|
Introduction
Purine-rich element binding protein alpha (Purα) is a transcription factor with a molecular weight of ~35 kDa encoded by the PURA gene. It possesses ATP-independent dsDNA unwinding activity, and is known to bind sequence-specific purine-rich regions of ssDNA and ssRNA, recognizing GGN motifs. Purα is a member of the PUR family of proteins, which includes Purβ and two isoforms of Purγ. In its functional dimeric form Purα is known to repress expression of smooth muscle alpha actin (SMαA) encoded by the Acta2 gene. It is also known to be involved in DNA replication and cell cycle regulation, as well as mRNA translation. It plays a crucial role in nervous system development, and has been implicated in two neurological diseases: PURA syndrome and Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) (see Disease section).[1]
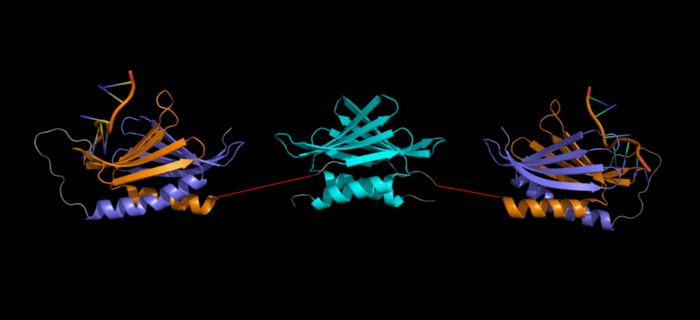 Artist representation of a Purα homodimer (linkers between repeats I-II and III (red) were drawn in PowerPoint and are NOT to scale). NOTE: This is NOT a verified model, but a rough placement to show all three repeats together. It is not known what the orientation of these domains are relative to one another. (Repeat I-II ( 5fgp): purple (I) and orange (II), repeat III ( 5fgo): cyan). Structure
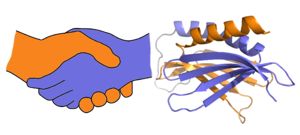 A PUR domain is analogous to a left-handed handshake. PUR repeat I-II represented from 5fgp. Purα functions as a dimer composed of two intramolecular domains and one intermolecular domain. The Purα monomer contains three semi-conserved repeated amino acid sequences, named in order from N->C: PUR repeats I, II, and III. These repeats fold to form two domains: associating to form the I-II domain or “intramolecular domain”, while facilitates dimerization through association with a repeat III from a second Purα monomer or repeat III of Purβ, forming an "intermolecular domain". Each PUR repeat is connected by a flexible linker region of 10-20 amino acids, depending on the species, linker and algorithm used to determine repeats. Each PUR repeat contains a beta-sheet composed of four beta-strands, followed by a single alpha-helix. While Purα is not yet officially classified by SCOP or CATH, its structure is that of an α+β protein.
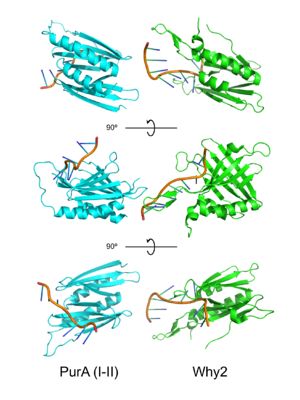 PUR domains are structurally similar to the fold in Whirly proteins. Left: PUR repeat I-II ( 5fgp), right: WHY2 ( 3n1k). The domains of Purα have been described as "Whirly-like" folds because of their structural similarity to the DNA-binding Whirly class of proteins found in plants.[2] Whirlys are also ssDNA binding proteins, however unlike PUR family proteins they are not sequence-specific.
The 2016 X-ray crystal structure of Purα repeat I-II (5fgp) shows DNA bound between repeats I and II. Residues indicated by this crystal structure to be involved in protein-DNA binding are: ; . K54 (repeat I) and K138 (repeat II) interact with the phosphate backbone, while Q52 (repeat I), S53 (repeat I), K54 (repeat I), R142 (repeat II), and N140 (repeat II) hydrogen bond directly with the DNA bases. Interestingly all bases appear to be stabilized by stacking interactions within the DNA strand except G4 which stacks directly with F145 in repeat II of the protein. This disrupts base-stacking within the DNA resulting in the neighboring cytosine being flipped out, introducing a strong kink in the DNA strand. This base-stacking interruption was shown to be responsible for Purα's DNA-unwinding activity by EMSA using a F145 mutant.[3]
Function
Purα binds to single stranded purine-rich regions of DNA or RNA. In particular, Purα (and Purβ) are known to bind the purine-rich tract containing an MCAT enhancer motif in the 5’ region of the sense strand of the smooth muscle alpha actin gene (Acta2). Purα functions as a repressor at both transcriptional and translational levels. At the level of transcription Purα (and Purβ) act in concert with Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1 in humans or MSY1 in mice) which binds the antisense pyrimidine-rich strand, together acting to repress Acta2 expression. At the level of translation Purα, Purβ and MSY-1 (YB-1 in humans) have been shown to bind a region in exon 3 of Acta2 mRNA that is structurally similar to the MCAT (AGGAATG) enhancer element and prevent transcription in fibroblasts.[4]
PurA has also been shown to enhance expression of myelin basic protein (MBP) in developing mouse brain tissue through its binding to an MB1 regulatory motif -15 to -40 nucleotides upstream of the transcription start site. MBP is an important protein found in myelin sheaths of the central nervous system.[5]
High-affinity nucleic acid-binding function is dependent on Purα dimerization. Purα forms homodimers in addition to heterodimers with Purβ. PurA is known to repress various genes including SMαA.
, Y57 (repeat I) and F145 (repeat II), located on the solvent-exposed surface of the beta-sheets, contribute to the DNA unwinding activity of Purα through base stacking interactions with DNA bases.[6] Although not shown in the 5fgp PDB file, Y57 interacts with a second strand of DNA via base stacking interactions with guanine. It was presumably omitted because repeat I has significantly less affinity for purine-rich DNA than does repeat II, and it is believed that most of the DNA binding and unwinding activity occurs via interactions of DNA with the beta-sheet of repeat II.[7] that could undergo base-stacking interactions with DNA, however Weber, et al. observed negligible unwinding activity in this repeat.[8] Furthermore, this group found repeat III to bind ssDNA with significantly less (~30-fold less) affinity than repeat I-II.
Development
Purα expression is highest during fetal development, specifically in the brain, spinal cord, and genitalia. In humans and mice Purα expression decreases in adulthood, and is restricted primarily to the brain and testes.
Tissue Specificity
While Purα is a ubiquitously expressed protein in all cell types, it is generally found at low levels in most tissues. However, in adult humans and mice Purα expression is highest in the brain and spinal cord, and to a lesser extent in the testes. Purα has been shown to be upregulated in cardiac myocyte gap junctions following heart transplant in mice, colocalizing with SMαA.[9]
Interactions
Purα is known to interact with:
- Purβ
- Serum response factor (SRF)
- Sp1[10]
- E2F-1[11]
- Y-box-binding protein 1 (YB-1) (MSY1 in mice)[12]
- Retinoblastoma protein (Rb)[13]
- Rm62 RNA helicase (Drosophila), p68 RNA helicase (mammalian)[14]
- JCV T-antigen[15]
- Cyclin A/Cdk2 (PurA binds to the Cdk2 moiety)[16]
Disease
Mutations in the PURA gene resulting in haploinsufficiency are known to cause the neurological disease PURA syndrome, which has no cure. PURA syndrome appears early in development, with patients exhibiting severe developmental delay, seizures, feeding difficulty, intellectual disabilities, vision problems, hypotonia, and premature thelarche.[17] Purα knock-out mice exhibit similar neurological symptoms such as severe tremor developing at about postnatal week two, and feeding difficulties. These mice die after approximately one month. Heterozygous mice display less severe symptoms including seizures upon handling. [18] Interestingly, to date there have been no published accounts of phenotypic abnormalities in humans or mice with mutations in Purβ.
Fragile X-associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) is another disease associated with abnormal activity of Purα. In 2006, Johnson et al. observed that Purα colocalized with Fragile-X Mental Retardation Protein (FMRP) in mouse neuronal dendrites.[19] Purα also was found to be involved in dendritic mRNA transport, and in a Drosophila model of Fragile-X Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome it was hypothesized that the overexpression of FMR1 mRNA (encoding FMRP) resulted in Purα being bound to these mRNAs leading to the apparent deficiency in Purα activity and accumulation of RNA-protein inclusion bodies resulting in FXTAS symptoms.[20][21]
The Storybook Version of Pur Protein History (Just for Fun!)
In a lab across from central park in Manhattan, Edward Johnson and his postdoctoral fellow Andrew Bergemann stumbled on a protein in 1991 that would in years to come open doors to understanding diseases of neurological and cardiovascular origin. They named the protein Pur (pronounced “purr”) after its ability to bind a sequence of bent DNA rich in As and Gs, or purine nucleotides, called the “PUR element.” This region of DNA, found near the origin of replication, was thought to be involved in the regulation of DNA replication.[22] At the time, no sequence-specific single-stranded DNA binding proteins were known to exist. The novelty of the findings were tremendous, and paved the way for many future studies of sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins.
While the focus of Johnson and Bergemann’s research was in DNA replication in cancer and AIDS, in the years that followed their discovery, Pur was found to interact with a tumor suppressor “retinoblastoma protein” or Rb. Likely as a result of funding available in cancer research and Rb, research has shifted from Pur’s role in DNA replication toward instead, its capacity to regulate transcription and translation, or the cellular processes involved in building proteins.
In 1992, Bergemann, Johnson and Ma found what appeared to be a cousin of Pur. With only a C-terminal sequence to work from, the protein appeared to be similar but not identical to Pur. They named the putative protein “Purβ” and from then on referred to the original Pur protein as Purα.[23] Shortly thereafter in 1997, Kelm, et al. working to deduce the sequence of a protein they termed “vascular actin single-stranded DNA binding factor 2” (VACssBF2), isolated two different proteins of identical molecular weight to Purα and the putative Purβ. Upon sequencing and cloning of isolated cDNA, the team published the first full length sequence of what is now known to be Purβ.[24] Since this time, in humans three splice variants have been found of Purα, one of Purβ and two isoforms of another Pur family member Purγ: Purγ-A and Purγ-B.
Purγ has been studied to a far lesser degree than Purα and Purβ. While little is yet known about the actions of the Purγ protein, Johnson and Liu in 2002 found that the Purγ-A isoform mRNA was expressed at very low levels or not at all in normal human tissues, but highly expressed in a panel of cancer cell types.[25] Similarly, Purγ-B mRNA was absent in human tissues except the testes, and in several tumor tissue types. Most of the research surrounding the Pur family of proteins has focused on Purα due to its involvement in neurological disorders, however interest in Purβ has increased in recent years as it has been implicated in cardiovascular disease, fibrosis and acute myelogenous leukemia.[26]
3D Structures of Purα
- 5fgp (I-II repeat complex with DNA. Drosophila m.)[27]
- 5fgo (III repeat dimer. Drosophila m.)[28]
- 3k44 (I-II repeat, apo. Drosophila m.)[29]
- 3nm7 (Apo. Borrelia b. Note: the Borrelia homolog of Purα contains only one PUR repeat)[30]
- 3n8b (Apo. Borrelia b. Note: the Borrelia homolog of Purα contains only one PUR repeat)[31]
Additional Resources
For more information on PURA syndrome, visit the PURA Syndrome Foundation website: [1]
This page was created using JSmol in Proteopedia [32]
References
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Graebsch A, Roche S, Niessing D. X-ray structure of Pur-alpha reveals a Whirly-like fold and an unusual nucleic-acid binding surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 3;106(44):18521-6. Epub 2009 Oct 21. PMID:19846792
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Kelm RJ Jr, Elder PK, Getz MJ. The single-stranded DNA-binding proteins, Puralpha, Purbeta, and MSY1 specifically interact with an exon 3-derived mouse vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin messenger RNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1999 Dec 31;274(53):38268-75. PMID:10608902
- ↑ Haas S, Thatikunta P, Steplewski A, Johnson EM, Khalili K, Amini S. A 39-kD DNA-binding protein from mouse brain stimulates transcription of myelin basic protein gene in oligodendrocytic cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Sep;130(5):1171-9. PMID:7657701
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Zhang A, David JJ, Subramanian SV, Liu X, Fuerst MD, Zhao X, Leier CV, Orosz CG, Kelm RJ Jr, Strauch AR. Serum response factor neutralizes Pur alpha- and Pur beta-mediated repression of the fetal vascular smooth muscle alpha-actin gene in stressed adult cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2008 Mar;294(3):C702-14. doi:, 10.1152/ajpcell.00173.2007. Epub 2008 Jan 9. PMID:18344281 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00173.2007
- ↑ Tretiakova A, Steplewski A, Johnson EM, Khalili K, Amini S. Regulation of myelin basic protein gene transcription by Sp1 and Puralpha: evidence for association of Sp1 and Puralpha in brain. J Cell Physiol. 1999 Oct;181(1):160-8. doi:, 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199910)181:1<160::AID-JCP17>3.0.CO;2-H. PMID:10457364 doi:<160::AID-JCP17>3.0.CO;2-H http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4652(199910)181:1<160::AID-JCP17>3.0.CO;2-H
- ↑ Darbinian N, Gallia GL, Kundu M, Shcherbik N, Tretiakova A, Giordano A, Khalili K. Association of Pur alpha and E2F-1 suppresses transcriptional activity of E2F-1. Oncogene. 1999 Nov 4;18(46):6398-402. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203011. PMID:10597240 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203011
- ↑ Safak M, Gallia GL, Khalili K. Reciprocal interaction between two cellular proteins, Puralpha and YB-1, modulates transcriptional activity of JCVCY in glial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Apr;19(4):2712-23. PMID:10082537
- ↑ Johnson EM, Chen PL, Krachmarov CP, Barr SM, Kanovsky M, Ma ZW, Lee WH. Association of human Pur alpha with the retinoblastoma protein, Rb, regulates binding to the single-stranded DNA Pur alpha recognition element. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):24352-60. PMID:7592647
- ↑ Qurashi A, Li W, Zhou JY, Peng J, Jin P. Nuclear accumulation of stress response mRNAs contributes to the neurodegeneration caused by Fragile X premutation rCGG repeats. PLoS Genet. 2011 Jun;7(6):e1002102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002102. Epub 2011 , Jun 2. PMID:21655086 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002102
- ↑ Krachmarov CP, Chepenik LG, Barr-Vagell S, Khalili K, Johnson EM. Activation of the JC virus Tat-responsive transcriptional control element by association of the Tat protein of human immunodeficiency virus 1 with cellular protein Pur alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Nov 26;93(24):14112-7. PMID:8943069
- ↑ Liu H, Barr SM, Chu C, Kohtz DS, Kinoshita Y, Johnson EM. Functional interaction of Puralpha with the Cdk2 moiety of cyclin A/Cdk2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Mar 25;328(4):851-7. doi:, 10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.01.038. PMID:15707957 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.01.038
- ↑ Reijnders MRF, Janowski R, Alvi M, Self JE, van Essen TJ, Vreeburg M, Rouhl RPW, Stevens SJC, Stegmann APA, Schieving J, Pfundt R, van Dijk K, Smeets E, Stumpel CTRM, Bok LA, Cobben JM, Engelen M, Mansour S, Whiteford M, Chandler KE, Douzgou S, Cooper NS, Tan EC, Foo R, Lai AHM, Rankin J, Green A, Lonnqvist T, Isohanni P, Williams S, Ruhoy I, Carvalho KS, Dowling JJ, Lev DL, Sterbova K, Lassuthova P, Neupauerova J, Waugh JL, Keros S, Clayton-Smith J, Smithson SF, Brunner HG, van Hoeckel C, Anderson M, Clowes VE, Siu VM, Ddd Study T, Selber P, Leventer RJ, Nellaker C, Niessing D, Hunt D, Baralle D. PURA syndrome: clinical delineation and genotype-phenotype study in 32 individuals with review of published literature. J Med Genet. 2018 Feb;55(2):104-113. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-104946. Epub, 2017 Nov 2. PMID:29097605 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2017-104946
- ↑ Hunt D, Leventer RJ, Simons C, Taft R, Swoboda KJ, Gawne-Cain M, Magee AC, Turnpenny PD, Baralle D. Whole exome sequencing in family trios reveals de novo mutations in PURA as a cause of severe neurodevelopmental delay and learning disability. J Med Genet. 2014 Dec;51(12):806-13. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102798. Epub, 2014 Oct 23. PMID:25342064 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102798
- ↑ Knapp AM, Ramsey JE, Wang SX, Godburn KE, Strauch AR, Kelm RJ Jr. Nucleoprotein interactions governing cell type-dependent repression of the mouse smooth muscle alpha-actin promoter by single-stranded DNA-binding proteins Pur alpha and Pur beta. J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 24;281(12):7907-18. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M509682200. Epub 2006 , Jan 25. PMID:16436378 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M509682200
- ↑ Jin P, Duan R, Qurashi A, Qin Y, Tian D, Rosser TC, Liu H, Feng Y, Warren ST. Pur alpha binds to rCGG repeats and modulates repeat-mediated neurodegeneration in a Drosophila model of fragile X tremor/ataxia syndrome. Neuron. 2007 Aug 16;55(4):556-64. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.020. PMID:17698009 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.020
- ↑ Qurashi A, Li W, Zhou JY, Peng J, Jin P. Nuclear accumulation of stress response mRNAs contributes to the neurodegeneration caused by Fragile X premutation rCGG repeats. PLoS Genet. 2011 Jun;7(6):e1002102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002102. Epub 2011 , Jun 2. PMID:21655086 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002102
- ↑ Bergemann AD, Johnson EM. The HeLa Pur factor binds single-stranded DNA at a specific element conserved in gene flanking regions and origins of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1257-65. PMID:1545807
- ↑ Bergemann AD, Ma ZW, Johnson EM. Sequence of cDNA comprising the human pur gene and sequence-specific single-stranded-DNA-binding properties of the encoded protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5673-82. PMID:1448097
- ↑ Kelm RJ Jr, Elder PK, Strauch AR, Getz MJ. Sequence of cDNAs encoding components of vascular actin single-stranded DNA-binding factor 2 establish identity to Puralpha and Purbeta. J Biol Chem. 1997 Oct 17;272(42):26727-33. PMID:9334258
- ↑ Liu H, Johnson EM. Distinct proteins encoded by alternative transcripts of the PURG gene, located contrapodal to WRN on chromosome 8, determined by differential termination/polyadenylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002 Jun 1;30(11):2417-26. PMID:12034829
- ↑ Rumora AE, Ferris LA, Wheeler TR, Kelm RJ Jr. Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions Mediate Single-Stranded DNA Recognition and Acta2 Repression by Purine-Rich Element-Binding Protein B. Biochemistry. 2016 May 17;55(19):2794-805. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00006. Epub, 2016 May 4. PMID:27064749 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00006
- ↑ Graebsch A, Roche S, Niessing D. X-ray structure of Pur-alpha reveals a Whirly-like fold and an unusual nucleic-acid binding surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Nov 3;106(44):18521-6. Epub 2009 Oct 21. PMID:19846792
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Weber J, Bao H, Hartlmuller C, Wang Z, Windhager A, Janowski R, Madl T, Jin P, Niessing D. Structural basis of nucleic-acid recognition and double-strand unwinding by the essential neuronal protein Pur-alpha. Elife. 2016 Jan 8;5. pii: e11297. doi: 10.7554/eLife.11297. PMID:26744780 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11297
- ↑ Graebsch A, Roche S, Kostrewa D, Soding J, Niessing D. Of bits and bugs--on the use of bioinformatics and a bacterial crystal structure to solve a eukaryotic repeat-protein structure. PLoS One. 2010 Oct 14;5(10):e13402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013402. PMID:20976240 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013402
- ↑ Graebsch A, Roche S, Kostrewa D, Soding J, Niessing D. Of bits and bugs--on the use of bioinformatics and a bacterial crystal structure to solve a eukaryotic repeat-protein structure. PLoS One. 2010 Oct 14;5(10):e13402. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013402. PMID:20976240 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0013402
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
|




