This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jennifer Taylor/Sandbox 4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
4Q7Q is a protein found in '''Chitinophaga pinensis''', a soil bacterium in the sphingobacterial family. Its structure has been previously characterized and exists in Protein Data Bank. Its function, however, has not. | 4Q7Q is a protein found in '''Chitinophaga pinensis''', a soil bacterium in the sphingobacterial family. Its structure has been previously characterized and exists in Protein Data Bank. Its function, however, has not. | ||
| - | After structural and sequential analysis via various databases including BLAST, Pfam, Dali, PyMOL, and ProMOL, we initially predicted that 4Q7Q is a hydrolase. More specifically, we hypothesized that | + | After structural and sequential analysis via various databases including BLAST, Pfam, Dali, PyMOL, and ProMOL, we initially predicted that 4Q7Q is a hydrolase. More specifically, we hypothesized that 4Q7Q is a lipase, an enzyme that can hydrolyze lipids to form fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. |
| - | ==4Q7Q | + | ==Characteristics of 4Q7Q== |
| + | |||
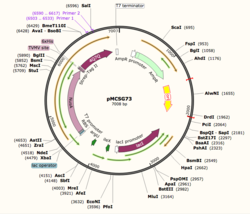
| + | [[Image:plasmid_Map.png|thumb|left|250px|Figure 1: Plasmid Map of pMCSG73, the expression vector for 4Q7Q.]] | ||
4Q7Q is composed of two chains; one chain can be seen <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_chain_a/9'>here</scene>. The colors indicate the translation direction of the peptide sequence from the N to C terminus; red represents the N-terminus while dark blue represents the C-terminus. Based on this structural model, we can see that 4Q7Q is an alpha-beta superfold; there are beta sheets (represented by the straighter strands) sandwiched between the alpha helices (represented by the coiled strands). | 4Q7Q is composed of two chains; one chain can be seen <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_chain_a/9'>here</scene>. The colors indicate the translation direction of the peptide sequence from the N to C terminus; red represents the N-terminus while dark blue represents the C-terminus. Based on this structural model, we can see that 4Q7Q is an alpha-beta superfold; there are beta sheets (represented by the straighter strands) sandwiched between the alpha helices (represented by the coiled strands). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through SnapGene, we analyzed the plasmid pMCSG73, which is the expression vector used to produce 4Q7Q. We found that our plasmid's open reading frame (ORF), the sequence of DNA that will be eventually translated, is 2237 base pairs in length. The size of our protein is 87.1 kDa. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Overall, our ORF is composed of NusA (a transcription elongation factor, two tags- 6XHis and Strep-Tag II, and a TVMV and TEV site. The plasmid map indicates the presence of a lac operon composed of three genes (lacZ, lacY, and lacA), a promoter, terminator, regulator (which codes for a repressor protein), and operator. | ||
== ''In silico'' Analysis == | == ''In silico'' Analysis == | ||
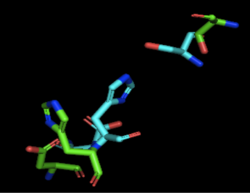
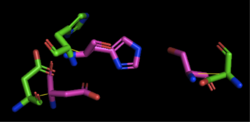
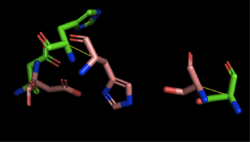
| - | [[Image:4Q7Q_3LIP_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure | + | [[Image:4Q7Q_3LIP_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 2: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 3LIP's catalytic triad (shown in blue). The RMS is 2.257.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1TAH_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 3: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1TAH's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.205.]][[Image:4Q7Q_1BWR_alignment.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 4: Alignment of 4Q7Q's putative catalytic triad (shown in green) and 1BWR's catalytic triad (shown in pink). The RMS is 2.049.]] |
We initially analyzed 4Q7Q through the protein structure databases BLAST, Pfam, and Dali. Our top hit was 4M8K, a GDSL-like lipase. Through BLAST, we found that 4M8K and 4Q7Q had a 36% sequence identity, with an E value of 0.002, indicating that it is a significant match. Since we can use the principle of homology to predict the function of an unknown protein, we first hypothesized that 4Q7Q was too a lipase. | We initially analyzed 4Q7Q through the protein structure databases BLAST, Pfam, and Dali. Our top hit was 4M8K, a GDSL-like lipase. Through BLAST, we found that 4M8K and 4Q7Q had a 36% sequence identity, with an E value of 0.002, indicating that it is a significant match. Since we can use the principle of homology to predict the function of an unknown protein, we first hypothesized that 4Q7Q was too a lipase. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 38: | ||
Before characterizing the function of 4Q7Q, we first needed to synthesize the protein through first transcribing 4Q7Q's DNA to amplify it and then translating it to express it. First, 4Q7Q's DNA was transcribed using its expression vector, the plasmid pMCS573. Since transformation must occur within a cell, the plasmid was transformed into DH5α cells using protocol from New England Biolabs. | Before characterizing the function of 4Q7Q, we first needed to synthesize the protein through first transcribing 4Q7Q's DNA to amplify it and then translating it to express it. First, 4Q7Q's DNA was transcribed using its expression vector, the plasmid pMCS573. Since transformation must occur within a cell, the plasmid was transformed into DH5α cells using protocol from New England Biolabs. | ||
| - | After transformation, DH5α cells were lysed and spread on plates containing LB and ampicillin. | + | After transformation, DH5α cells were lysed and spread on plates containing LB and ampicillin. Since 4Q7Q's plasmid is ampicillin resistant, only the bacteria that have been transformed with 4Q7Q's plasmid will grow on the plates. 4Q7Q's plasmid was then purified using Zyppy Plasmid Miniprep Kit. |
However, although DH5α cells maximize the efficiency of transformations, they do not contain T7 polymerase, which is essential for protein expression. Therefore, the purified plasmid underwent another bacterial transformation into BL21 (DE3) cells that do contain T7 polymerase using protocol from New England Biolabs. | However, although DH5α cells maximize the efficiency of transformations, they do not contain T7 polymerase, which is essential for protein expression. Therefore, the purified plasmid underwent another bacterial transformation into BL21 (DE3) cells that do contain T7 polymerase using protocol from New England Biolabs. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 46: | ||
After the second bacterial transformation, BL21 cells were lysed and spread on LB+amp plates. A bacterial colony was then selected from a plate and suspended in liquid culture. After incubation overnight, the OD<sub>260</sub>, which essentially measures the concentration of the plasmid DNA, was measured with a biophotometer. | After the second bacterial transformation, BL21 cells were lysed and spread on LB+amp plates. A bacterial colony was then selected from a plate and suspended in liquid culture. After incubation overnight, the OD<sub>260</sub>, which essentially measures the concentration of the plasmid DNA, was measured with a biophotometer. | ||
| - | Our | + | Our plasmid concentration was low, 28.7 (μg/ mL), probably due to the large size of our ORF. |
| + | The sample was then induced with IPTG. Essentially, IPTG is a reagent that prevents the repressor from binding to the lac operator to allow expression to occur. | ||
| + | == Protein Purification == | ||
| + | == pNPB Lipase Assay == | ||
| + | == Vocabulary Words == | ||
| + | 1) Hydrolase | ||
| + | 2) Lipase | ||
| + | 3) Open-reading frame (ORF) | ||
| + | 4) | ||
| - | == Protein Purification == | ||
| - | |||
| - | == pNPB Lipase Assay == | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 00:13, 23 May 2018
4Q7Q
| |||||||||||