Proteopedia:Featured JRN/1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <table> <tr><td>Image:Anim Samatey2 FigA I.gif</td></tr> <tr><td>'''Structural flexibility of the periplasmic protein, FlgA, regulates flagellar P-ring assembly in Salmonella enterica....) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<tr><td>[[Image:Anim Samatey2 FigA I.gif]]</td></tr> | <tr><td>[[Image:Anim Samatey2 FigA I.gif]]</td></tr> | ||
<tr><td>'''Structural flexibility of the periplasmic protein, FlgA, regulates flagellar P-ring assembly in Salmonella enterica.'''</td></tr> | <tr><td>'''Structural flexibility of the periplasmic protein, FlgA, regulates flagellar P-ring assembly in Salmonella enterica.'''</td></tr> | ||
| - | <tr><td>''Hideyuki Matsunami, Young-Ho Yoon, Vladimir Meshcheryakov, Keiichi Namba, and Fadel A. Samatey''</td></tr> | + | <tr><td>''Hideyuki Matsunami, Young-Ho Yoon, Vladimir Meshcheryakov, Keiichi Namba, and Fadel A. Samatey''<br>Scientific Reports 6:27399 2016 [http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep27399 doi:10.1038/srep27399]</td></tr> |
<tr><td>A periplasmic flagellar chaperone protein, FlgA, is required for P-ring assembly in bacterial flagella of taxa such as Salmonella enterica or Escherichia coli. The mechanism of chaperone-mediated P-ring formation is poorly understood. Here we present the open and closed crystal structures of FlgA from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, grown under different crystallization conditions. An intramolecular disulfide cross-linked form of FlgA caused a dominant negative effect on motility of the wild-type strain.</td></tr> | <tr><td>A periplasmic flagellar chaperone protein, FlgA, is required for P-ring assembly in bacterial flagella of taxa such as Salmonella enterica or Escherichia coli. The mechanism of chaperone-mediated P-ring formation is poorly understood. Here we present the open and closed crystal structures of FlgA from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, grown under different crystallization conditions. An intramolecular disulfide cross-linked form of FlgA caused a dominant negative effect on motility of the wild-type strain.</td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Revision as of 09:03, 18 October 2018
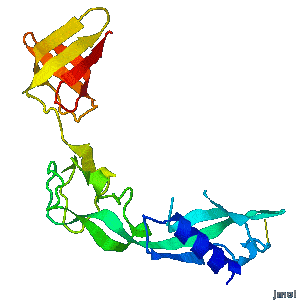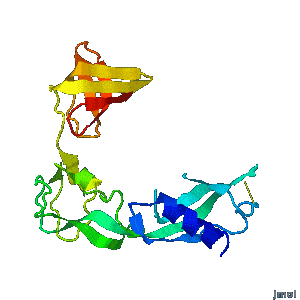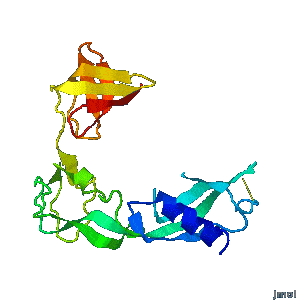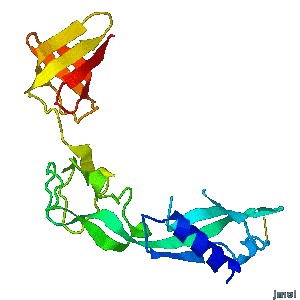 |
| Structural flexibility of the periplasmic protein, FlgA, regulates flagellar P-ring assembly in Salmonella enterica. |
| Hideyuki Matsunami, Young-Ho Yoon, Vladimir Meshcheryakov, Keiichi Namba, and Fadel A. Samatey Scientific Reports 6:27399 2016 doi:10.1038/srep27399 |
| A periplasmic flagellar chaperone protein, FlgA, is required for P-ring assembly in bacterial flagella of taxa such as Salmonella enterica or Escherichia coli. The mechanism of chaperone-mediated P-ring formation is poorly understood. Here we present the open and closed crystal structures of FlgA from Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, grown under different crystallization conditions. An intramolecular disulfide cross-linked form of FlgA caused a dominant negative effect on motility of the wild-type strain. |
