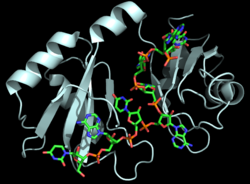
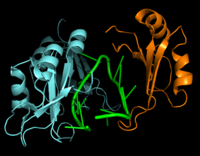
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
=Relationship to other proteins= | =Relationship to other proteins= | ||
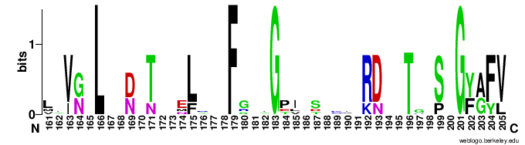
| - | The RNP-type RBD is found in many proteins involved in post-transcriptional [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-transcriptional_modification pre-mRNA processing] (5'-end capping, splicing, 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation, and transport from the nucleus)<ref name="RRMB">PMID: 18515081</ref>. The unique RBD of Hrp1 enables the protein to bind an RNA sequence that differs in both length and content from the RNA sequences of other RNA-binding and mRNA processing proteins such as [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2sxl sex lethal], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poly(A)-binding_protein Poly (A)-binding protein (PABP)], and [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1fxl HuD] <ref name="GM3H"/>. These proteins, in addition to Hrp1 and Srp20, | + | The RNP-type RBD is found in many proteins involved in post-transcriptional [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Post-transcriptional_modification pre-mRNA processing] (5'-end capping, splicing, 3'-end cleavage and polyadenylation, and transport from the nucleus)<ref name="RRMB">PMID: 18515081</ref>. The unique RBD of Hrp1 enables the protein to bind an RNA sequence that differs in both length and content from the RNA sequences of other RNA-binding and mRNA processing proteins such as [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2sxl sex lethal], [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Poly(A)-binding_protein Poly (A)-binding protein (PABP)], and [http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/1fxl HuD] <ref name="GM3H"/>. These proteins, in addition to Hrp1 and Srp20, contain conserved hydrophobic residues which contribute to hydrophobic interactions between secondary structures of the proteins. Each protein also contains conserved residues L166 and G201 which form a hydrogen bond, linking the β-sheets in the βαβ complex of Hrp1 (Figure 3). [[Image:Conserved_Hrp1_sequence_logo.png|525 px|center|thumb|Figure 3: Sequence logo for residues 161-205 of Hrp1.]] Like Hrp1, each of these proteins belongs to the class of single-stranded proteins composed of two canonical RBDs; however, each protein is differentiated by respective target RNA sequences, interactions with RNA at the atomic level, and interdomain contacts <ref name="GM3H"/>. Hrp1 is unique in that HuD, sex lethal, and PABP all contain at least one intra-RNA base-base stacking interaction, a feature that is lacking in the Hrp1-PEE complex <ref name="GM3H"/>. It is possible that the intra-RNA interactions found in these other protein-RNA complexes is replaced by the crucial Trp168-Ade4 stacking interaction found in the Hrp1 complex <ref name="GM3H"/>. This may help explain why the Hrp1-RNA interface involves only 6 nucleotides whereas PABP, sex lethal, and HuD require a longer 8-10 nucleotide sequence in the RNA binding pocket <ref name="GM3H"/>. |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 02:27, 24 April 2018
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 Perez-Canadillas JM. Grabbing the message: structural basis of mRNA 3'UTR recognition by Hrp1. EMBO J. 2006 Jul 12;25(13):3167-78. Epub 2006 Jun 22. PMID:16794580
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Leeper TC, Qu X, Lu C, Moore C, Varani G. Novel protein-protein contacts facilitate mRNA 3'-processing signal recognition by Rna15 and Hrp1. J Mol Biol. 2010 Aug 20;401(3):334-49. Epub 2010 Jun 19. PMID:20600122 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.032
- ↑ Kessler MM, Henry MF, Shen E, Zhao J, Gross S, Silver PA, Moore CL. Hrp1, a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, is required for mRNA 3'-end formation in yeast. Genes Dev. 1997 Oct 1;11(19):2545-56. PMID:9334319
- ↑ Clery A, Blatter M, Allain FH. RNA recognition motifs: boring? Not quite. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Jun;18(3):290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002. PMID:18515081 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Cory A. Wuerch, Matthew Douglas Moore, Savannah Davis, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky