Function
B-cell-specific Moloney leukemia virus insertion site 1 (BMI1) is a ring finger protein that is component of a , which epigenetically repress regulatory genes, such as Hox genes, related to embryonic development and self-renewal of somatic stem-cells. The name come from the original identification of BMI1 as an oncogene cooperating with a myc transgene in lymphomagenesis (ref van Lohuizen et al, 1991). It became clear that the Bmi1 protein is part of an E3 ubiquitin ligase complex (PRC1) (ref Wang et al, 2004) and that this complex has an important role in gene regulation during development (ref van der Lugt et al, 1994).
Monoubiquitinated H2A is enriched on the inactive human female X-chromosome. The inactivation of one of the X-chromosome is responsible for “dosing” the X-chromosome expression, which leads to the physiological X expression levels in females similar to the X expression levels in males (which has only one X).
PcG PRC1 is responsible for chromatin remodeling and histone modification, mediating monoubiquitination of histone H2A at Lysine 119, rendering chromatin heritably changed in its expressibility. BMI1 regulates the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity of RING1b, which is also a protein component of the PcG PRC1 complex. Other monomers such as CBX2, CBX4, CBX8, PHC1, PHC2 and RNF2/RING2 are capable of forming a PRC1-like complex replacing the RING1b, also forming a heterodimer with E3 ubiquitin activity.
The PRC1 complex is composed of four core subunits: CBX (polycomb; CBX2/4/6/7/8), PCGF (polycomb group factors; PCGF1–6, one of which is the BMI1), PHC (polyhomeotic homologues; PHC1/2/3) and RING E3 ligase (RING1A/B). However, a complex formed just by a polycomb group factor and RING1b is sufficient for the E3 ubiquitin ligase activity, being BMI1 the PCGF4. The PCGF2/RING1b (being PCGF2 the MEL-18 protein) and BMI1/RING1b represent canonical PRC1 complex, while PCGF1, PCGF 3, PCGF5 and PCGF 6 forms non-canonical PRC1 complexes.
In the complex, and form a heterodimer and only RING1b interacts with , which is a Ubiquitin Conjugating Enzyme E2.
Structure
BMI1 is a 37 kDa protein composed of three distinct regions: an N-terminal RING domain, a central domain and a C-terminal proline-serine rich domain involved in the regulation of protein stability (ref Gray 2016). In the PRC1 complex, BMI1 and RING1b heterodimerize via their N-terminal RING domains, forming an active E3 ubiquitin ligase. The heterodimerization occurs by the wrapping of the N-terminal arm of Ring1b around a groove on the surface of Bmi1 (ref Buchwald et al, 2006; Li et al, 2006), which stabilizes the structure of Ring1b and greatly stimulates ligase activity (ref Wang et al, 2004). Is worth noting that RING-domains, such as the found in BMI1 and RING1b, are structurally stabilized through the binding of two zinc atoms (ref Jackson et al, 2000), hence the interacts with 4 Zinc atoms to the correct folding (Zn highlighted in magenta). X-ray crystallography shows prominent salt bridges being formed by the Bmi1/Ring1b pairs of Asp72/Arg70, Glu11/Lys112, Lys81/Glu48, and Thr41/Arg26 (ref EMBOJ 2011).
A RING-domain E3 is responsible for promoting the transfer of ubiquitin (Ub) from the active site of the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme to an acceptor lysine residue in the substrate. The PRC1 complex promote the monoubiquitination of histone H2A on lysine 119 (uH2A), which leads to the stalling of the RNA polymerase at the promotor of the monoubiquitinated gene, hence the transcription doesn't occur.
How can the PRC1 complex promote such a epigenetic modification? The complex itself doesn't attach to a ubiquitin in any moment, instead PRC1 binds to a previously ubiquitin loaded E2 enzyme UbcH5c, then the complex binds to the duplex of DNA, in a non-sequence-specific manner, through a surface patch unique to the BMI1/RING1b RING–RING dimer. In the to the right, you can see , and . In the to the right, you can see , and . In the to the right, you can see , and . Only the RING1b interacts with the E2 enzyme UbcH5c. The ubiquitination is a cascade of events, in which PRC1 takes part in the end. First, E1 activating enzyme receives the ubiquitin through the covalent attaching of the ubiquitin C terminus to a cysteine of the E1 through a thioester bond, only possible due to ATP hydrolysis. Then, the E1 ubiquitin conjugate binds to an E2, catalyzing the transfer of the ubiquitin onto the E2 active site cysteine, also by a thio ester bond. Finally, the E3 ligase brings together the loaded E2 and the substrate, catalyzing the transfer of ubiquitin from the active site cysteine of the E2 to the amino group of a lysine sidechain, forming an isopeptide bond . Therefore, the PRC1 complex promotes the transfer of the ubiquitin attached to E2 enzyme UbcH5c to the lysine 119 on histone H2A. Computational modelling suggests that the heterodimer BMI1/RING1b interacts with both nucleosomal DNA and an acidic patch on histone H4 to promote the specific monoubiquitination of H2A(ref EMBOJ 2011). Although non-intuitive, the H2A ubiquitination is dispensable for chromatin compaction but essential for maintaining repression of specific genes and for maintaining ES cells in a dedifferentiated state. The fact that uH2A is dispensable for chromatin compaction was found by the introduction of a catalytically inactive RING1B mutant into Ring1A-/- Ring1B conditional knockout embryonic stem (ES) cells(ref taherboy).
In humans, there are multiple E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, but only UbcH5 and UbcH6 interact with the BMI1/RING1b heterodimer and promote the monoubiquitination of histone H2A at Lysine 119. The subtype UbcH5c is capable of making more polyubiquitin chains then UbcH5a and UbcH5b, in contrast UbcH6 doesn't make polyubiquitin chains (ref Buchwalld 2006). The BMI1/RING1b heterodimer interface buries a total of 2500 Ų surface area from the two proteins while the UbcH5c/RING1b interface has only 507Ų. The discrepancy between the areas of interface is reflected in the low affinity interaction between BMI1/RING1b and UbcH5c (Buchwald et al, 2006). The RING1b-binding surface on UbcH5c consists of two loops (L4 and L7), as well as residues from the N-terminal a helix (a1).
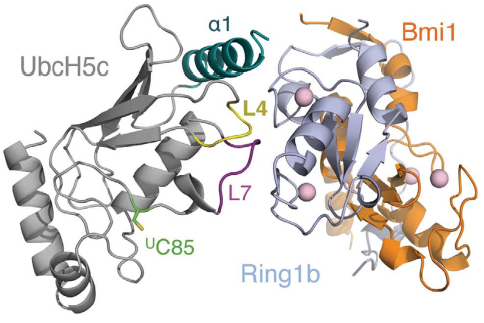
Representation of Bmi1/Ring1b-UbcH5c complex structure, with UbcH5c in grey, L4 in yellow, L7 in purple, Ring1b in light blue, and Bmi1 in orange. [1]
Salt bridges are formed between Lys4 and Lys8 from the a1 helix of UbcH5c (ULys4 and ULys8) with Asp56 on Ring1b (RAsp56)
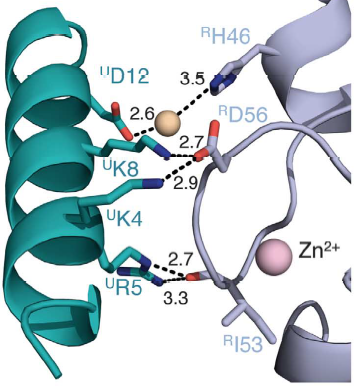
Interactions between Ring1b, in gray, and UbcH5c, in green, along the N-terminal a-helix. The sidechains involved are shown in stick format. Hydrogen-bond distances are given in angstroms. [1]
In the SPA motif of the UbcH5 (L7 residues USer94, UPro95, and UAla96), the sidechain hydroxyl of USer94 makes a hydrogen bond with the backbone carbonyl of RPro88 (from RING1b). Hydrophobic interactions between UPro95 and UAla96 with RIle53 and RPro88 help to stabilize the interaction between UbcH5 and RING1b.
Canonical PRC1 such as BMI1/RING1b have intrinsically very low enzymatic activity compared with non-canonical PRC1, although there are only subtle differences between the structure of canonical and non-canonical complexes. Two charged helix alpha 3 residues present in a modeled BMI1 (ref taherbhoy 2015) seems responsible for the low activity of BMI1/RING1b, K73 and D77 form a salt bridge that may limit efficient ubiquitin transfer. In a computational modeling, BMI1 K73 clashes sterically with Ubiquitin, which implies that K73 must move to allow Ub to bind in an activated conformation or that Ub adopts a less optimal position during monoubiquitination. Either of these events could provide an energy barrier, slowing transfer catalyzed by BMI1. The intrinsically low activity of the BMI1/RING1b is offset by a relatively favorable interaction between E3–E2-Ub and nucleosome substrate, resulting in a site-specific monoubiquitination efficient enough. The energy barrier may be responsible for increasing the fidelity of the transfer to the appropriate substrate. Also, canonical and non-canonical differ in targeting sub-units, target genomic loci, and genes expression regulation.
(fig destacando os resíduos K73 and D77 de BMI1 no complexo PRC1)
The central domain of BMI1 forms an , which is involved in protein-protein interactions, including interactions with the transcription factors E4F1, Zfp277 and the PLZF-RARA fusion protein. The best characterized binding partners of the UBL domain are the polyhomeotic proteins (PHC1, PHC2, PHC3) (ref Gray 2016). The UBL domain binds a short, 24 amino acid fragment, of PHC2 in a b-hairpin conformation. Also, UBL domain is involved in homo-oligomerization of BMI1. NMR and carbon detected NMR found that residues 30-51 are strongly conserved between PHC2, PHC1 and PHC3 suggesting that BMI1 interacts with the three members of the polyhomeotic family in a very similar manner and with similar affinities. Deletion of the corresponding motif abolished the interaction with BMI1. In the , PHC2 residues 33–47 adopt a in the complex, in greenyellow. The PHC2-BMI1 interaction involves an formed between the beta-hairpin of PHC2 and the beta 2 strand of BMI1 UBL, in magenta. The antiparallel b-sheet is stabilized by the hydrogen bonds between BMI1 Tyr163 and PHC2 Gly46.
(fig destacando as pontes de hidrogenio entre BMI1 Tyr163 e PHC2 Gly46, da beta-hairpin da PHC2 e folha beta 2 da BMI1 UBL)
MEL18, BMI1 homolog, also binds to PHC2, but with slightly reduced affinity. All BMI1 residues involved in contacts with PHC2 are identical with MEL18 and strongly suggests very similar binding mode for MEL18–PHC2. The similarity is explained by the 60% sequence identity between UBL domain and MEL18. MEL18 is capable of biding to RING1b to form a PRC1 complex too, but the MEL18/RING1b complex is significantly less active than the BMI1/RING1b complex.
Besides biding to PHC1-3, the UBL domain also has a propensity of forming homo-oligomers in solution. This tendency is probably due to one hydrophobic region of UBL domain, which mutation at Ile212 impairs homo-oligomerization of the BMI1–PHC2 complex and the homo-oligomerization of UBL domain itself. This suggests that the same hydrofobic region might be responsible for the oligomerization of the BMI1/RING1b complex, such as the PRC1 complex tetramer found in vitro (ref Buchwald 2006).
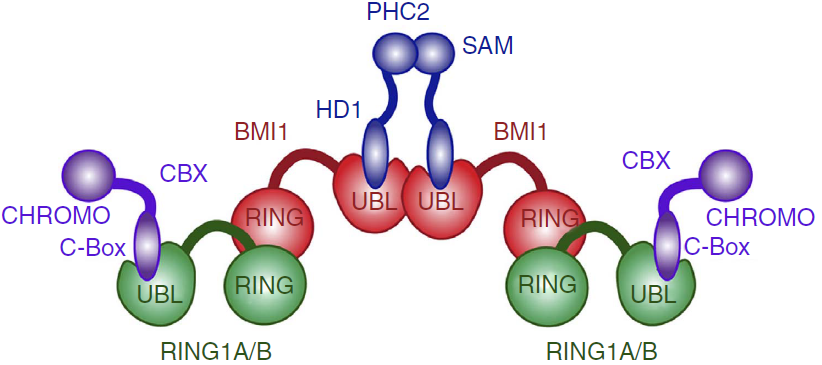
Proposed architecture of the PRC1 complex oligomer.[2]
Conservation
In Drosophila, the corresponding BMI1 variant (Psc) also cause low intrinsic E3 ligase activity, suggesting that it may be biologically important to closely regulate the catalytic rate of the canonical PRC1 complex.
The residues forming the interface between the PCGFs and RING1B are highly conserved: of 18 residues in the interface region, only 2, both from helix alpha 1, differ between PCGF4 and PCGF5.
Gene duplication in mammals has created a RING1b homologous, the RING1a protein, and the BMI1 homologous, the MEL18 protein. The homologous proteins have very high sequence similarity, but they appear to fulfil different functions. The alignment of RING1a sequences from several species reveals that part of the N-terminal sequence (aa 11–30) of RING1a is well conserved in RING1b. (ref Buchwald 2006) In a knockout in vivo experiment, most of the ubiquitinated H2A is depleted upon loss of RING1b and only a few of the remaining is depleted upon loss of RING1a.

Sequence alignment of Ring-domain proteins in PRC1 with secondary structure indicated. Zn binding site I is highlighted in blue and Zn binding site II is highlighted in cyan. The autoubiquitination site in Ring1b is marked with a filled triangle.
Disease
The bmi1 gene was first associated with lymphoma, in cooperation with the oncogene myc. BMI1-deficient fibroblasts and lymphocytes show high expression of the tumour suppressors p16 and p19Arf, which are encoded by ink4a locus. Conversely, overexpression of bmi1 allows fibroblast immortalization, downregulates expression of p16 and p19Arf and, leading to neoplastic transformation (ref jacobs 1999). The modulation of the ink4a expression probably is due to the ubiquitination of a H2A in the region, compacting the chromatin and downregulating the expression of p16 and p19Arf. The B- and T-cell lymphomas are highly dose-dependent phenotypes regarding bmi1 gene expression. The overexpression can lead to B- and T-cell lymphomas and partial reduction of Bmi1 leads to significant reduction in lymphoma formation (ref Jacobs et al, 1999) and brain tumour formation (ref Bruggeman et al, 2005)
BMI1 is also associated with colon cancer, in which BMI1 activates WNT signaling mainly through the downregulation of IDAX expression. (ref jacobs 1999) The BMI1 protein binds to the promoter of IDAX, a Wnt antagonist, and decreases it’s transcription. The WNT signaling pathway is very important in cell fate determination and tissue development and stem cell maintenance. Excessive activation of this pathway leads to tumorigenesis in several types of human cancers. According to The Cancer Genome Atlas Network, the WNT pathway is hyper-activated in over 90% of colon cancer.
(Fig BMI1 regulates IDAX transcription: legenda: IDAX as a target from BMI1. In the left is shown that the BMI1 knockdown by short hairpin RNAs leads to the increased IDAX transcription in colon cancer cell lines. In the right is shown the binding of the BMI1 protein to the promoter of IDAX, analyzed by ChIP-PCR.)
BMI1 can bind to the promoter of HoxC13 gene to regulate it and also can regulate other Hox genes, which define axial patterning and segment identity. BMI1 is central in the DNA damage repair, being the aberrant expression associated with numerous cancers and resistance to some types of chemotherapies, because misregulation of PRC1 can lead to repression of tumour suppressors, such as p16 or INK4a/ARF (ref Jacobs et al, 1999a, b). BMI1 also inhibits the CDKN1A gene, an important inhibitor of the cellular cycle, promoting the cellular proliferation. The inhibition of CDKN1A gene is promoted when a lncRNA, FALEC (focally amplified long non-coding RNA on chromosome 1 gene), stabilizes BMI1.
(fig shRNA assay to study the effect of BMI1 on cell proliferation)




