User:Khadar Abdi/Sandbox1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Function/Mechanism == | == Function/Mechanism == | ||
| - | '''Threonyl t-RNA Synthetase''' or '''Threonyl-tRNA ligase''' or '''TARS''' is class II '''Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase''' enzymes. These enzymes primary function are The main function of the enzyme is to add Threonine amino acid (Thr) to threonine specific tRNA (tRNA-thr) a necessity prep for the protein synthesis pathway. Below displays the overview of the Aminoacylation rxn<ref>PMID:29305884</ref> | + | '''Threonyl t-RNA Synthetase''' or '''Threonyl-tRNA ligase''' or '''TARS''' is class II '''Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase''' enzymes. These enzymes primary function are The main function of the enzyme is to add Threonine amino acid (Thr) to threonine specific tRNA (tRNA-thr) a necessity prep for the protein synthesis pathway. Below displays the overview of the Aminoacylation rxn<ref>PMID:29305884</ref>[[Image:TARS_protein_rxn.jpeg |left|thumb|500px| '''Overall TARS protein rxn. Substrates includes Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), Threonine (Thr) and threonine specific transfer Ribonucleic Acid (tRNA-thr).''']] |
| - | + | ||
| - | [[Image:TARS_protein_rxn.jpeg |left|thumb|500px| '''Overall TARS protein rxn. Substrates includes Adenosine triphosphate (ATP), Threonine (Thr) and threonine specific transfer Ribonucleic Acid (tRNA-thr).''']] | + | |
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
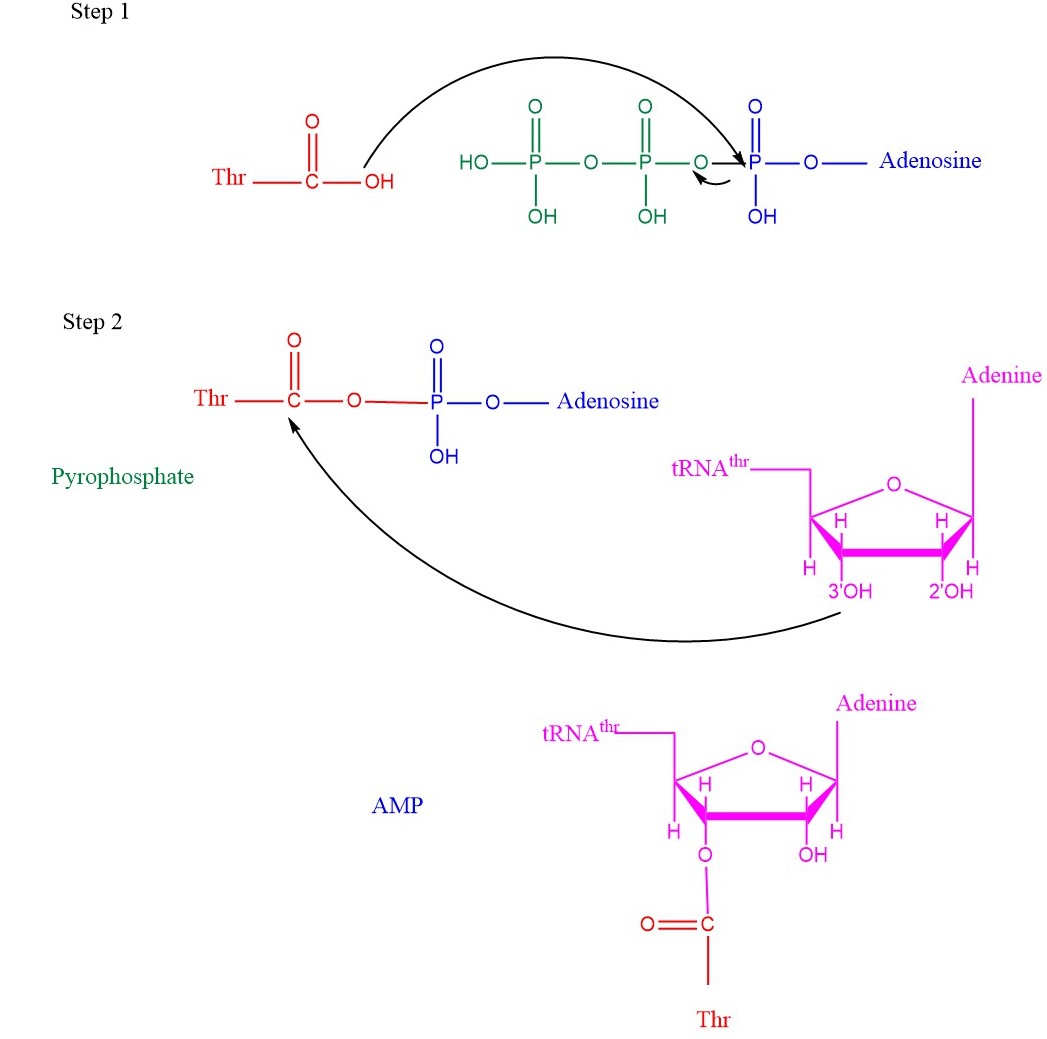
| - | TARS adds amino acid to tRNA by a two-step mechanism. First the enzyme binds to both Threonine and ATP in the catalytic domain to perform an adenylation reaction in which pyrophosphate is released as a byproduct. This is then follow up by a transferring Thr from Adenosine monophosphate molecule to 3'OH site of tRNA-thr. <ref>Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2000). ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry.'' New York: Worth Publishers.</ref> Image below demonstrates the arrow pushing occuring to generate threonine bound tRNA-thr.[[Image:TARSmechanism.jpg]] | + | TARS adds amino acid to tRNA by a two-step mechanism. First the enzyme binds to both Threonine and ATP in the catalytic domain to perform an adenylation reaction in which pyrophosphate is released as a byproduct. This is then follow up by a transferring Thr from Adenosine monophosphate molecule to 3'OH site of tRNA-thr. <ref>Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., & Cox, M. M. (2000). ''Lehninger principles of biochemistry.'' New York: Worth Publishers.</ref> Image below demonstrates the arrow pushing occuring to generate threonine bound tRNA-thr. |
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:TARSmechanism.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 18:37, 28 April 2018
Threonyl-tRNA Synthetase/ligase
| |||||||||||