This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Acyl carrier protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
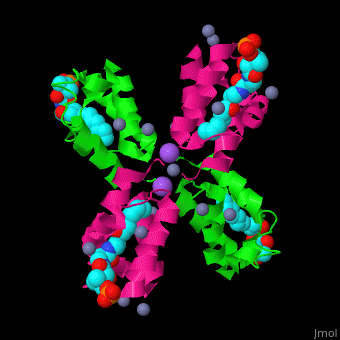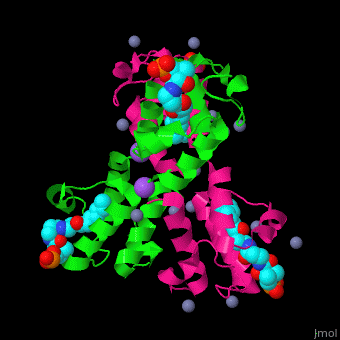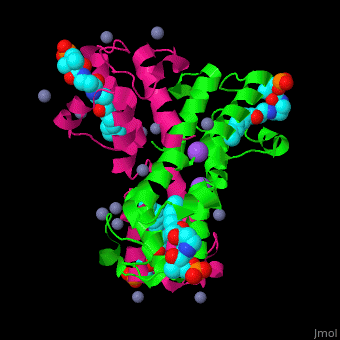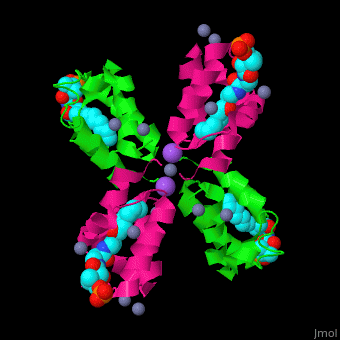
| - | <scene name='59/592131/Cv/11'>Biological Assembly of ''E. coli'' acyl carrier protein</scene> ([[2fad]]). <scene name='59/592131/Cv/9'>Active site</scene> of ''E. coli'' acyl carrier protein . Water molecules are shown as red spheres. | + | <scene name='59/592131/Cv/11'>Biological Assembly of ''E. coli'' acyl carrier protein</scene> ([[2fad]]). <scene name='59/592131/Cv/9'>Active site</scene> of ''E. coli'' acyl carrier protein. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
The <scene name='59/592131/Cv/10'>thioester - heptanethioate - is bound to ACP serine residue</scene> (colored in darkmagenta) in an expandable hydrophobic cavity.<ref>PMID:17059829</ref> | The <scene name='59/592131/Cv/10'>thioester - heptanethioate - is bound to ACP serine residue</scene> (colored in darkmagenta) in an expandable hydrophobic cavity.<ref>PMID:17059829</ref> | ||
Revision as of 10:57, 18 December 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of acyl carrier protein
Updated on 18-December-2018
References
- ↑ Byers DM, Gong H. Acyl carrier protein: structure-function relationships in a conserved multifunctional protein family. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Dec;85(6):649-62. PMID:18059524 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/o07-109
- ↑ Roujeinikova A, Simon WJ, Gilroy J, Rice DW, Rafferty JB, Slabas AR. Structural studies of fatty acyl-(acyl carrier protein) thioesters reveal a hydrophobic binding cavity that can expand to fit longer substrates. J Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 5;365(1):135-45. Epub 2006 Sep 23. PMID:17059829 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2006.09.049