We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1489
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
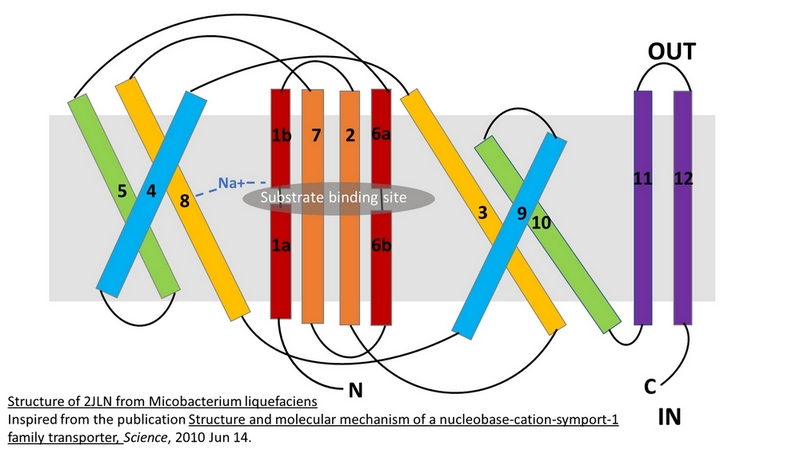
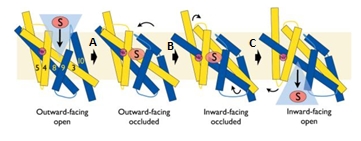
| - | The central bundle is composed of TMs 1 and 2, twined to the TMs 6 and 7 respectively. In addition, the protein presents a V-shape structure formed by TMs 3 to 5, twined to TMs 8 to 10 (''Figure 2 | + | The central bundle is composed of TMs 1 and 2, twined to the TMs 6 and 7 respectively. In addition, the protein presents a V-shape structure formed by TMs 3 to 5, twined to TMs 8 to 10 (''Figure 2''). |
The substrate- and cation-binding sites are located in the space between the central four-helix-bundle and the outer helix layer. | The substrate- and cation-binding sites are located in the space between the central four-helix-bundle and the outer helix layer. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
===Structure of the substrate binding site=== | ===Structure of the substrate binding site=== | ||
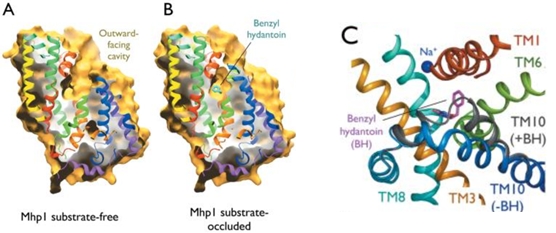
| - | The substrate binding site is located at the break of the TMs 1 and 6. | + | The substrate binding site is located at the break of the TMs 1 and 6. (''Figure 2'') |
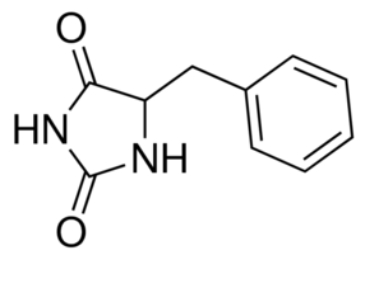
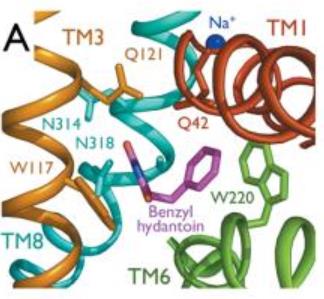
| - | The benzyl-hydantoin interacts with the amino acids of the binding site. The hydantoin group establisches pi-stacking interactions with the indole ring of Trp 117 and Trp 220 and hydrogen bounds with Asn 318 and Gln 121. The benzyl ring interacts with Trp 220 and Gln 42 (''Figure 3''). | + | The substrate, the benzyl-hydantoin interacts with the amino acids of the binding site. The hydantoin group establisches pi-stacking interactions with the indole ring of Trp 117 and Trp 220 and hydrogen bounds with Asn 318 and Gln 121. The benzyl ring interacts with Trp 220 and Gln 42 (''Figure 3''). |
[[Image:Substrate binding site.jpg]] | [[Image:Substrate binding site.jpg]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
===Structure of the cation binding site=== | ===Structure of the cation binding site=== | ||
| - | Mhp1 is a sodium dependent protein. The sodium binds at the C-terminal end of TM1a and interacts with TM8 (''Figure 2 | + | Mhp1 is a sodium dependent protein. The sodium binds at the C-terminal end of TM1a and interacts with TM8 (''Figure 2''). The dipole moment at the C-terminus of TM1a contributes to the binding. |
Experiments have shown that benzyl-hydantoin increases the affinity of sodium for Mhp1 and reciprocally sodium increases the affinity of benzyl-hydantoin for Mhp1. Therefore, the binding of the substrate and the cation are closely coupled. | Experiments have shown that benzyl-hydantoin increases the affinity of sodium for Mhp1 and reciprocally sodium increases the affinity of benzyl-hydantoin for Mhp1. Therefore, the binding of the substrate and the cation are closely coupled. | ||
Revision as of 20:24, 9 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2JLN
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644