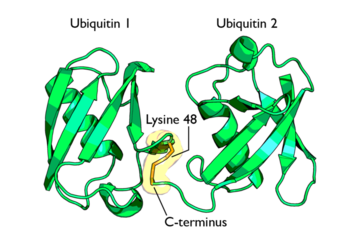Ubiquitin is a single 8565 Mr polypeptide consisting of 76 amino acid residues and is highly known for its role in ATP-dependent protein degradation[1]
Introduction
Ubiquitin is one of the most highly conserved eukaryotic proteins. Primary structures found throughout ubiquitin are identical in all bovine, insects and human ubiquitin [1]. The only difference observed amongst these species is seen in the terminal Gly-Gly residues. Yeast and oat ubiquitin only differ in three of the 76 residues when compared to ubiquitin found in higher eukaryotes[1].
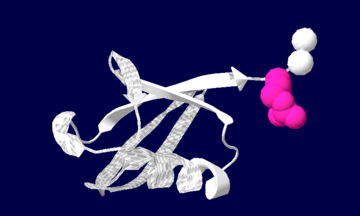
Ubiquitin structure: Arg74 in pink and Gly75 Gly76 in white.
Evolutionary Conservation
Check
, as determined by ConSurfDB.
You may read the explanation
of the method and the full data available from
ConSurf.
Ubiquitin can not only be found in the nucleus, but in the cytoplasm and cell-surface membrane as well[1].
One interesting characteristic of ubiquitin is its stability. Ubiquitin is able to withstand a range of pH levels and temperatures and is very resistant to tryptic digestion, while still containing seven lysine and four arginine residues[2]. Many aspects of ubiquitin's structure aids in this durability. Ubiquitin contains a hydrophobic core. Three hydrophobic residues found on the α-helix and 11 of the 13 hydrophobic residues from the β-sheet are involved in constructing this hydrophobic core[1]. The main contributor to the ubiquitin stability is the vast amount of hydrogen-bonding interactions observed. The whole structure of ubiquitin undergoes significant hydrogen bonding, aside from the COOH terminus[1].
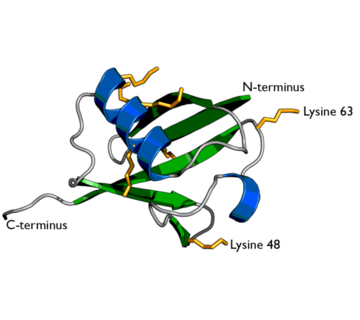
Ubiquitin structure with lysine residues highlighted in Yellow.
Secondary structures found throughout ubiquitin include three and one half turns of α-helix, a short 310 helix, a mixed β-sheet with five strands and seven reverse turns. Several unusual secondary structures are also seen including parallel G1 β-bulge, two reverse Asx turns and a symmetrical hydrogen-bonding region between two helices and two reverse turns.
Function
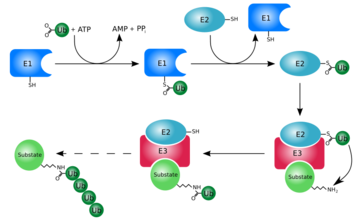
At first, ubiquitin was believed to be a hormone involed in inducing the differentiation of lymphocytes and activating adenylate cyclase [2]. However, today, ubiquitin is primarily known for its role in intracellular ATP-dependent protein degradation. This is accomplished through the process of several seperate reactions:
Activation
The first step of ubiquitin activation involves the formation of a ubiquitin-adenylate intermediate. This reaction requires an E1 ubiquitin-activating enzyme. The second step of ubiquitin activation transfers ubiquitin to the E1 active site cysteine residue and AMP is released. This step results in a thioester linkage between the C-terminal carboxyl group of ubiquitin and the E1 cysteine sulfhydryl group[1].
Ubiquitin Conjugation
The activated ubiquitin in then transferred to a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, E2, through a trans-thiolesteration reaction. Ubiquitin is then transferred to the ε-amino group of a lysine chain on the target protein. An isopeptide bond is now formed between the carboxyl terminal of ubiquitin and the ε-amino group of the target protein lysine residue. This is accomplished by E2 directly[1].
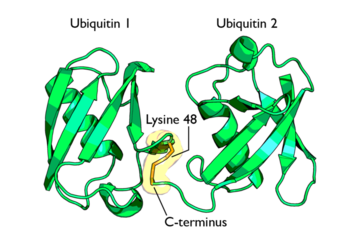
Isopeptide bond between two Ubiquitin molecules
Some proteins may be selected for degradation through the use of protein E3. E3 binds and catalyzes the isopeptide bond between ubiquitin and the target protein. Several activated ubiquitin may be added while still bound to E2 following the first ubiquitin addition[1].
Proofreading
Before degradation is complete, the system must ensure that the protein that has been ubiquitinylated is in fact damaged. Enzymes associated with proofreading will either inhibit or stimulate the ubiquitin-dependent process of protein degradation. If the target protein is found to not be damaged, deconjugation of ubiquitin from mono- or polyubiquitinylated proteins will result in order to inhibit any further degradation processes. This reverse reaction is known as a "futile cycle"[3]. This is done through the actions of deubiquitinating thiol proteases which recognize the native conformation of ubiquitin and cleave the isopeptide bond located at the carboxyl-terminal Gly76 of ubiquitin[4].
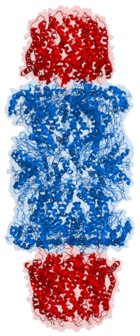
Length view of Proteasome
Conjugate Metabolism
If, however, the target protein is found to be damaged, the ubiquitinylated protein is lead to its degradation by the 26S proteasome[5]. The 26S proteasome is made up of a 20S core and a 19S cap. The targeted protein must be unfolded, deubiquitinylated and translocated through the 19S cap channels and into the proteasome interior. The 20S proteasome than cleaves the polypeptide into short peptides of roughly 7-9 fragment residues. This process is ATP-independent. Cytosolic peptidases then degrade the fragments into their appropriate amino acids. The ubiquitin molecules are returned to the cell where they are reused.
Types of Ubiquitin Conjugates
There are 3 different types of ubiquitin conjugates known:
Ubiquitinylation
Ubiquitinylation simply refers to the isopeptide bond formation between the carboxyl-terminal of ubiquitin and the ε-amino acid side chain of the target protein.
Multi-ubiquitinylation
This type of ubiquitin conjugate is a critical step in the process of protein degradation. This process refers to the addition of single ubiquitin molecules to numerous lysine residues on a target protein.
Polyubiquitinylation
This conjugate formation is the most important process in protein degradation as it is believed to signal the protein for degradation. Polyubiquitinylation refers to the addition of several ubiquitin molecules to a single lysine residue on a protein. Isopeptide bonds are formed between the carboxyl-terminus of one ubiquitin and a lysine residue on an adjacent ubiquitin.
Diseases
There are numerous diseases that may develop as a result of ubiquitin abnormalities. There are two disease categories possible in non-lethal states. One being the result of function loss and the other being function gain. Loss of function may occur due to a target substrate mutation or a mutation in a ubiquitin enzyme causing protein stabilization and a decrease in protein degradation. Function gain, on the other hand, results in an increase in protein degradation.
Cancer may result from either case. Oncoproteins may become stabilized while tumor suppressor genes may become destabilized. Liddle's Syndrome is a type of early-onset hypertension[6]. Sodium ions and water are excessively reabsorbed caused by E3 ligase non-recognition. Angleman syndrome is caused by a E3 ligase defect. This defect causes affects in human brain development resulting in symptoms such as mental retardation, seizures and abnormal gait. Lastly, neurogenetive diseases are caused by the accumulation of ubiquitin-conjugates. Diseases of this nature include Alzheimers and Parkinson's.
Infectious agents can manipulate ubiquitin or deubiquitination and one such protein is Chlamydia trachomatis. Chlamydia trachomatis' protein Cdu-1 catalyzes the hydrolysis of ubiquitin chains from Mcl-1. When polyubiquitnated, Mcl-1 is destined to be degraded by the proteasome, lowering the level of Mcl-1 and subsequently leading to apoptosis. The activity of Cdu-1 counteracts this by removing the ubiquitin, thus leading to higher levels of Mcl-1 in the cell. Additional information can be found here User:Karsten Theis/5B5Q