This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1480
From Proteopedia
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
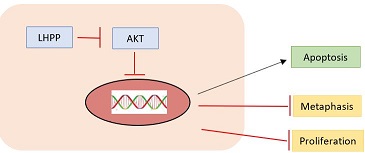
It has also been shown that LHPP is a histidine phosphatase and a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma that removes histidine-linked phosphate groups from proteins. The absence of LHPP promotes the growth of tumors via increasing histidine-phosphorylated proteins. This study shown that LHPP was downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, but also that two histidine kinases (NME1 and NME2) were upregulated. Thus, the regulation of protein phosphorylation is important for the integrity of the cell and when deregulated could lead to tumorigenesis. Collectively, this study provides unprecedented hints on cellular functions of LHPP, and shows that LHPP inactivation together with high NME1/2 expression and - activity is a key tumorigenic event in hepatocellular carcinomas. | It has also been shown that LHPP is a histidine phosphatase and a tumour suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma that removes histidine-linked phosphate groups from proteins. The absence of LHPP promotes the growth of tumors via increasing histidine-phosphorylated proteins. This study shown that LHPP was downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, but also that two histidine kinases (NME1 and NME2) were upregulated. Thus, the regulation of protein phosphorylation is important for the integrity of the cell and when deregulated could lead to tumorigenesis. Collectively, this study provides unprecedented hints on cellular functions of LHPP, and shows that LHPP inactivation together with high NME1/2 expression and - activity is a key tumorigenic event in hepatocellular carcinomas. | ||
| - | LHPP | + | LHPP regulates AKT to control the growth of liver cancer because AKT can block apoptosis and thereby promote cell survival and is considered as an essential factor in the development of many types of cancer. |
Moreover, LHPP apparently inhibited the metastasis of cervical cancer cells, as evidenced by the reduced expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9, TGF-β1, Fibronectin, N-cadherin and Vimentin, and the enhanced E-cadherin. | Moreover, LHPP apparently inhibited the metastasis of cervical cancer cells, as evidenced by the reduced expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9, TGF-β1, Fibronectin, N-cadherin and Vimentin, and the enhanced E-cadherin. | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
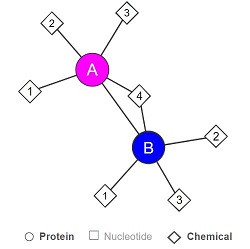
''Fig 3. Simplified structure of LHPP. 1: Pyrophosphate, 2: Magnesium ion, 3: 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-Piperazine ethanesulfonic acid, 4: Glycerol. | ''Fig 3. Simplified structure of LHPP. 1: Pyrophosphate, 2: Magnesium ion, 3: 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-Piperazine ethanesulfonic acid, 4: Glycerol. | ||
| - | A, B: | + | A, B: the two protein subunits of the homodimer. Source : Uniprot, 2018'' |
Revision as of 13:24, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure of the protein LHPP
| |||||||||||
References
"Molecular cloning of a cDNA for the human phospholysine phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase." Yokoi F., Hiraishi H., Izuhara K. J. Biochem. 133:607-614(2003) [PubMed] [Europe PMC] [Abstract]
"The protein histidine phosphatase LHPP is a tumour suppressor." Sravanth K. Hindupur, Marco Colombi, Stephen R. Fuhs, Matthias S. Matter, Yakir Guri, Kevin Adam, Marion Cornu, Salvatore Piscuoglio, Charlotte K. Y. Ng, Charles Betz, Dritan Liko, Luca Quagliata, Suzette Moes, Paul Jenoe, Luigi M. Terracciano, Markus H. Heim, Tony Hunter & Michael N. Hall. (2018) [PubMed] [Main]
"Do metabolic HAD phosphatases moonlight as protein phosphatases?." Antje Gohla. (2018) [BBA - Molecular Cell Research]
"Down-regulation of LHPP in cervical cancer influences cell proliferation, metastasis and apoptosis by modulating AKT", (2018), [PubMed] [Main]