We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Christian Fjeld/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
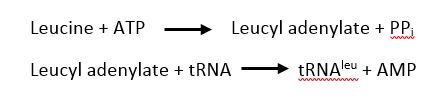
The <scene name='78/786656/Ls/1'>leucine-specific domain</scene>, specifically the KMSKS loop, plays a major role in catalysis in many species. The domain is highly variable between species but the KMSKS loop is highly conserved<ref>doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317</ref>. In catalysis the domain functions by closing over the 3' terminal adenine of the tRNA, closing the catalytic site and allowing catalysis to take place. | The <scene name='78/786656/Ls/1'>leucine-specific domain</scene>, specifically the KMSKS loop, plays a major role in catalysis in many species. The domain is highly variable between species but the KMSKS loop is highly conserved<ref>doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317</ref>. In catalysis the domain functions by closing over the 3' terminal adenine of the tRNA, closing the catalytic site and allowing catalysis to take place. | ||
| - | In ''E.coli'' the leucine-specific domain is composed of 2 3-strand antiparallel β-sheets and pivots on a flexible loop. The KMSKS loop spans residues 619-623 and can contact A76 of the tRNA within the catalytic site<ref>doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317</ref>. There is also a β-hairpin in ''E. coli'' that contacts bases 10 and 27 of the tRNA<ref>doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317</ref>. | + | In ''E.coli'' the leucine-specific domain is composed of 2 3-strand antiparallel β-sheets and pivots on a flexible loop. The KMSKS loop spans residues 619-623 and can contact A76 of the tRNA within the catalytic site<ref>doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317</ref>. There is also a β-hairpin in ''E. coli'' that contacts bases 10 and 27 of the tRNA for stabilization<ref>doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317</ref>. |
Revision as of 15:23, 2 May 2018
| |||||||||||
3D Structure of LARS
Updated on 02-May-2018
References
- ↑ Mirande M. The Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Complex. Subcell Biochem. 2017;83:505-522. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_18. PMID:28271488 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46503-6_18
- ↑ Han JM, Kim JY, Kim S. Molecular network and functional implications of macromolecular tRNA synthetase complex. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003 Apr 18;303(4):985-93. doi: , 10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00485-6. PMID:12684031 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0006-291x(03)00485-6
- ↑ Raina M, Elgamal S, Santangelo TJ, Ibba M. Association of a multi-synthetase complex with translating ribosomes in the archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis. FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 30;586(16):2232-8. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.039. Epub, 2012 Jun 7. PMID:22683511 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.039
- ↑ Han JM, Jeong SJ, Park MC, Kim G, Kwon NH, Kim HK, Ha SH, Ryu SH, Kim S. Leucyl-tRNA synthetase is an intracellular leucine sensor for the mTORC1-signaling pathway. Cell. 2012 Apr 13;149(2):410-24. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.044. Epub 2012 Mar, 15. PMID:22424946 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.044
- ↑ Seiradake E, Mao W, Hernandez V, Baker SJ, Plattner JJ, Alley MR, Cusack S. Crystal structures of the human and fungal cytosolic Leucyl-tRNA synthetase editing domains: A structural basis for the rational design of antifungal benzoxaboroles. J Mol Biol. 2009 Jul 10;390(2):196-207. Epub 2009 May 6. PMID:19426743 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.073
- ↑ Palencia A, Crepin T, Vu MT, Lincecum TL Jr, Martinis SA, Cusack S. Structural dynamics of the aminoacylation and proofreading functional cycle of bacterial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 10. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317. PMID:22683997 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2317
- ↑ Cusack S, Yaremchuk A, Tukalo M. The 2 A crystal structure of leucyl-tRNA synthetase and its complex with a leucyl-adenylate analogue. EMBO J. 2000 May 15;19(10):2351-61. PMID:10811626 doi:10.1093/emboj/19.10.2351
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00098-4
- ↑ Seiradake E, Mao W, Hernandez V, Baker SJ, Plattner JJ, Alley MR, Cusack S. Crystal structures of the human and fungal cytosolic Leucyl-tRNA synthetase editing domains: A structural basis for the rational design of antifungal benzoxaboroles. J Mol Biol. 2009 Jul 10;390(2):196-207. Epub 2009 May 6. PMID:19426743 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.073
- ↑ Seiradake E, Mao W, Hernandez V, Baker SJ, Plattner JJ, Alley MR, Cusack S. Crystal structures of the human and fungal cytosolic Leucyl-tRNA synthetase editing domains: A structural basis for the rational design of antifungal benzoxaboroles. J Mol Biol. 2009 Jul 10;390(2):196-207. Epub 2009 May 6. PMID:19426743 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.073
- ↑ Liu Y, Liao J, Zhu B, Wang ED, Ding J. Crystal structures of the editing domain of Escherichia coli leucyl-tRNA synthetase and its complexes with Met and Ile reveal a lock-and-key mechanism for amino acid discrimination. Biochem J. 2006 Mar 1;394(Pt 2):399-407. PMID:16277600 doi:10.1042/BJ20051249
- ↑ Palencia A, Crepin T, Vu MT, Lincecum TL Jr, Martinis SA, Cusack S. Structural dynamics of the aminoacylation and proofreading functional cycle of bacterial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 10. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317. PMID:22683997 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2317
- ↑ Palencia A, Crepin T, Vu MT, Lincecum TL Jr, Martinis SA, Cusack S. Structural dynamics of the aminoacylation and proofreading functional cycle of bacterial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 10. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317. PMID:22683997 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2317
- ↑ Palencia A, Crepin T, Vu MT, Lincecum TL Jr, Martinis SA, Cusack S. Structural dynamics of the aminoacylation and proofreading functional cycle of bacterial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 10. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317. PMID:22683997 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2317
- ↑ Palencia A, Crepin T, Vu MT, Lincecum TL Jr, Martinis SA, Cusack S. Structural dynamics of the aminoacylation and proofreading functional cycle of bacterial leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Jun 10. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2317. PMID:22683997 doi:10.1038/nsmb.2317