Proteopedia:Featured JRN/0
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<tr><td>'''Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß'''</td></tr> | <tr><td>'''Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß'''</td></tr> | ||
<tr><td>''G. Atilla-Gocumen, L. Di Costanzo, E. Meggers''</td></tr> | <tr><td>''G. Atilla-Gocumen, L. Di Costanzo, E. Meggers''</td></tr> | ||
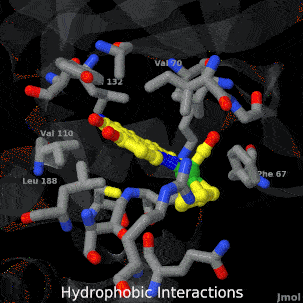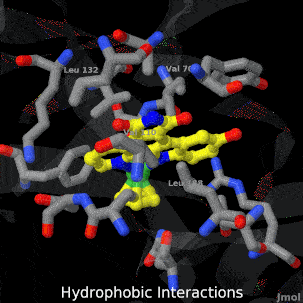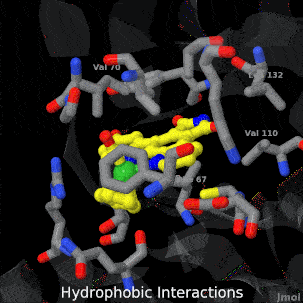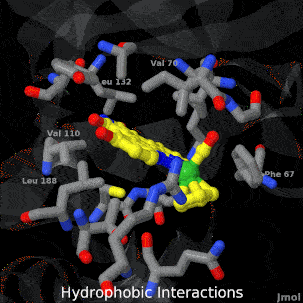
| - | <tr><td>A crystal structure of an organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the ATP binding site via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role.<ref group='xtra'>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref><br><references group=' | + | <tr><td>A crystal structure of an organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the ATP binding site via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role.<ref group='xtra'>DOI 10.1007/s00775-010-0699-x</ref><br><references group='xtra'/></td></tr> |
</table> | </table> | ||
Revision as of 08:55, 18 October 2018
| Structure of Anticancer Ruthenium Half-Sandwich Complex Bound to Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3ß |
| G. Atilla-Gocumen, L. Di Costanzo, E. Meggers |
A crystal structure of an organometallic half-sandwich ruthenium complex bound to the protein kinase glycogen synthase kinase 3ß (GSK-3ß) has been determined and reveals that the inhibitor binds to the ATP binding site via an induced fit mechanism utlizing several hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions. Importantly, the metal is not involved in any direct interaction with the protein kinase but fulfills a purely structural role.
|