We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1491
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
| - | ==2xml== | + | =='''2xml'''== |
==Preview== | ==Preview== | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Genes regulation is directly related to the condensation state of the chromatin. Indeed, chromatin can be in the form of heterochromatin (condensed form of DNA) or euchromatin (relaxed form of DNA) which correspond respectively to the transcriptionally silent and active forms of DNA. Chromatin is composed of DNA wrapped around histone octamers forming nucleosomes. The histone tails residues can be acetylated, methylated or demethylated by enzymes in order to modify chromatin state and therefore gene expression. Different types of proteins involved in this process exist, such as histone acetylase (HAT), histone methylase (HMT) or histone demethylase (HDM). | Genes regulation is directly related to the condensation state of the chromatin. Indeed, chromatin can be in the form of heterochromatin (condensed form of DNA) or euchromatin (relaxed form of DNA) which correspond respectively to the transcriptionally silent and active forms of DNA. Chromatin is composed of DNA wrapped around histone octamers forming nucleosomes. The histone tails residues can be acetylated, methylated or demethylated by enzymes in order to modify chromatin state and therefore gene expression. Different types of proteins involved in this process exist, such as histone acetylase (HAT), histone methylase (HMT) or histone demethylase (HDM). | ||
| - | Two families of histone-lysine demethylases (KDM) have been identified as follows : the flavin (FAD) -dependent lysine-specific demethylases and the Fe(II)-dependent Jumonji C (JmjC) family. JmjC[1] is subfamily of histone demethylases which regroups several proteins containing a specific catalytic domain called Jmjc found in 2xml structure. KDM4 demethylases belong to the JmjC family and contains six members : KDM4A-F | + | Two families of histone-lysine demethylases (KDM) have been identified as follows : the flavin (FAD) -dependent lysine-specific demethylases and the Fe(II)-dependent Jumonji C (JmjC) family. JmjC[1] is subfamily of histone demethylases which regroups several proteins containing a specific catalytic domain called Jmjc found in 2xml structure. KDM4 demethylases belong to the JmjC family and contains six members : KDM4A-F |
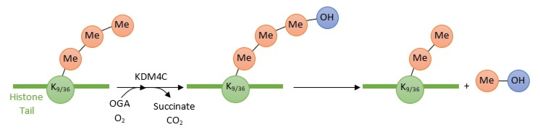
| - | [[Image:Reactionjpg.jpg | thumb | upright=3 | + | [[Image:Reactionjpg.jpg | thumb | upright=3 | Enzymatic reaction of demethylation of H3K9(me3) and H3K36(me3) by KDM4C ]] |
| - | KDM4C/JMJD2 is a protein which converts specific trimethylated histone residues to the dimethylated form. Indeed, it catalyzes the demethylation of both histone H3 Lysine 9 (H3K9me3) and Lysine 36 (H3K36me3) by hydroxylation of the lysine methyl group leading to a dissociation of the methyl group from the lysine histone tail. KDM4C employs 2-oxoglutarate (OG), Fe2+ and oxygen as cosubstrates to promote its enzymatic reaction, thus the dissociation of methyl groups. | + | KDM4C/JMJD2 is a protein which converts specific trimethylated histone residues to the dimethylated form. Indeed, it catalyzes the demethylation of both histone H3 Lysine 9 (H3K9me3) and Lysine 36 (H3K36me3) by hydroxylation of the lysine methyl group leading to a dissociation of the methyl group from the lysine histone tail. KDM4C employs 2-oxoglutarate (OG), Fe2+ and oxygen as cosubstrates to promote its enzymatic reaction, thus the dissociation of methyl groups. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Revision as of 12:11, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2xml
Preview
2xml is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the Human KDM4C protein.
KDM4C is a histone demethylase involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3). These marks are specific tags for epigenetic activation. KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells.
| |||||||||||