We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Jennifer Taylor/Sandbox 3
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m |
m |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
==Hypothesis== | ==Hypothesis== | ||
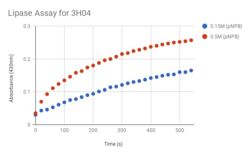
| - | In the beginning, we predicted that our protein was an esterase, because originally our most promising homologs were an aminopeptidase and an esterase. And even though the most hits from our Promol search were enzyme class 3.4 (aminopeptidases), no further information was found about the catalytic triads of these hits. We decided to use a homolog in E.C. 3.1 (esterase) because there was information about their catalytic triads. We knew that our protein is a hydrolase, and we believe that 3H04 is characterized as an esterase (3.1), instead of an aminopeptidase (3.4). Even though the 3.4 category proteins had the most motif structure similarity in Promol, we chose <scene name='78/787193/1tah/1'>1TAH</scene> (a lipase) as our target homolog. 1TAH is a characterized protein and has a similar catalytic triad to what we predict for our protein (3H04). When we aligned the two catalytic triads <scene name='78/787193/Catalytic_triad_of_1tah/2'>1TAH</scene> and 3H04, they had an RMS of 0.016. In the beginning we were looking for a homolog with more protein sequence and structure similarity, but because neither protein sequence or structure determine the function of 3H04, we decided that those two factors matter much less than the catalytic triad of the protein. So, we used Promol to find what the catalytic triad of 3H04 is and we used 1TAH as our target homolog for the catalytic triad. We predict, because the RMS was so low, that 3H04 and 1TAH will be having very similar enzymatic functions. | + | In the beginning, we predicted that our protein was an esterase, because originally our most promising homologs were an aminopeptidase and an esterase. And even though the most hits from our Promol search were enzyme class 3.4 (aminopeptidases), no further information was found about the catalytic triads of these hits. We decided to use a homolog in E.C. 3.1 (esterase) because there was information about their catalytic triads. We knew that our protein is a hydrolase, and we believe that 3H04 is characterized as an esterase (3.1), instead of an aminopeptidase (3.4). Even though the 3.4 category proteins had the most motif structure similarity in Promol, we chose <scene name='78/787193/1tah/1'>1TAH</scene> (a lipase) as our target homolog. 1TAH is a characterized protein and has a similar catalytic triad to what we predict for our protein (3H04). When we aligned the two catalytic triads <scene name='78/787193/Catalytic_triad_of_1tah/2'>1TAH</scene> and <scene name='78/787193/Catalytic_triad_3h04/1'>3H04</scene>, they had an RMS of 0.016. In the beginning we were looking for a homolog with more protein sequence and structure similarity, but because neither protein sequence or structure determine the function of 3H04, we decided that those two factors matter much less than the catalytic triad of the protein. So, we used Promol to find what the catalytic triad of 3H04 is and we used 1TAH as our target homolog for the catalytic triad. We predict, because the RMS was so low, that 3H04 and 1TAH will be having very similar enzymatic functions. |
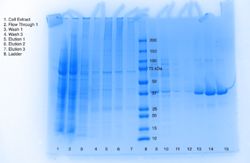
== Methods == | == Methods == | ||
Revision as of 14:50, 21 May 2018
3H04 Test Page
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644