This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
User:Jennifer Taylor/Sandbox 4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
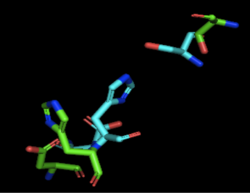
Through analyzing the sequence of 4Q7Q in SnapGene and then analyzing the 3D structure in PyMOL, we hypothesized that a possible catalytic triad of 4Q7Q is Ser164, Asp193, and His196. We believe that this group of amino acids are involved in the active site of 4Q7Q and therefore affects how the protein works. As seen in this <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_active_site/8'>image</scene>, all three amino acids are close in proximity to one another and are brought together in a single orientation. | Through analyzing the sequence of 4Q7Q in SnapGene and then analyzing the 3D structure in PyMOL, we hypothesized that a possible catalytic triad of 4Q7Q is Ser164, Asp193, and His196. We believe that this group of amino acids are involved in the active site of 4Q7Q and therefore affects how the protein works. As seen in this <scene name='78/787192/4q7q_active_site/8'>image</scene>, all three amino acids are close in proximity to one another and are brought together in a single orientation. | ||
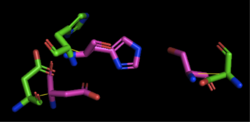
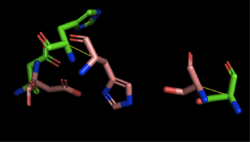
| - | We also performed further analysis in PyMOL and ProMOL which involved the homology of active sites. Top hits included 3LIP, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia cepacia'' (a human pathogen that can cause pneumonia), 1TAH, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia glumae'' (a soil bacterium), and 1BWR, a hydrolase found in ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). We aligned putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q with each of the catalytic triads of these known proteins. | + | We also performed further analysis in PyMOL and ProMOL which involved the homology of active sites. Top hits included 3LIP, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia cepacia'' (a human pathogen that can cause pneumonia), 1TAH, a lipase found in ''Burkholderia glumae'' (a soil bacterium), and 1BWR, a hydrolase found in ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). We aligned the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q with each of the catalytic triads of these known proteins. |
3LIP has two chains. As seen in Figure 2, when aligning the catalytic triad of 3LIP (Asp264, Ser87, His286) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.257. | 3LIP has two chains. As seen in Figure 2, when aligning the catalytic triad of 3LIP (Asp264, Ser87, His286) to the putative catalytic triad of 4Q7Q, the RMS is 2.257. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
| - | == Protein Expression == | + | == Protein Expression and Measuring Plasmid Concentration== |
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
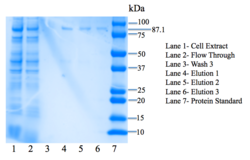
4Q7Q was then purified using the HisPUR Ni-NTA Purification kit. A nickel column as well as equilibration, wash, and elution buffers were used. We then tested for expression using SDS-PAGE, an electrophoresis method that separates proteins by mass in a polyacrylamide gel. BioRad's mini protean tetra protocol was utilized for SDS-PAGE. | 4Q7Q was then purified using the HisPUR Ni-NTA Purification kit. A nickel column as well as equilibration, wash, and elution buffers were used. We then tested for expression using SDS-PAGE, an electrophoresis method that separates proteins by mass in a polyacrylamide gel. BioRad's mini protean tetra protocol was utilized for SDS-PAGE. | ||
| - | Lanes in our gel contain samples of the cell extract, flow through, the third step of washing our protein through the column, as well as all three elutions. We are most interested in seeing our protein eluted in the three | + | Lanes in our gel contain samples of the cell extract, flow through, the third step of washing our protein through the column, as well as all three elutions. We want to see everything– our protein and all extra nucleic acids– in the cell extract lane. In the flow-through lane, we do not want to see the protein being expressed. In the wash lanes, we want to be able to see a little bit of the protein; each wash step should show more protein, as the buffer removes more and more unwanted nucleic acids. We are most interested in seeing our protein eluted in the three elution lanes. As seen in Figure 7, there are bands in the three elution lanes corresponding to our protein's weight: 87.1 kDa, confirming that we have successfully expressed 4Q7Q. |
| - | == | + | == Measuring Protein Concentration == |
| + | [[Image:Beer's_Law.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 8: Beer's Law.]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Calculation.png|thumb|right|250px|Figure 9: Using Beer's Law, we calculated that the concentration of our purified protein is 19.3μ.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We measured the absorbance of a purified 4Q7Q sample (not used in the gel) at 280 nm in a spectrometer. We found that the A<sub>280</sub> is 0.886. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to calculate the concentration of 4Q7Q, we had to use Beer's Law, shown in figure 8. Using SnapGene, we found that ε for 4Q7Q was 45840 M<sup>-1</sup>cm<sup>-1</sup>. The cuvette in our spectrometer was 1 cm in width, therefore path length was also 1 cm. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Through plugging in these values, shown in figure 9, we found that the concentration of our purified protein is 19.3μ. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == pNPB Lipase Assay == | ||
| + | We performed a lipase assay using p-nitrophenyl butyrate, | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 03:52, 23 May 2018
4Q7Q
| |||||||||||