We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1490
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | This is a sample scene created with SAT to <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/1">color</scene> by Group, and another to make <scene name="/12/3456/Sample/2">a transparent representation</scene> of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes. | ||
| - | === | + | ===• Catalytic activation=== |
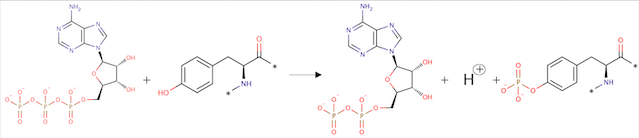
ATP + L-tyrosyl-[protein] = ADP + H+ + O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] | ATP + L-tyrosyl-[protein] = ADP + H+ + O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] | ||
Angiopoietin binding leads to receptor dimerization and activation by autophosphorylation at Tyr-992 on the kinase activation loop. | Angiopoietin binding leads to receptor dimerization and activation by autophosphorylation at Tyr-992 on the kinase activation loop. | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
| - | === | + | ===• Mutagénèse=== |
– '''Transfer in position 855''' : Loss of kinase activity | – '''Transfer in position 855''' : Loss of kinase activity | ||
– '''Transfer in position 1102''' : Deletes interaction with CHS1 | – '''Transfer in position 1102''' : Deletes interaction with CHS1 | ||
Revision as of 15:52, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Kinase Domain of Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2 (PDB:6MWE)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644