Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Acetyl-CoA carboxylase''' (ACC) catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is a building block in in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. ACC is biotin- and ATP-dependent enzyme. In mammals, 2 forms of ACC exist. ACC1 and ACC2 differ in their tissue distribution and function. | '''Acetyl-CoA carboxylase''' (ACC) catalyzes the irreversible carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA. Malonyl-CoA is a building block in in the biosynthesis of fatty acids. ACC is biotin- and ATP-dependent enzyme. In mammals, 2 forms of ACC exist. ACC1 and ACC2 differ in their tissue distribution and function. | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
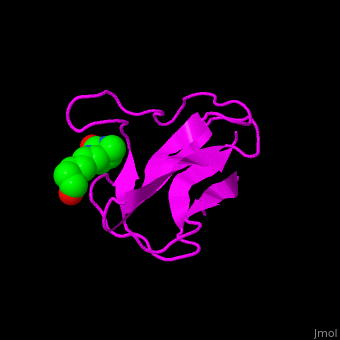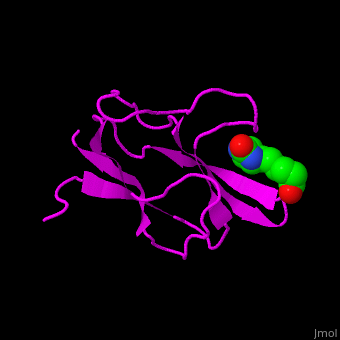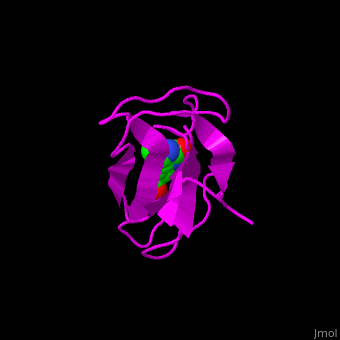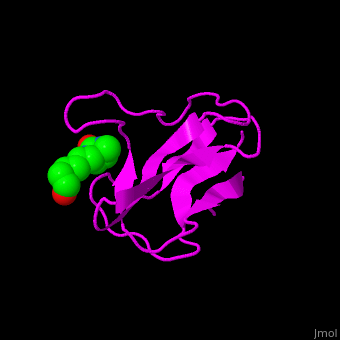
| - | ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in prokaryotes and plants. Each subunit catalyzes different reaction. These are – '''biotin carboxylase''' (BC) which carboxylates the biotin prosthetic group, '''biotin carboxyl carrier protein''' (BCCP) which is linked covalently to biotin and '''carboxyltransferase''' (CT) which transfers the carboxyl group from biotin to acetyl-CoA. In eukaryotes these functions are performed by a single polypeptide chain. The biotin moiety is located in the beta turn connecting the N and C halves of BCCP. <scene name='49/492046/Cv/6'>E.coli biotin carboxylase complex with biotin</scene> ([[1bdo]]) is shown. <ref>PMID:8747466</ref> | + | ACC is a multi-subunit enzyme in prokaryotes and plants. Each subunit catalyzes different reaction. These are – '''biotin carboxylase''' (BC) which carboxylates the biotin prosthetic group, '''biotin carboxyl carrier protein''' (BCCP) which is linked covalently to biotin and '''carboxyltransferase''' (CT) which transfers the carboxyl group from biotin to acetyl-CoA. In eukaryotes these functions are performed by a single polypeptide chain. The biotin moiety is located in the beta turn connecting the N and C halves of BCCP. <scene name='49/492046/Cv/6'>E.coli biotin carboxylase complex with biotin</scene> ([[1bdo]]) is shown. <ref>PMID:8747466</ref> Water molecules shown as red spheres. |
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 13:38, 16 April 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of acetyl-CoA carboxylase
Updated on 16-April-2018
References
- ↑ Athappilly FK, Hendrickson WA. Structure of the biotinyl domain of acetyl-coenzyme A carboxylase determined by MAD phasing. Structure. 1995 Dec 15;3(12):1407-19. PMID:8747466