in the biological assembly structure. The 4 RRM domains that are the primary interacting sites for the adenosine recognition exist as globular domains, each having four antiparallel β-strands and two α-helices. With the N-terminal to C-terminal motifs labeled as S1 to S4 for the β-strands and H1 to H2 for the α-helices, the strands are spatially arranged as S2-S3-S1-S4. Furthermore, there are two conserved sequences in each RRM, called RNP1 and 2. RNP 1 consists of a conserved sequence of 8 residues, while RNP2 consists of a conserved sequence of 6 residues. Much of the weak intermolecular interactions with adenosine from the RRMs occur from the <scene name='78/781946/Rnp1_rnp2_primary_a_binding/1'>RNP1 and RNP2</scene> conserved sequences, which correspond to the two central β-strands, with specific interactions shown in Figure 2.The support for adenosine recognition by the RRMs occurs as a type of binding trough with the sheets, primarily <scene name='78/781946/Rnp1_rnp2_primary_a_binding/1'>RNP1 and RNP2 forming the Primary Binding Trough</scene>, and the interstrand loop between β-strands 2 and 3 as well as the domain linker forming the <scene name='78/781946/Adenosine_binding_wall/1'> Adenosine Binding Wall</scene>. Additionally, the primary binding trough is stabilized by <scene name='78/781946/Rrm1_2_packing_intxn/2'>Stabilizing Packing Interactions of RRM1 RRM2 Binding Trough</scene>. | ||
| - | [[Image: Adenosine_backbone.png |250 px|right|thumb|Figure 3: Basic residues of RRM 1 and 2 make stabilizing electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged adenosine phosphates. ]] | + | [[Image: Adenosine_backbone.png |250 px|right|thumb|Figure 3: Basic residues of RRM 1 and 2 (shown in blue) make stabilizing electrostatic interactions with the negatively charged adenosine phosphates. ]] |
====Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns==== | ====Adenosine Stabilization Interaction Patterns==== | ||
Revision as of 04:29, 29 March 2018
Poly(A) binding protein
Structure
| |||||||||||