Sandbox Reserved 1481
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
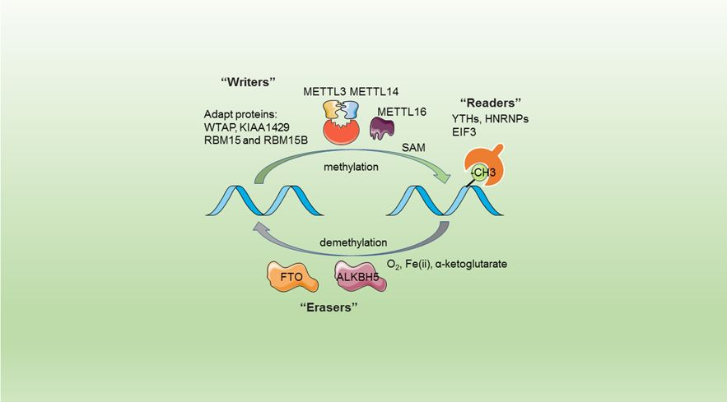
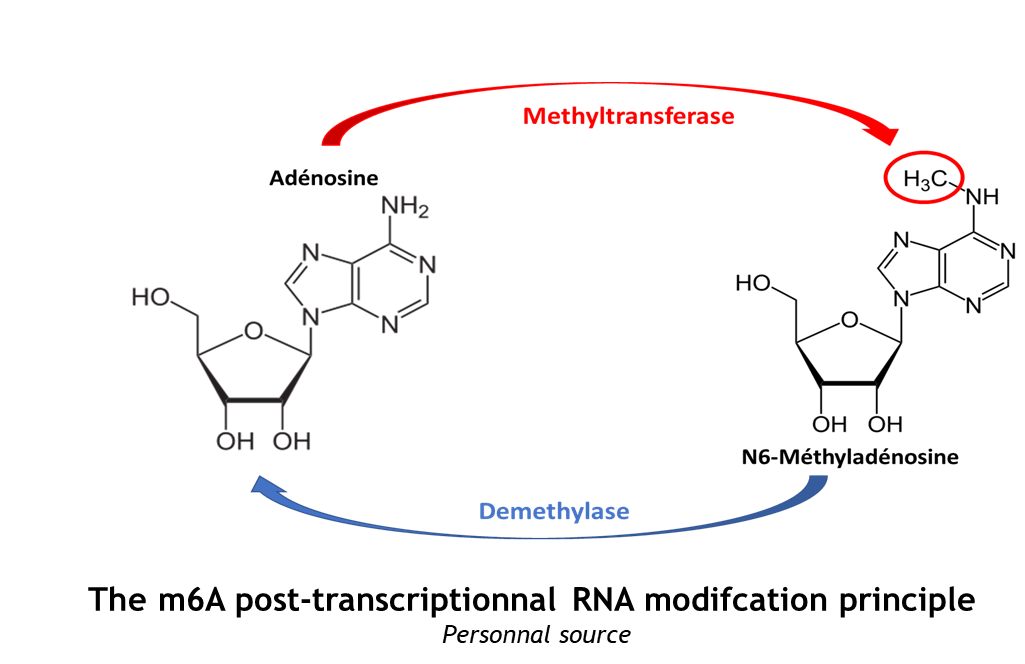
The complex METTL3/METTL14 is a heterodimer enzymatic complex involved into RNA post-transcription modifications by humans. | The complex METTL3/METTL14 is a heterodimer enzymatic complex involved into RNA post-transcription modifications by humans. | ||
This complex is abble to add a methyl group on adenosin of the RNA, by catalyzing a m6(A) modification.The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a quite common, reversible chemical modifications of RNAs molecules which plays a key role in several biological fonctions. This post transcriptional modification can be added by WRITERS, recognized by READERS and also removed byr ERASERS. The METTL3/METTL14 complex plays the role of writer. | This complex is abble to add a methyl group on adenosin of the RNA, by catalyzing a m6(A) modification.The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a quite common, reversible chemical modifications of RNAs molecules which plays a key role in several biological fonctions. This post transcriptional modification can be added by WRITERS, recognized by READERS and also removed byr ERASERS. The METTL3/METTL14 complex plays the role of writer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This enzymatic complex belongs to the second class of enzyme, which are the transferases. The complex is formed by 574 amino acid residues, divided into two different proteins nammed as Methyltransferase Like number 3 and 14. | ||
[[Image:writers.png]] | [[Image:writers.png]] | ||
| Line 38: | Line 40: | ||
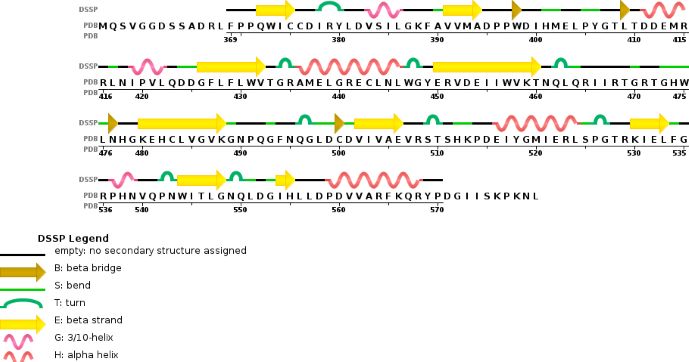
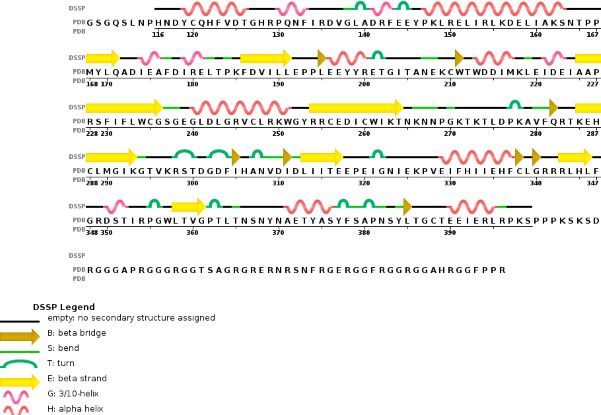
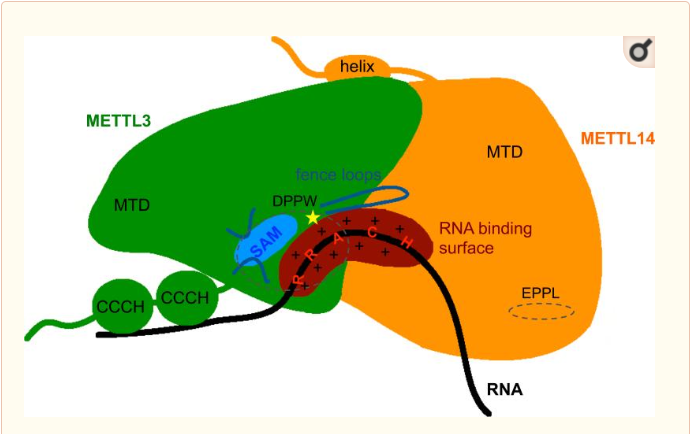
Thanks to their primary amino acid sequences both A and B chains have some specific conserved domains directly linked to their function and functionning. | Thanks to their primary amino acid sequences both A and B chains have some specific conserved domains directly linked to their function and functionning. | ||
| - | METTL3 and MTTL14 have both a methyltranferase domain | + | '''MTD : Methyltransferase domain ''' |
| + | |||
| + | METTL3 and MTTL14 have both a methyltranferase domain, which is the domain able to catalyze a methyltransferase reaction.But the complex METTL3/METTL14 has a better methyltransferase activity, than one single subunit activity. Moreover, a mutation in the catalytic center of METTL3 inhibits the hole methyltransferase activity of the complex, whereas a mutation in the catalytic center of METTL14 does not. | ||
| + | Thus, METTL3 is the catalytic subunit of the complex and METTL14 enhances the methyltransferasese activity by stabilizing the complex structure and binding to messenger RNA by enabling the recognition of its consensus sequence. | ||
Zinc finger domain of the METTL3-METTL14 N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase, is a RNA binding domain of the complex. This perticular domain of the two proteins complex allow the protein to make interactions with the RNA molecule to modify | Zinc finger domain of the METTL3-METTL14 N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase, is a RNA binding domain of the complex. This perticular domain of the two proteins complex allow the protein to make interactions with the RNA molecule to modify | ||
| Line 46: | Line 51: | ||
== Cristal structure == | == Cristal structure == | ||
| - | To study the | + | To study the cristal structure of the METTL3/METTL14 some cristalograghy experiments have been realized under the following experimental conditions to cristalyze the protein complex: |
'''Method''' : Vapor Diffusion Hanging Drop | '''Method''' : Vapor Diffusion Hanging Drop | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 29 December 2018
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Crystal structure of the catalytic domains of Mettl3/Mettl14 complexInsert caption here
Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate
Insert caption here |
| Drag the structure with the mouse to rotate |
The complex METTL3/METTL14 is a heterodimer enzymatic complex involved into RNA post-transcription modifications by humans. This complex is abble to add a methyl group on adenosin of the RNA, by catalyzing a m6(A) modification.The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a quite common, reversible chemical modifications of RNAs molecules which plays a key role in several biological fonctions. This post transcriptional modification can be added by WRITERS, recognized by READERS and also removed byr ERASERS. The METTL3/METTL14 complex plays the role of writer.
This enzymatic complex belongs to the second class of enzyme, which are the transferases. The complex is formed by 574 amino acid residues, divided into two different proteins nammed as Methyltransferase Like number 3 and 14.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ . PMID:216315890657
- ↑ . PMID:216315890657
- ↑ Wang P, Doxtader KA, Nam Y. Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases. Mol Cell. 2016 Jul 21;63(2):306-17. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.041. Epub 2016 , Jun 30. PMID:27373337 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.05.041
- ↑ Wang X, Feng J, Xue Y, Guan Z, Zhang D, Liu Z, Gong Z, Wang Q, Huang J, Tang C, Zou T, Yin P. Structural basis of N(6)-adenosine methylation by the METTL3-METTL14 complex. Nature. 2016 May 25;534(7608):575-8. doi: 10.1038/nature18298. PMID:27281194 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature18298
- ↑ Sledz P, Jinek M. Structural insights into the molecular mechanism of the m(6)A writer complex. Elife. 2016 Sep 14;5. pii: e18434. doi: 10.7554/eLife.18434. PMID:27627798 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.18434
- ↑ Wang X, Huang J, Zou T, Yin P. Human m(6)A writers: Two subunits, 2 roles. RNA Biol. 2017 Mar 4;14(3):300-304. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1282025. Epub 2017, Jan 25. PMID:28121234 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2017.1282025
- ↑ doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/pdb5K7M/pdb