We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
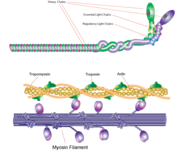
Myosin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
*Unconventional myosin I | *Unconventional myosin I | ||
| + | **[[5v7x]] – raMIB + calmodulin – rat – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6c1h]], [[6c1g]] – raMIB + calmodulin + actin – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4l79]] – raMIB + calmodulin <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6c1d]] – raMIB + calmodulin + actin + phalloidin – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5xgg]], [[5xg9]] – MIB C-terminal SH3 – ''Entamoeba histolytica''<br /> | ||
**[[4r8g]] – mMIC C-terminal + calmodulin<br /> | **[[4r8g]] – mMIC C-terminal + calmodulin<br /> | ||
| Line 101: | Line 106: | ||
**[[2bl0]] – MII RLC +RHC – ''Physarum polycephalum''<br /> | **[[2bl0]] – MII RLC +RHC – ''Physarum polycephalum''<br /> | ||
**[[5w1a]] - MII HC MD + LC – ''Drosophila melanogaster''<br /> | **[[5w1a]] - MII HC MD + LC – ''Drosophila melanogaster''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5e4h]] - smMII HC kinase domain – slime mold<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5e9e]] - smMII HC kinase domain + AMPPNP <br /> | ||
* Myosin III | * Myosin III | ||
| Line 138: | Line 145: | ||
**[[5hmp]], [[4zg4]] – hMVC <br /> | **[[5hmp]], [[4zg4]] – hMVC <br /> | ||
**[[4l8t]] – hMVC cargo binding domain<br /> | **[[4l8t]] – hMVC cargo binding domain<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4l79]] – raMIB + calmodulin - rat<br /> | ||
* Myosin VI | * Myosin VI | ||
| Line 154: | Line 160: | ||
**[[4dbr]] – pMVI HC (mutant) <br /> | **[[4dbr]] – pMVI HC (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[4anj]] - pMVI HC/GFP + calmodulin<br /> | **[[4anj]] - pMVI HC/GFP + calmodulin<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2x51]] - pMVI d insert1 + calmodulin | + | **[[2x51]] - pMVI d insert1 + calmodulin<br /> |
| + | **[[6bnw]], [[6bnq]], [[6bnp]] – pMVI + actin – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6bnv]] – pMVI + actin + calmodulin – Cryo EM<br /> | ||
*Unconventional myosin VI | *Unconventional myosin VI | ||
| Line 160: | Line 168: | ||
**[[5v6h]] – mMVI + GIPC2 <br /> | **[[5v6h]] – mMVI + GIPC2 <br /> | ||
**[[5v6e]] – mMVI + GIPC1 <br /> | **[[5v6e]] – mMVI + GIPC1 <br /> | ||
| - | **[[4pfp]], [[4pfo]] – pMVI MD <br /> | + | **[[4pfp]], [[4pfo]], [[5o2l]] – pMVI MD <br /> |
**[[4pjl]] – pMVI MD (mutant) <br /> | **[[4pjl]] – pMVI MD (mutant) <br /> | ||
**[[4pjj]] – pMVI MD + calmodulin <br /> | **[[4pjj]] – pMVI MD + calmodulin <br /> | ||
| Line 168: | Line 176: | ||
**[[2i0n]] - DdMVII SH3 domain - NMR<br /> | **[[2i0n]] - DdMVII SH3 domain - NMR<br /> | ||
**[[3pvl]] - mMVII SH3 domain+hUsher syndrome type 1G protein<br /> | **[[3pvl]] - mMVII SH3 domain+hUsher syndrome type 1G protein<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4db1]] – hMVII HC | + | **[[4db1]] – hMVII HC<br /> |
| + | **[[5n6a]] – bMVII HC <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5tby]] – bMVII HC + MIII LC + MLC-2V <br /> | ||
| + | **[[6fsa]], [[5n69]] – bMVII HC + MIII LC <br /> | ||
*Unconventional myosin VII | *Unconventional myosin VII | ||
Revision as of 09:04, 9 August 2018
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of Myosin
Updated on 09-August-2018
References
- ↑ Spudich JA, Finer J, Simmons B, Ruppel K, Patterson B, Uyeda T. Myosin structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1995;60:783-91. PMID:8824453
- ↑ Kalhammer G, Bahler M. Unconventional myosins. Essays Biochem. 2000;35:33-42. PMID:12471888
- ↑ Matsumura F. Regulation of myosin II during cytokinesis in higher eukaryotes. Trends Cell Biol. 2005 Jul;15(7):371-7. PMID:15935670 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2005.05.004
- ↑ Mehta AD, Rock RS, Rief M, Spudich JA, Mooseker MS, Cheney RE. Myosin-V is a processive actin-based motor. Nature. 1999 Aug 5;400(6744):590-3. PMID:10448864 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/23072
- ↑ Buss F, Spudich G, Kendrick-Jones J. Myosin VI: cellular functions and motor properties. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2004;20:649-76. PMID:15473855 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.cellbio.20.012103.094243
- ↑ Hasson T, Skowron JF, Gilbert DJ, Avraham KB, Perry WL, Bement WM, Anderson BL, Sherr EH, Chen ZY, Greene LA, Ward DC, Corey DP, Mooseker MS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA. Mapping of unconventional myosins in mouse and human. Genomics. 1996 Sep 15;36(3):431-9. PMID:8884266 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/geno.1996.0488
- ↑ Cox D, Berg JS, Cammer M, Chinegwundoh JO, Dale BM, Cheney RE, Greenberg S. Myosin X is a downstream effector of PI(3)K during phagocytosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Jul;4(7):469-77. PMID:12055636 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/ncb805
- ↑ Tamura K, Iwabuchi K, Fukao Y, Kondo M, Okamoto K, Ueda H, Nishimura M, Hara-Nishimura I. Myosin XI-i links the nuclear membrane to the cytoskeleton to control nuclear movement and shape in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol. 2013 Sep 23;23(18):1776-81. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.035. Epub 2013 , Aug 22. PMID:23973298 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.035
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Rayment I, Rypniewski WR, Schmidt-Base K, Smith R, Tomchick DR, Benning MM, Winkelmann DA, Wesenberg G, Holden HM. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50-8. PMID:8316857
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Nelson, D. and Cox, M.(2005). Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. 4th ed. p.1119.
- ↑ Tajsharghi H, Hilton-Jones D, Raheem O, Saukkonen AM, Oldfors A, Udd B. Human disease caused by loss of fast IIa myosin heavy chain due to recessive MYH2 mutations. Brain. 2010 May;133(Pt 5):1451-9. doi: 10.1093/brain/awq083. PMID:20418530 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/brain/awq083
- ↑ Weil D, Blanchard S, Kaplan J, Guilford P, Gibson F, Walsh J, Mburu P, Varela A, Levilliers J, Weston MD, et al.. Defective myosin VIIA gene responsible for Usher syndrome type 1B. Nature. 1995 Mar 2;374(6517):60-1. PMID:7870171 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/374060a0
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner, Laurel Koopmans, Jaime Prilusky