We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Pyruvate Kinase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
This particular protein is found in Homo sapiens and has the abbreviation PK. Pyruvate kinase belongs to the all beta proteins class and has the PK beta-barrel domain-like fold. It belongs to the PK beta-barrel domain-like superfamily and pyruvate kinase beta-barrel domain family<ref>{{website| title=SCOP: Protein: Pyruvate kinase (PK) from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606]|url=http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html|}}</ref>. | This particular protein is found in Homo sapiens and has the abbreviation PK. Pyruvate kinase belongs to the all beta proteins class and has the PK beta-barrel domain-like fold. It belongs to the PK beta-barrel domain-like superfamily and pyruvate kinase beta-barrel domain family<ref>{{website| title=SCOP: Protein: Pyruvate kinase (PK) from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606]|url=http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html|}}</ref>. | ||
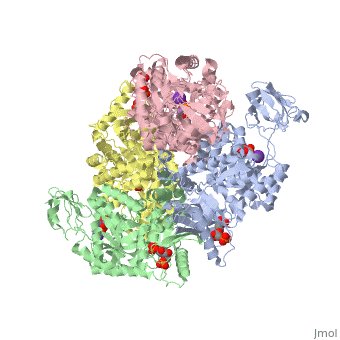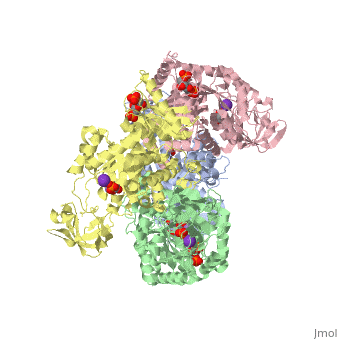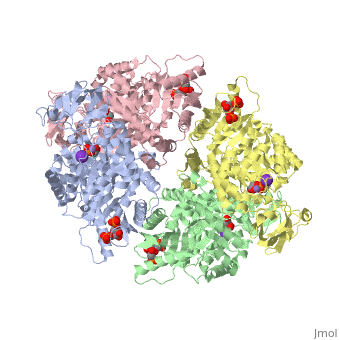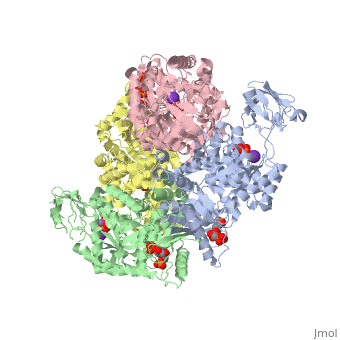
| - | Though pyruvate kinase is classified into all beta proteins, pyruvate kinase's <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Secondary_structure/1'>secondary structure</scene> comprises of both alpha helices and beta sheets. In the quaternary structure of pyruvate kinase, it can be observed to have <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Structure_4_domains/1'>four domains</scene> in humans. Thus, this enzyme is tetrameric with <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Metal_binding_sites/1'>metal binding sites</scene> on each domain for the <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Ligands/1'>K+</scene> and Mg2+ ligands to bind to. There are four types of tissue-specific isozymes: L (liver), R (red blood cells), M1 (muscle, heart, and brain), and M2 (early fetal tissue)<ref>{{website| title=SCOP: Protein: Pyruvate kinase (PK) from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606]|url=http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html|}}</ref>. | + | Though pyruvate kinase is classified into all beta proteins, pyruvate kinase's <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Secondary_structure/1'>secondary structure</scene> comprises of both alpha helices and beta sheets. In the quaternary structure of pyruvate kinase, it can be observed to have <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Structure_4_domains/1'>four domains</scene> in humans. Thus, this enzyme is tetrameric with <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Metal_binding_sites/1'>metal binding sites</scene> on each domain for the <scene name='Keegan_Gelvoria_Sandbox_1/Ligands/1'>K+</scene> and Mg2+ ligands to bind to. There are four types of tissue-specific isozymes: '''L''' (liver), '''R''' (red blood cells), '''M1''' (muscle, heart, and brain), and '''M2''' (early fetal tissue)<ref>{{website| title=SCOP: Protein: Pyruvate kinase (PK) from Human (Homo sapiens) [TaxId: 9606]|url=http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html|}}</ref>. |
==Mechanism== | ==Mechanism== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
**[[3khd]] – PyK – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | **[[3khd]] – PyK – ''Plasmodium falciparum''<br /> | ||
**[[3gg8]], [[3eoe]] – PyK – ''Toxoplasma gondii''<br /> | **[[3gg8]], [[3eoe]] – PyK – ''Toxoplasma gondii''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3bjf]], [[3bjt]], [[1t5a]], [[1zjh]] - hPyK M2 - human<br /> | + | **[[3bjf]], [[3bjt]], [[1t5a]], [[1zjh]], [[3srf]], [[3srh]] - hPyK M1/M2 - human<br /> |
| - | **[[4wj8]], [[4qg6]], [[4qg8]], [[4qg9]], [[4qgc]], [[3g2g]], [[4yj5]] - hPyK M2 (mutant)<br /> | + | **[[4wj8]], [[4qg6]], [[4qg8]], [[4qg9]], [[4qgc]], [[3g2g]], [[4yj5]] - hPyK M1/M2 (mutant)<br /> |
| - | **[[2vgb | + | **[[2vgb]] – hPyK R/L<br /> |
| - | **[[2vgf]], [[2vgg]], [[2vgi | + | **[[2vgf]], [[2vgg]], [[2vgi]] - hPyK R/L (mutant) <br /> |
**[[3ma8]], [[4drs]] – PyK – ''Cryptosporidium parvum''<br /> | **[[3ma8]], [[4drs]] – PyK – ''Cryptosporidium parvum''<br /> | ||
**[[2e28]] - PyK (mutant) – ''Geobacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | **[[2e28]] - PyK (mutant) – ''Geobacillus stearothermophilus''<br /> | ||
**[[1f3w]] – rPyK – rabbit<br /> | **[[1f3w]] – rPyK – rabbit<br /> | ||
**[[1f3x]] - rPyK (mutant) <br /> | **[[1f3x]] - rPyK (mutant) <br /> | ||
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1pky]], [[4yng]] – EcPyK - ''Eschericia coli''<br /> |
| - | **[[ | + | **[[1e0t]], [[1e0u]] - EcPyK (mutant) <br /> |
**[[1pkm]], [[1pyk]] – PyK – cat<br /> | **[[1pkm]], [[1pyk]] – PyK – cat<br /> | ||
**[[3t05]], [[3t0t]] – SaPyK – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | **[[3t05]], [[3t0t]] – SaPyK – ''Staphylococcus aureus''<br /> | ||
**[[3qtg]] – PyK – ''Pyrobaculum aerophilum''<br /> | **[[3qtg]] – PyK – ''Pyrobaculum aerophilum''<br /> | ||
**[[4krz]] - TcPyK – ''Trypanosoma cruzei''<br /> | **[[4krz]] - TcPyK – ''Trypanosoma cruzei''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5wrp]] - MtPyK – ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''<br /> | ||
*Pyruvate kinase binary complex | *Pyruvate kinase binary complex | ||
| Line 77: | Line 78: | ||
**[[3is4]], [[3ktx]] – LmPyK + pyrenetetrasulfonic acid<br /> | **[[3is4]], [[3ktx]] – LmPyK + pyrenetetrasulfonic acid<br /> | ||
**[[3t07]] – SaPyK + bis-indole alkaloid<br /> | **[[3t07]] – SaPyK + bis-indole alkaloid<br /> | ||
| - | **[[4b2d]] - hPyK + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[4b2d]] - hPyK M1/M2 + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[4rpp]] - hPyK (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[4fxj]] - hPyK + phenylalanine<br /> | + | **[[4fxj]] - hPyK M1/M2 + phenylalanine<br /> |
| + | **[[6gg4]] - hPyK M2 + phenylalanine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6gg5]] - hPyK M2 + tryptophan<br /> | ||
| + | **[[6gg6]] - hPyK M2 + serine<br /> | ||
**[[5x1v]], [[5x1w]] - hPyK M2 + inhibitor<br /> | **[[5x1v]], [[5x1w]] - hPyK M2 + inhibitor<br /> | ||
**[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | **[[4rpp]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
**[[4hyw]] – TbPyK + fructose bisphosphate – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | **[[4hyw]] – TbPyK + fructose bisphosphate – ''Trypanosoma brucei''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5ws8]] - MtPyK + oxalate<br /> | ||
| - | *Pyruvate kinase | + | *Pyruvate kinase higher complex |
**[[3hqo]] – LmPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | **[[3hqo]] – LmPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | ||
| Line 90: | Line 95: | ||
**[[3qv7]] – LmPyK + acid blue 25 + Ponceau S<br /> | **[[3qv7]] – LmPyK + acid blue 25 + Ponceau S<br /> | ||
**[[3srk]] – LmPyK + saccharine + inhibitor<br /> | **[[3srk]] – LmPyK + saccharine + inhibitor<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3n25]] – rPyK + proline + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | + | **[[3n25]] – rPyK M1/M2 + proline + Mn + pyruvate<br /> |
| - | **[[2g50]] - rPyK + alanine + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | + | **[[2g50]] - rPyK M1/M2 + alanine + Mn + pyruvate<br /> |
**[[1pkn]] - rPyK + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | **[[1pkn]] - rPyK + Mn + pyruvate<br /> | ||
**[[1aqf]] – rPyK + Mg + phospholactate<br /> | **[[1aqf]] – rPyK + Mg + phospholactate<br /> | ||
**[[1a49]], [[1a5u]] - rPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | **[[1a49]], [[1a5u]] - rPyK + ATP + oxalate<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3me3]] – hPyK M2 + aniline derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[3me3]] – hPyK M1/M2 + aniline derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[4g1n]] - hPyK M2 + pyridazine derivative + oxalate<br /> | + | **[[4g1n]] - hPyK M1/M2 + pyridazine derivative + oxalate<br /> |
| - | **[[3h6o]] - hPyK M2 + pyridazine derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[3h6o]] - hPyK M1/M2 + pyridazine derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[3gqy]], [[3gr4]], [[3u2z]] - hPyK M2 + piperazine derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[3gqy]], [[3gr4]], [[3u2z]] - hPyK M1/M2 + piperazine derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[4jpg]] - hPyK M2 + pyrimidine derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[5x0i]] - hPyK M2 (mutant) + serine + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[3srd]] - hPyK + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[5x1v]], [[5x1w]] - hPyK M2 + activator + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[4fxf]] - hPyK + oxalate + ATP + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[4jpg]] - hPyK M1/M2 + pyrimidine derivative + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| - | **[[4ima]], [[4ip7]] - hPyK (mutant) + citrate + adenosine + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | + | **[[3srd]] - hPyK M1/M2 + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate<br /> |
| + | **[[4fxf]] - hPyK M1/M2 + oxalate + ATP + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
| + | **[[4ima]], [[4ip7]] - hPyK L (mutant) + citrate + adenosine + fructose bisphosphate<br /> | ||
**[[1a3w]] – yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid + fructose bisphosphate – yeast<br /> | **[[1a3w]] – yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid + fructose bisphosphate – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[1a3x]] - yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid<br /> | **[[1a3x]] - yPyK + Mn + phosphoglycolic acid<br /> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 118: | ||
**[[4kcw]] – TbPyK + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate <br /> | **[[4kcw]] – TbPyK + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate <br /> | ||
**[[4ks0]] – TcPyK + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate <br /> | **[[4ks0]] – TcPyK + oxalate + fructose bisphosphate <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5ws9]] – MtPyK + oxalate + AMP + ATP <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5wsa]] – MtPyK + oxalate + glucose-6-phosphate <br /> | ||
| + | **[[5wsb]], [[5wsc]] – MtPyK + oxalate + glucose-6-phosphate + AMP<br /> | ||
| + | |||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:09, 30 August 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of pyruvate kinase
Updated on 30-August-2018
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Carbohydrate Metabolism
References
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008, 501-503.
- ↑ authors, The scop. "Structural Classification of Proteins". 2009. 2/26 2010. <http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html>.
- ↑ authors, The scop. "Structural Classification of Proteins". 2009. 2/26 2010. <http://scop.berkeley.edu/data/scop.b.c.jh.b.b.d.html>.
- ↑ Robergs, Robert. "Exercise-Induced Metabolic Acidosis: Where do the Protons come from?". 2009. 2/27 2010. <http://www.sportsci.org/jour/0102/rar.htm>.
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008, 501-503.
- ↑ Voet, Donald, Judith G. Voet, and Charlotte W. Pratt. Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecular Level. 3rd ed. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2008, 501-503.
- ↑ Dann LG, Britton HG. Kinetics and mechanism of action of muscle pyruvate kinase. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):39-54. PMID:629752
- ↑ Mattevi A, Bolognesi M, Valentini G. The allosteric regulation of pyruvate kinase. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jun 24;389(1):15-9. PMID:8682196
- ↑ Jurica MS, Mesecar A, Heath PJ, Shi W, Nowak T, Stoddard BL. The allosteric regulation of pyruvate kinase by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate. Structure. 1998 Feb 15;6(2):195-210. PMID:9519410
- ↑ Oria-Hernandez J, Cabrera N, Perez-Montfort R, Ramirez-Silva L. Pyruvate kinase revisited: the activating effect of K+. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 11;280(45):37924-9. Epub 2005 Sep 7. PMID:16147999 doi:10.1074/jbc.M508490200
- ↑ Dann LG, Britton HG. Kinetics and mechanism of action of muscle pyruvate kinase. Biochem J. 1978 Jan 1;169(1):39-54. PMID:629752
- ↑ Oria-Hernandez J, Cabrera N, Perez-Montfort R, Ramirez-Silva L. Pyruvate kinase revisited: the activating effect of K+. J Biol Chem. 2005 Nov 11;280(45):37924-9. Epub 2005 Sep 7. PMID:16147999 doi:10.1074/jbc.M508490200
- ↑ Zanella A, Fermo E, Bianchi P, Chiarelli LR, Valentini G. Pyruvate kinase deficiency: the genotype-phenotype association. Blood Rev. 2007 Jul;21(4):217-31. Epub 2007 Mar 13. PMID:17360088 doi:10.1016/j.blre.2007.01.001
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Keegan Gelvoria, David Canner, Ann Taylor, Andrew Alexander