Sandbox RDE-1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| - | <Structure load='4krf' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption=' | + | <Structure load='4krf' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Structure of Human Argonaute-1 let-7 complex as representation of RDE-1 since they have similar function. Thus, this complex is a model for Argonaute proteins in general.<ref> PMID: 23746446</ref>' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> |
The rde-1 gene is a member of the ''Argonaute'' gene family. Proteins from "Argonaute" family form an evolutionarily conserved family whose members silence gene expression in pathways such as RNA interference (RNAi). Argonaute family proteins can be divided into two types, AGO and Piwi proteins, depending on the small RNA they bonded to. Both types of Argonaute proteins bind 21–35 nucleotide-long small RNA guides whose sequence identifies the genes to be silenced.<ref name=four/> | The rde-1 gene is a member of the ''Argonaute'' gene family. Proteins from "Argonaute" family form an evolutionarily conserved family whose members silence gene expression in pathways such as RNA interference (RNAi). Argonaute family proteins can be divided into two types, AGO and Piwi proteins, depending on the small RNA they bonded to. Both types of Argonaute proteins bind 21–35 nucleotide-long small RNA guides whose sequence identifies the genes to be silenced.<ref name=four/> | ||
'''RDE-1''' (RNAi-DEfective 1), a primary Argonaute protein, is required for RNA-mediated interference in ''Caenorhabditis elegans''; thus, it is also known as RNAi promoting factor. Its gene locus was first characterized in ''C. elegans'' mutants resistant to RNAi, and was found to be a member of the Piwi gene family that includes plant, Drosophila, and vertebrate homologs.<ref name=two>PMID: 10535731</ref> | '''RDE-1''' (RNAi-DEfective 1), a primary Argonaute protein, is required for RNA-mediated interference in ''Caenorhabditis elegans''; thus, it is also known as RNAi promoting factor. Its gene locus was first characterized in ''C. elegans'' mutants resistant to RNAi, and was found to be a member of the Piwi gene family that includes plant, Drosophila, and vertebrate homologs.<ref name=two>PMID: 10535731</ref> | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
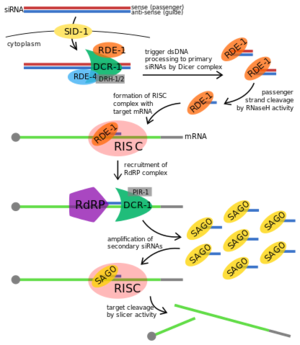
| - | [[Image:RDE-1 Proposed Fxn.png|300px||left|thumb|Proposed RNAi pathway for exogenous trigger dsRNA in C. elegans.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RDE-1#/media/File:Exogenous_RNAi_Pathway_in_C._elegans,_edited.svg</ref>]] | + | [[Image:RDE-1 Proposed Fxn.png|300px||left|thumb|Proposed RNAi pathway for exogenous trigger dsRNA in C. elegans.<ref>https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RDE-1#/media/File:Exogenous_RNAi_Pathway_in_C._elegans,_edited.svg</ref>]] RDE-1 is not required for the initial processing of the trigger RNA into siRNAs in RNAi, but it is required in the effector step.<ref>PMID: 11680844</ref> The trigger dsRNA is bound by RDE-4 onto a '''Dicer''' complex and this complex cleaves the dsRNA into 21-25nt primary siRNA. The siRNA binds to RDE-1 promoting the formation of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) and RDE-1 shuttles the siRNA to that effector complex.<ref name=promo>DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00793-6</ref><ref name=shuttle>PMID: 12110901</ref> The RNase H activity in PIWI domain in RDE-1 facilitates siRNA maturation, cleaving siRNA into a single stranded siRNA or guide RNA<ref name=cleave>DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1541</ref> while RISC is activated when ATP is added to the complex and utilized the guide RNA on RDE-1 to base pair with the target transcript.<ref name=shuttle/> The activation of RISC promotes the recruitment of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) which triggers the amplification of the secondary siRNAs to exhibit target transcript degradation.<ref>DOI: 10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_2</ref> |
== Importance == | == Importance == | ||
Revision as of 04:11, 9 October 2018
Introduction
| |||||||||||