We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1491
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells. | KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells. | ||
<StructureSection load='2xml' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of 2xml - monomeric domain of KDM4C' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2xml' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of 2xml - monomeric domain of KDM4C' scene=''> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 17: | ||
Two families of histone-lysine demethylases (KDM) have been identified as follows : the flavin (FAD) -dependent lysine-specific demethylases and the Fe(II)-dependent Jumonji C (JmjC) family. JmjC[1] is subfamily of histone demethylases which regroups several proteins containing a specific catalytic domain called Jmjc found in 2xml structure. KDM4 demethylases belong to the JmjC family and contains six members : KDM4A-F. | Two families of histone-lysine demethylases (KDM) have been identified as follows : the flavin (FAD) -dependent lysine-specific demethylases and the Fe(II)-dependent Jumonji C (JmjC) family. JmjC[1] is subfamily of histone demethylases which regroups several proteins containing a specific catalytic domain called Jmjc found in 2xml structure. KDM4 demethylases belong to the JmjC family and contains six members : KDM4A-F. | ||
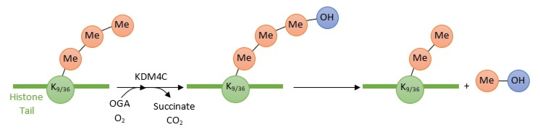
| - | [[Image:Reactionjpg.jpg | thumb]] | + | [[Image:Reactionjpg.jpg | thumb | upright=3,5 | Enzymatic reaction of demethylation of H3K9(me3) and H3K36(me3) by KDM4C ]] |
| - | KDM4C/JMJD2 is a protein which converts specific trimethylated histone residues to the dimethylated form. Indeed, it catalyzes the demethylation of both histone H3 Lysine 9 (H3K9me3) and Lysine 36 (H3K36me3) by hydroxylation of the lysine methyl group leading to a dissociation of the methyl group from the lysine histone tail. KDM4C employs 2-oxoglutarate (OG), Fe2+ and oxygen as cosubstrates to promote its enzymatic reaction, thus the dissociation of methyl groups. | + | KDM4C/JMJD2 is a protein which converts specific trimethylated histone residues to the dimethylated form. Indeed, it catalyzes the demethylation of both histone H3 Lysine 9 (H3K9me3) and Lysine 36 (H3K36me3) by hydroxylation of the lysine methyl group leading to a dissociation of the methyl group from the lysine histone tail. KDM4C employs 2-oxoglutarate (OG), Fe2+ and oxygen as cosubstrates to promote its enzymatic reaction, thus the dissociation of methyl groups. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 11:52, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2xml
Preview
2xml is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the Human KDM4C protein.
KDM4C is a histone demethylase involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3). These marks are specific tags for epigenetic activation. KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells.
| |||||||||||