Sandbox Reserved 1481
From Proteopedia
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
[http://www.rcsb.org/structure/5K7M] | [http://www.rcsb.org/structure/5K7M] | ||
| - | |||
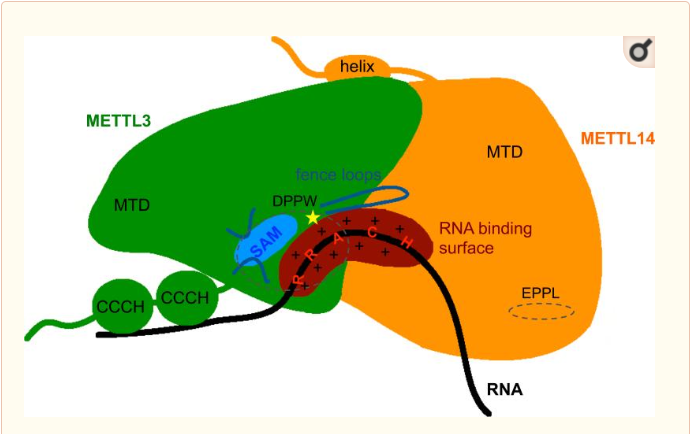
| - | METTL3 and MTTL14 have both a methyltranferase domain but the complex METTL3/METTL14 has a better methyltransferase activity. Moreover, a mutatio in the catalytic center of METTL3 inhibits the hole methyltransferase activity of the complex, whereas a mutation in the catalytic center of METTL14 does not. Thus, METTL3 is the catalytic subunit of the complex and METTL14 enhances the methyltransfearse activity by stabilizing the complex and enables the recognition of consensus sequence on messenger RNA. | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:MET.PNG]] | ||
'''Primary structure''' | '''Primary structure''' | ||
| - | This complex is composed of two differents proteins forming two distinct but linked subunit of the enzymatic complex/. Each of these two protein is coded by two differents genes. The mettl3 gene codes for the N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit, which is a 225 Amino acid chain, whereas the Mettl14 codes for the N6-adenosine-methyltransferase subunit METTL14, which is composed of 349 amino acids. Each of these two proteins are corresponding to the A [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/5K7M_A]or the B chain [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/5K7M_B] of the complex. | + | This complex is composed of two differents proteins forming two distinct but linked subunit of the enzymatic complex/. Each of these two protein is coded by two differents genes. The mettl3 gene codes for the N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit, which is a 225 Amino acid chain, whereas the Mettl14 codes for the N6-adenosine-methyltransferase subunit METTL14, which is composed of 349 amino acids. |
| + | |||
| + | Each of these two proteins are corresponding to the A [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/5K7M_A]or the B chain [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/5K7M_B] of the complex. | ||
'''Secondary structure''' | '''Secondary structure''' | ||
| + | Both polypeptides METTL3 and METTL14 are able to form some secondary structure thank interchain and intrachain hydrogen bond formation. | ||
| + | Chain A METTL3'secondary structure, is mainly composed of 20% helical (7 helices; 46 residues)and 24% beta sheet (13 strands; 55 residues) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:chain 1 METTL3]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chain B METTL14 is made of 24% helical s (14 helices; 87 residues) and 18% beta sheet (16 strands; 63 residues) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:chain 2 METTL14]] | ||
'''Tertiary structure''' | '''Tertiary structure''' | ||
| Line 29: | Line 35: | ||
'''Domains and specific site or sequences''' | '''Domains and specific site or sequences''' | ||
| - | Thanks to their primary amino acid sequences both A and B chains have some specific conserved domains directly linked to their function and functionning. | + | Thanks to their primary amino acid sequences both A and B chains have some specific conserved domains directly linked to their function and functionning. |
| + | |||
| + | METTL3 and MTTL14 have both a methyltranferase domain but the complex METTL3/METTL14 has a better methyltransferase activity. Moreover, a mutatio in the catalytic center of METTL3 inhibits the hole methyltransferase activity of the complex, whereas a mutation in the catalytic center of METTL14 does not. Thus, METTL3 is the catalytic subunit of the complex and METTL14 enhances the methyltransfearse activity by stabilizing the complex and enables the recognition of consensus sequence on messenger RNA. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:MET.PNG]] | ||
== Cristal structure == | == Cristal structure == | ||
Revision as of 13:35, 29 December 2018
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Crystal structure of the catalytic domains of Mettl3/Mettl14 complexInsert caption here
Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate
Insert caption here |
| Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate |
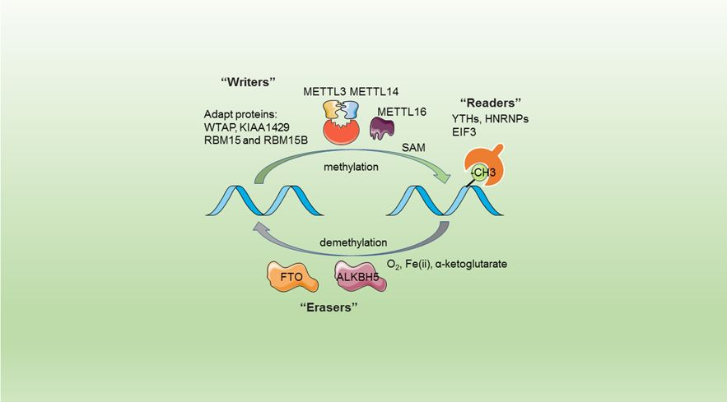
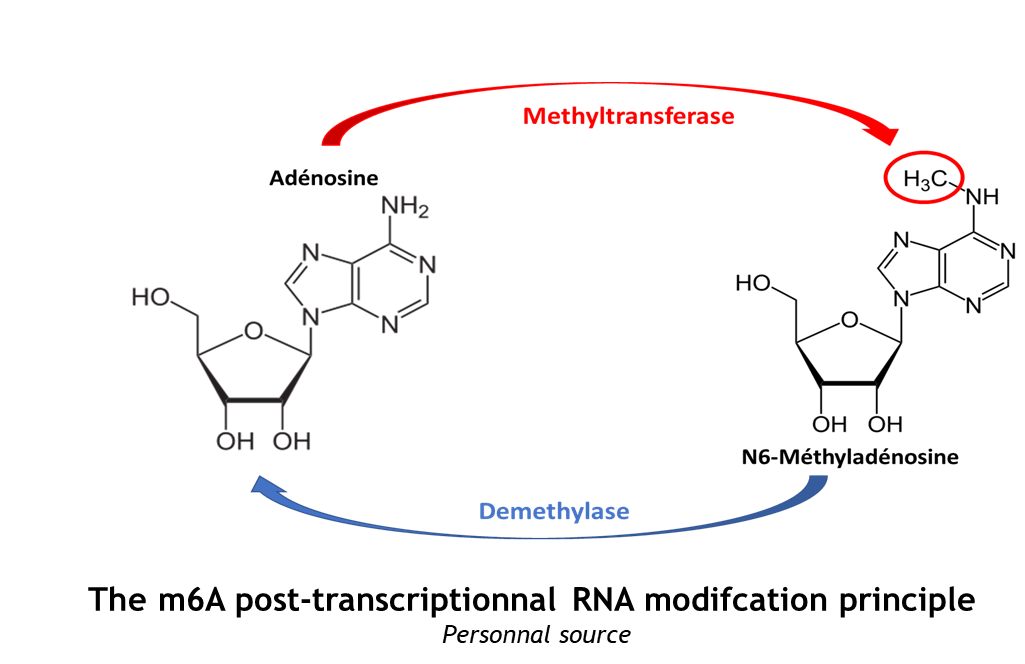
The complex METTL3/METTL14 is a heterodimer enzymatic complex involved into RNA post-transcription modifications by humans. This complex is abble to add a methyl group on adenosin of the RNA, by catalyzing a m6(A) modification.The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a quite common, reversible chemical modifications of RNAs molecules which plays a key role in several biological fonctions. This post transcriptional modification can be added by WRITERS, recognized by READERS and also removed byr ERASERS. The METTL3/METTL14 complex plays the role of writer.
| |||||||||||
References
<Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases/>[1] <Structural basis of N(6)-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex./>[2]
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644