Sandbox Reserved 1481
From Proteopedia
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
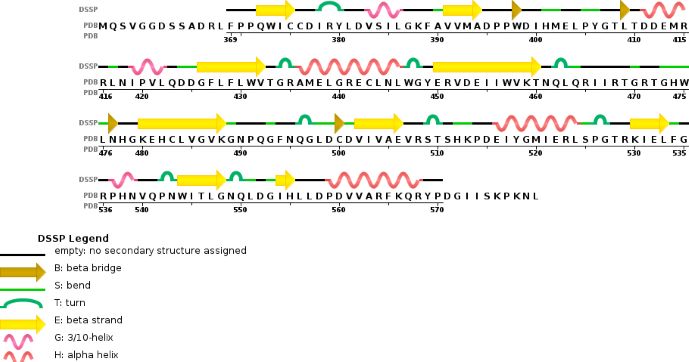
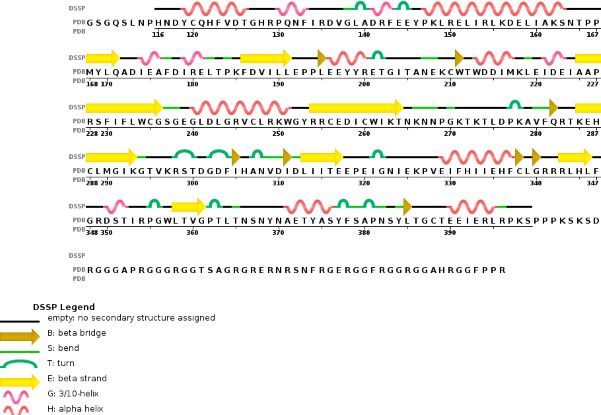
Chain B METTL14 is made of 24% helical s (14 helices; 87 residues) and 18% beta sheet (16 strands; 63 residues) | Chain B METTL14 is made of 24% helical s (14 helices; 87 residues) and 18% beta sheet (16 strands; 63 residues) | ||
| - | [[Image:chain 2 METTL14.jpg]] | + | [[Image:chain 2 METTL14.jpg]]<ref>[http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=5K7M]</ref> |
'''Tertiary structure''' | '''Tertiary structure''' | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
| + | <ref>DOI 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.041.</ref> | ||
<Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases/>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=27373337] | <Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases/>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=27373337] | ||
<Structural basis of N(6)-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex./>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27281194] | <Structural basis of N(6)-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex./>[https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27281194] | ||
Revision as of 14:14, 29 December 2018
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Crystal structure of the catalytic domains of Mettl3/Mettl14 complexInsert caption here
Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate
Insert caption here |
| Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate |
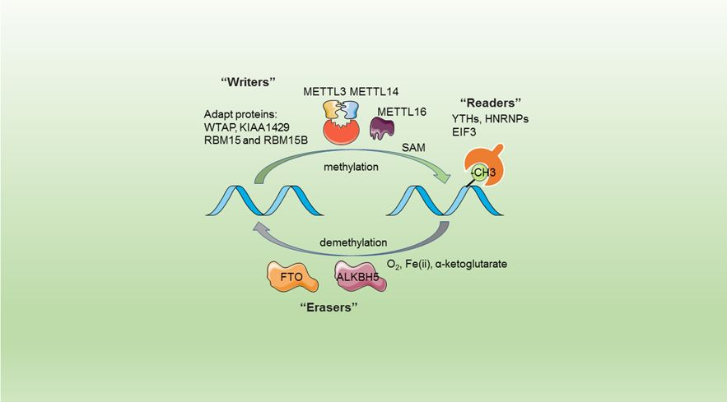
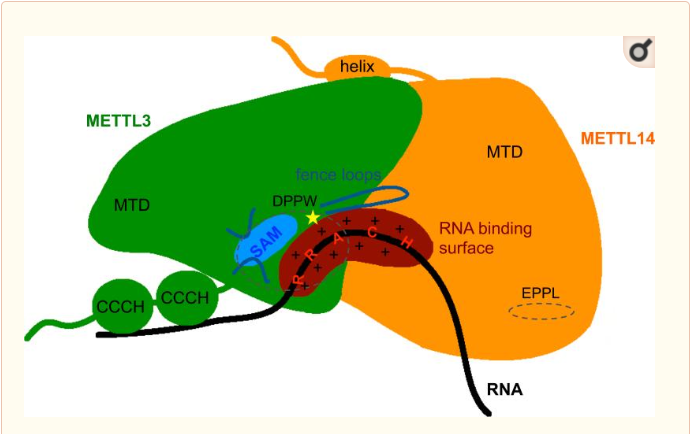
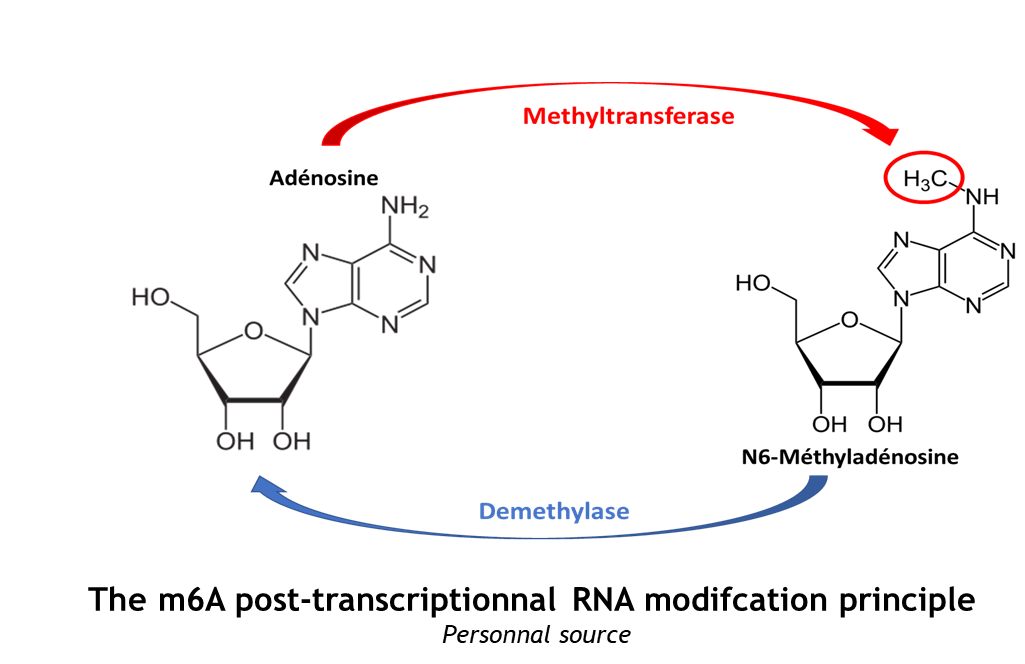
The complex METTL3/METTL14 is a heterodimer enzymatic complex involved into RNA post-transcription modifications by humans. This complex is abble to add a methyl group on adenosin of the RNA, by catalyzing a m6(A) modification.The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a quite common, reversible chemical modifications of RNAs molecules which plays a key role in several biological fonctions. This post transcriptional modification can be added by WRITERS, recognized by READERS and also removed byr ERASERS. The METTL3/METTL14 complex plays the role of writer.
| |||||||||||
References
[5] <Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases/>[3] <Structural basis of N(6)-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex./>[4]
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644
- ↑ [1]
- ↑ [2]
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.041.