User:Patrick Wiencek/AHNAK
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
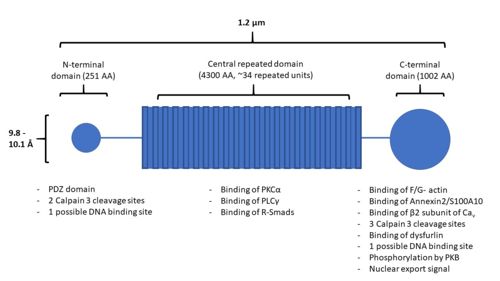
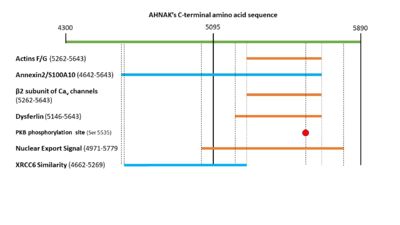
PKB will phosphorylate serine 5535 in AHNAK’s C-terminal domain <ref name="a6" />. This will activate AHNAK’s nuclear export signal, allowing it to move out of the nucleus. AHNAK’s nuclear export signal is made up of 5 different motifs in the C-terminal domain: (4971-4979), (5019-5027), (5034-5039), (5706-5716), and (5772-5779) <ref name="a18">AHNAK - Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK - Homo sapiens (Human) - AHNAK gene & protein. Available at: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q09666#ptm_processing. (Accessed: 1st May 2018)</ref>. | PKB will phosphorylate serine 5535 in AHNAK’s C-terminal domain <ref name="a6" />. This will activate AHNAK’s nuclear export signal, allowing it to move out of the nucleus. AHNAK’s nuclear export signal is made up of 5 different motifs in the C-terminal domain: (4971-4979), (5019-5027), (5034-5039), (5706-5716), and (5772-5779) <ref name="a18">AHNAK - Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK - Homo sapiens (Human) - AHNAK gene & protein. Available at: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q09666#ptm_processing. (Accessed: 1st May 2018)</ref>. | ||
*'''Protein Kinase C α (PKCα)''' | *'''Protein Kinase C α (PKCα)''' | ||
| - | PKCα will bind to and is activated by AHNAK < | + | PKCα will bind to and is activated by AHNAK <ref name="a19">PMID:18174170</ref>. This interaction occurs in AHNAK’s central repeated domain (3859-4412). |
*'''Phospholipase C γ (PLCγ)''' | *'''Phospholipase C γ (PLCγ)''' | ||
| - | PLCγ will bind AHNAK in its central repeated domain in residues 3740-3882 and 3859-4412 < | + | PLCγ will bind AHNAK in its central repeated domain in residues 3740-3882 and 3859-4412 <ref name="a20">PMID:10318799</ref>. AHNAK also activated bound PLCγ. |
*'''Regulatory Samds (R-Smads)''' | *'''Regulatory Samds (R-Smads)''' | ||
| - | The MH2 domain of Smad2 will bind to the central repetitive domain of AHNAK from residues 4105-4633 < | + | The MH2 domain of Smad2 will bind to the central repetitive domain of AHNAK from residues 4105-4633 <ref name="a21">DOI:10.1038/onc.2014.69</ref>. |
| - | It is also of not that AHNAK does not have a calcium binding domain, despite it responding to calcium signaling. Calcium sensing might be facilitated by AHNAK’s interaction with annexin 2, which is calcium sensitive <ref name="a1" />< | + | It is also of not that AHNAK does not have a calcium binding domain, despite it responding to calcium signaling. Calcium sensing might be facilitated by AHNAK’s interaction with annexin 2, which is calcium sensitive <ref name="a1" /><ref name="a22">DOI:10.1155/2012/852430</ref><ref name="a23">PMID:21949189</ref>. |
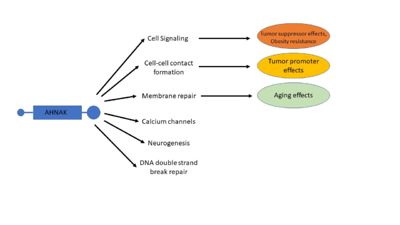
== '''Function''' == | == '''Function''' == | ||
Revision as of 20:34, 4 May 2018
AHNAK
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 Davis TA, Loos B, Engelbrecht AM. AHNAK: the giant jack of all trades. Cell Signal. 2014 Dec;26(12):2683-93. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.08.017. Epub, 2014 Aug 27. PMID:25172424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.08.017
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Hashimoto T, Amagai M, Parry DA, Dixon TW, Tsukita S, Tsukita S, Miki K, Sakai K, Inokuchi Y, Kudoh J, et al.. Desmoyokin, a 680 kDa keratinocyte plasma membrane-associated protein, is homologous to the protein encoded by human gene AHNAK. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105 ( Pt 2):275-86. PMID:8408266
- ↑ Chen B, Wang J, Dai D, Zhou Q, Guo X, Tian Z, Huang X, Yang L, Tang H, Xie X. AHNAK suppresses tumour proliferation and invasion by targeting multiple pathways in triple-negative breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 May 12;36(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0522-4. PMID:28494797 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0522-4
- ↑ Zhao Z, Xiao S, Yuan X, Yuan J, Zhang C, Li H, Su J, Wang X, Liu Q. AHNAK as a Prognosis Factor Suppresses the Tumor Progression in Glioma. J Cancer. 2017 Aug 25;8(15):2924-2932. doi: 10.7150/jca.20277. eCollection 2017. PMID:28928883 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7150/jca.20277
- ↑ Davis T, van Niekerk G, Peres J, Prince S, Loos B, Engelbrecht AM. Doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer: A novel role for the human protein AHNAK. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;148:174-183. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.012. Epub, 2018 Jan 5. PMID:29309757 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.012
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Sussman J, Stokoe D, Ossina N, Shtivelman E. Protein kinase B phosphorylates AHNAK and regulates its subcellular localization. J Cell Biol. 2001 Sep 3;154(5):1019-30. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200105121. PMID:11535620 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200105121
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Benaud C, Gentil BJ, Assard N, Court M, Garin J, Delphin C, Baudier J. AHNAK interaction with the annexin 2/S100A10 complex regulates cell membrane cytoarchitecture. J Cell Biol. 2004 Jan 5;164(1):133-44. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200307098. Epub 2003 Dec , 29. PMID:14699089 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200307098
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Shtivelman E, Cohen FE, Bishop JM. A human gene (AHNAK) encoding an unusually large protein with a 1.2-microns polyionic rod structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5472-6. PMID:1608957
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Cell atlas - AHNAK - The Human Protein Atlas. Available at: http://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000124942-AHNAK/cell. (Accessed: 30th April 2018)
- ↑ Komuro A, Masuda Y, Kobayashi K, Babbitt R, Gunel M, Flavell RA, Marchesi VT. The AHNAKs are a class of giant propeller-like proteins that associate with calcium channel proteins of cardiomyocytes and other cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Mar 23;101(12):4053-8. doi:, 10.1073/pnas.0308619101. Epub 2004 Mar 8. PMID:15007166 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308619101
- ↑ Lee HJ, Zheng JJ. PDZ domains and their binding partners: structure, specificity, and modification. Cell Commun Signal. 2010 May 28;8:8. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-8-8. PMID:20509869 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-8-8
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 de Morree A, Droog M, Grand Moursel L, Bisschop IJ, Impagliazzo A, Frants RR, Klooster R, van der Maarel SM. Self-regulated alternative splicing at the AHNAK locus. FASEB J. 2012 Jan;26(1):93-103. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-187971. Epub 2011 Sep 22. PMID:21940993 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.11-187971
- ↑ Hohaus A, Person V, Behlke J, Schaper J, Morano I, Haase H. The carboxyl-terminal region of ahnak provides a link between cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels and the actin-based cytoskeleton. FASEB J. 2002 Aug;16(10):1205-16. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0855com. PMID:12153988 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1096/fj.01-0855com
- ↑ Huang, Y. et al. Calpain 3 is a modulator of the dysferlin protein complex in skeletal muscle. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17, 1855–1866 (2008).
- ↑ Huang, Y. et al. AHNAK, a novel component of the dysferlin protein complex, redistributes to the cytoplasm with dysferlin during skeletal muscle regeneration. FASEB J. 21, 732–742 (2006).
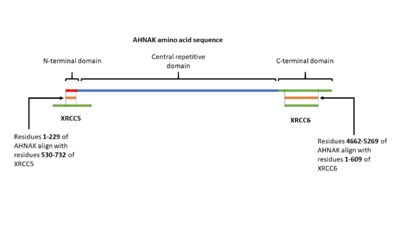
- ↑ Stiff T, Shtivelman E, Jeggo P, Kysela B. AHNAK interacts with the DNA ligase IV-XRCC4 complex and stimulates DNA ligase IV-mediated double-stranded ligation. DNA Repair (Amst). 2004 Mar 4;3(3):245-56. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2003.11.001. PMID:15177040 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2003.11.001
- ↑ EMBOSS Needle < Pairwise Sequence Alignment < EMBL-EBI. Available at: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/psa/emboss_needle/. (Accessed: 2nd May 2018)
- ↑ AHNAK - Neuroblast differentiation-associated protein AHNAK - Homo sapiens (Human) - AHNAK gene & protein. Available at: https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q09666#ptm_processing. (Accessed: 1st May 2018)
- ↑ Lee IH, Lim HJ, Yoon S, Seong JK, Bae DS, Rhee SG, Bae YS. Ahnak protein activates protein kinase C (PKC) through dissociation of the PKC-protein phosphatase 2A complex. J Biol Chem. 2008 Mar 7;283(10):6312-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M706878200. Epub 2008, Jan 3. PMID:18174170 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M706878200
- ↑ Sekiya F, Bae YS, Jhon DY, Hwang SC, Rhee SG. AHNAK, a protein that binds and activates phospholipase C-gamma1 in the presence of arachidonic acid. J Biol Chem. 1999 May 14;274(20):13900-7. PMID:10318799
- ↑ Lee IH, Sohn M, Lim HJ, Yoon S, Oh H, Shin S, Shin JH, Oh SH, Kim J, Lee DK, Noh DY, Bae DS, Seong JK, Bae YS. Ahnak functions as a tumor suppressor via modulation of TGFbeta/Smad signaling pathway. Oncogene. 2014 Sep 18;33(38):4675-84. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.69. Epub 2014 Mar 24. PMID:24662814 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.69
- ↑ Grieve AG, Moss SE, Hayes MJ. Annexin A2 at the interface of actin and membrane dynamics: a focus on its roles in endocytosis and cell polarization. Int J Cell Biol. 2012;2012:852430. doi: 10.1155/2012/852430. Epub 2012 Feb 22. PMID:22505935 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/852430
- ↑ Rezvanpour A, Santamaria-Kisiel L, Shaw GS. The S100A10-annexin A2 complex provides a novel asymmetric platform for membrane repair. J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 18;286(46):40174-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.244038. Epub, 2011 Sep 26. PMID:21949189 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.244038