We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1489
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== '''Function''' == | == '''Function''' == | ||
| + | |||
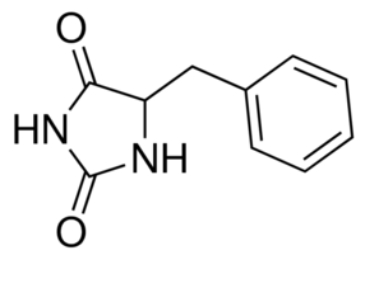
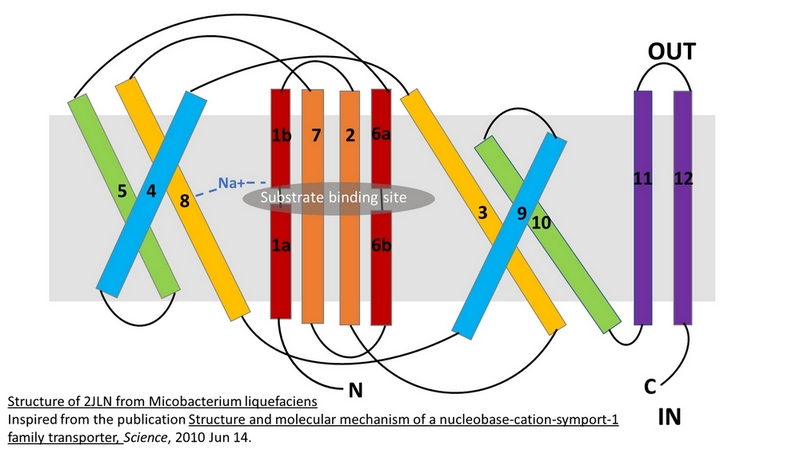
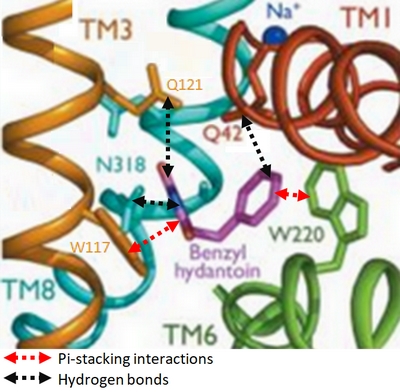
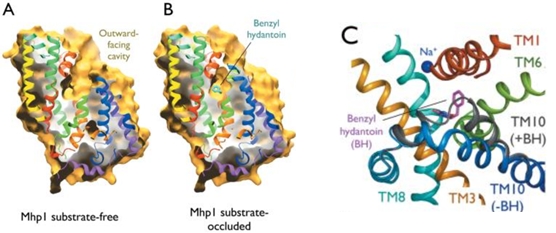
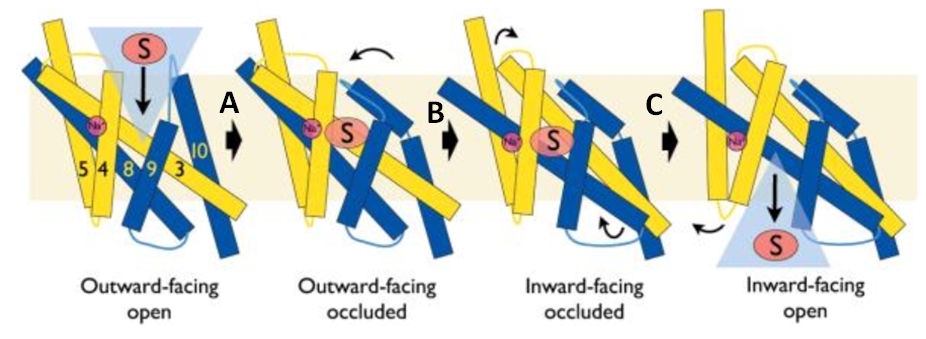
Mhp1 is a transmembrane protein bellowing to the nucleobase-cation-symport-1 (NCS1) transporter family from Microbacterium liquefaciens. It allows the sodium dependent income of indolyl methyl- and benzyl-hydantoins (''Figure 1'') in the cell. Those are part of a salvage metabolic pathway leading to their conversion in amino acids. | Mhp1 is a transmembrane protein bellowing to the nucleobase-cation-symport-1 (NCS1) transporter family from Microbacterium liquefaciens. It allows the sodium dependent income of indolyl methyl- and benzyl-hydantoins (''Figure 1'') in the cell. Those are part of a salvage metabolic pathway leading to their conversion in amino acids. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
| - | ==Relevance== | + | =='''Relevance'''== |
| - | ==Disease== | + | =='''Disease'''== |
| + | Dysfunction of members of the transporters family in humans can lead to diseases including neurological and kidney disorders. Other members are implicated in cancer as they can supply tumor cells with nutrients, cause drug resistance and/or provide a means of treatment. | ||
Revision as of 22:23, 9 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2JLN
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644