We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1491
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Two families of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demethylase histone-lysine demethylase] (KDM) have been identified as follows : the '''flavin (FAD)-dependent lysine-specific demethylases''' and the '''Fe(II)-dependent Jumonji C (JmjC) family'''. JmjC is subfamily of histone demethylases which regroups several proteins containing a specific catalytic domain called '''Jmjc''' found in ''' 2xml structure'''<ref>Shi, Y. G., and Y.-i. Tsukada. “The Discovery of Histone Demethylases.” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5, no. 9 (September 1, 2013): a017947–a017947. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a017947.</ref>. KDM4 demethylases belong to the JmjC family and contains six members : KDM4A-F<ref>Labbé, Roselyne M., Andreana Holowatyj, and Zeng-Quan Yang. “Histone Lysine Demethylase (KDM) Subfamily 4: Structures, Functions and Therapeutic Potential.” American Journal of Translational Research 6, no. 1 (2013): 1–15</ref>. | Two families of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Demethylase histone-lysine demethylase] (KDM) have been identified as follows : the '''flavin (FAD)-dependent lysine-specific demethylases''' and the '''Fe(II)-dependent Jumonji C (JmjC) family'''. JmjC is subfamily of histone demethylases which regroups several proteins containing a specific catalytic domain called '''Jmjc''' found in ''' 2xml structure'''<ref>Shi, Y. G., and Y.-i. Tsukada. “The Discovery of Histone Demethylases.” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5, no. 9 (September 1, 2013): a017947–a017947. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a017947.</ref>. KDM4 demethylases belong to the JmjC family and contains six members : KDM4A-F<ref>Labbé, Roselyne M., Andreana Holowatyj, and Zeng-Quan Yang. “Histone Lysine Demethylase (KDM) Subfamily 4: Structures, Functions and Therapeutic Potential.” American Journal of Translational Research 6, no. 1 (2013): 1–15</ref>. | ||
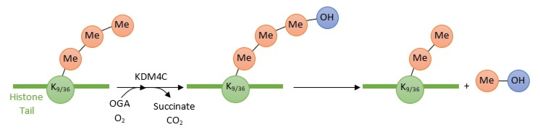
| - | [[Image:Reactionjpg.jpg | thumb | | + | [[Image:Reactionjpg.jpg | thumb | upright=3,5 | Enzymatic reaction of demethylation of H3K9(me3) and H3K36(me3) by KDM4C ]] |
'''KDM4C/JMJD2''' is a protein which converts specifically trimethylated histone residues to the dimethylated form. Indeed, it catalyzes the demethylation of both '''Lysine 9 and Lysine 36 of histone 3''' (respectively H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 by hydroxylation of the lysine methyl group. This reaction leads to a dissociation of the methyl group from the lysine histone tail. KDM4C employs [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-Ketoglutaric_acid 2-oxoglutarate] (OG), Fe2+ and oxygen as cosubstrates to promote its enzymatic reaction, thus the '''dissociation of one methyl group'''<ref>Leurs, Ulrike, Brian Lohse, Kasper D. Rand, Shonoi Ming, Erik S. Riise, Philip A. Cole, Jesper L. Kristensen, and Rasmus P. Clausen. “Substrate- and Cofactor-Independent Inhibition of Histone Demethylase KDM4C.” ACS Chemical Biology 9, no. 9 (September 19, 2014): 2131–38. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb500374f.</ref>. | '''KDM4C/JMJD2''' is a protein which converts specifically trimethylated histone residues to the dimethylated form. Indeed, it catalyzes the demethylation of both '''Lysine 9 and Lysine 36 of histone 3''' (respectively H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 by hydroxylation of the lysine methyl group. This reaction leads to a dissociation of the methyl group from the lysine histone tail. KDM4C employs [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha-Ketoglutaric_acid 2-oxoglutarate] (OG), Fe2+ and oxygen as cosubstrates to promote its enzymatic reaction, thus the '''dissociation of one methyl group'''<ref>Leurs, Ulrike, Brian Lohse, Kasper D. Rand, Shonoi Ming, Erik S. Riise, Philip A. Cole, Jesper L. Kristensen, and Rasmus P. Clausen. “Substrate- and Cofactor-Independent Inhibition of Histone Demethylase KDM4C.” ACS Chemical Biology 9, no. 9 (September 19, 2014): 2131–38. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb500374f.</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 17:10, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
2xml - KDM4C catalytic domain
2xml is a 2 chain structure. This domain belongs to the Human KDM4C protein.
KDM4C is a histone demethylase involved in the specific demethylation of trimethylated residues (Lys 9 and Lys 36 of histone 3). These marks are specific tags for genes expression modification. KDM4C plays a main role in the modification of cell cycle genes expression and thus involved in the growth of tumoral cells.
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Tamaru, H. “Confining Euchromatin/Heterochromatin Territory: Jumonji Crosses the Line.” Genes & Development 24, no. 14 (July 15, 2010): 1465–78. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1941010.
- ↑ Nasir Javaid, and Sangdun Choi. “Acetylation- and Methylation-Related Epigenetic Proteins in the Context of Their Targets.” Genes 8, no. 8 (August 7, 2017): 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8080196
- ↑ Shi, Y. G., and Y.-i. Tsukada. “The Discovery of Histone Demethylases.” Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5, no. 9 (September 1, 2013): a017947–a017947. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a017947.
- ↑ Labbé, Roselyne M., Andreana Holowatyj, and Zeng-Quan Yang. “Histone Lysine Demethylase (KDM) Subfamily 4: Structures, Functions and Therapeutic Potential.” American Journal of Translational Research 6, no. 1 (2013): 1–15
- ↑ Leurs, Ulrike, Brian Lohse, Kasper D. Rand, Shonoi Ming, Erik S. Riise, Philip A. Cole, Jesper L. Kristensen, and Rasmus P. Clausen. “Substrate- and Cofactor-Independent Inhibition of Histone Demethylase KDM4C.” ACS Chemical Biology 9, no. 9 (September 19, 2014): 2131–38. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb500374f.
- ↑ http://consurf.tau.ac.il/fgij/fg.htm?mol=/temp/2XMLA_ConSurf_DB_pipe.pdb
- ↑ Kupershmit, Ilana, Hanan Khoury-Haddad, Samah W. Awwad, Noga Guttmann-Raviv, and Nabieh Ayoub. “KDM4C (GASC1) Lysine Demethylase Is Associated with Mitotic Chromatin and Regulates Chromosome Segregation during Mitosis.” Nucleic Acids Research 42, no. 10 (June 2, 2014): 6168–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku253.
- ↑ Berry, W. L., and R. Janknecht. “KDM4/JMJD2 Histone Demethylases: Epigenetic Regulators in Cancer Cells.” Cancer Research 73, no. 10 (May 15, 2013): 2936–42.
- ↑ Douglas Hanahan et Robert A. Weinberg, « The hallmarks of cancer », Cell, vol. 100, 7 janvier 2000, p. 57-70 (PMID 10647931)
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cancer
- ↑ Gregory, Brittany L., and Vivian G. Cheung. ‘Natural Variation in the Histone Demethylase, KDM4C, Influences Expression Levels of Specific Genes Including Those That Affect Cell Growth’. Genome Research 24, no. 1 (January 2014): 52–63. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.156141.113
- ↑ Garcia, Jeison, and Fernando Lizcano. ‘KDM4C Activity Modulates Cell Proliferation and Chromosome Segregation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer’. Breast Cancer : Basic and Clinical Research 10 (2 November 2016): 169–75. https://doi.org/10.4137/BCBCR.S40182.