We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1491
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
- <scene name='80/802665/Oga/1'>OGA</scene>: two binding sites (chains A and B). | - <scene name='80/802665/Oga/1'>OGA</scene>: two binding sites (chains A and B). | ||
| - | - EDO: three binding sites, only in chain A. They are linked to 2xml by hydrogen bond. | + | - <scene name='80/802665/Edo/1'>EDO</scene>: three binding sites, only in chain A. They are linked to 2xml by hydrogen bond. |
| - | - Zn2+: two binding sites (chains A and B). It makes four coordination bonds : with three cysteines and one histidine. | + | - <scene name='80/802665/Zn/1'>Zn2+</scene>: two binding sites (chains A and B). It makes four coordination bonds : with three cysteines and one histidine. |
| - | - Ni2+ : two binding sites (chains A and B). It makes five coordination bonds : two with OGA, two with two histidine and a last one with a glutamic acid. | + | - <scene name='80/802665/Ni/1'>Ni2+</scene> : two binding sites (chains A and B). It makes five coordination bonds : two with OGA, two with two histidine and a last one with a glutamic acid. |
| - | - Cl- : one binding site, only in chain A. | + | - <scene name='80/802665/Cl/1'>Cl-</scene> : one binding site, only in chain A. |
| - | 2xml presents, in each of the two chains, parallel [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet β sheets] around OGA, forming an '''hydrophobic pocket''' (mainly made of aromatic acid). OGA interacts with 2xml amino acids through hydrogen bonds and coordination bonds with Ni2+. | + | 2xml presents, in each of the two chains, parallel [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet β sheets] around <scene name='80/802665/Oga_pocket/1'>OGA</scene>, forming an '''hydrophobic pocket''' (mainly made of aromatic acid). OGA interacts with 2xml amino acids through hydrogen bonds and coordination bonds with Ni2+. |
The sequence of the domain has been particularly preserved around OGA (when the protein is folded)<ref>http://consurf.tau.ac.il/fgij/fg.htm?mol=/temp/2XMLA_ConSurf_DB_pipe.pdb </ref>. Thus, the 3D structure has been very preserved as well, indicating that the structure around OGA is essential. | The sequence of the domain has been particularly preserved around OGA (when the protein is folded)<ref>http://consurf.tau.ac.il/fgij/fg.htm?mol=/temp/2XMLA_ConSurf_DB_pipe.pdb </ref>. Thus, the 3D structure has been very preserved as well, indicating that the structure around OGA is essential. | ||
Revision as of 16:00, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2xml
Preview
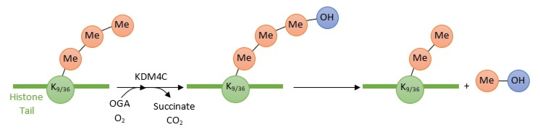
2xml is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the Human KDM4C protein.
KDM4C is a histone demethylase involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3). These marks are specific tags for epigenetic activation. KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ http://consurf.tau.ac.il/fgij/fg.htm?mol=/temp/2XMLA_ConSurf_DB_pipe.pdb
- ↑ Douglas Hanahan et Robert A. Weinberg, « The hallmarks of cancer », Cell, vol. 100, 7 janvier 2000, p. 57-70 (PMID 10647931)
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cancer
- ↑ Gregory, Brittany L., and Vivian G. Cheung. ‘Natural Variation in the Histone Demethylase, KDM4C, Influences Expression Levels of Specific Genes Including Those That Affect Cell Growth’. Genome Research 24, no. 1 (January 2014): 52–63. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.156141.113
- ↑ Garcia, Jeison, and Fernando Lizcano. ‘KDM4C Activity Modulates Cell Proliferation and Chromosome Segregation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer’. Breast Cancer : Basic and Clinical Research 10 (2 November 2016): 169–75. https://doi.org/10.4137/BCBCR.S40182.