This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox GGC14
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
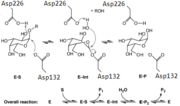
This a-Galactosidase, along with Human a-Galactosidase, reacts via a double displacement mechanism. Asp132 acts as the nucleophile while Asp226 functions as the acid/base catalyst.<ref>DOI 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.062</ref> | This a-Galactosidase, along with Human a-Galactosidase, reacts via a double displacement mechanism. Asp132 acts as the nucleophile while Asp226 functions as the acid/base catalyst.<ref>DOI 10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.062</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Mechanism_Pic2.png | thumb]] | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 11:10, 23 April 2018
1T0O - a-Galactosidase from Trichoderma reesei and Complex with Galactose
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ Guce AI, Clark NE, Salgado EN, Ivanen DR, Kulminskaya AA, Brumer H 3rd, Garman SC. Catalytic mechanism of human alpha-galactosidase. J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 5;285(6):3625-32. Epub 2009 Nov 25. PMID:19940122 doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.060145
- ↑ Golubev AM, Nagem RA, Brandao Neto JR, Neustroev KN, Eneyskaya EV, Kulminskaya AA, Shabalin KA, Savel'ev AN, Polikarpov I. Crystal structure of alpha-galactosidase from Trichoderma reesei and its complex with galactose: implications for catalytic mechanism. J Mol Biol. 2004 May 28;339(2):413-22. PMID:15136043 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.03.062