We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1490
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
[[Image:controlANG.png]] | [[Image:controlANG.png]] | ||
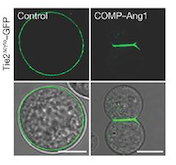
| - | + | ''Fig 1. These cells express Tie2 and are marked with GFP. They were incubated with vehicle (control; left column) and COMP–Ang1 (right column). The scale bars represent 10 μm.'' | |
| - | Fig 1. These cells express Tie2 and are marked with GFP. They were incubated with vehicle (control; left column) and COMP–Ang1 (right column). The scale bars represent 10 μm. | + | |
===• Signal transduction and kinase activity=== | ===• Signal transduction and kinase activity=== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 46: | ||
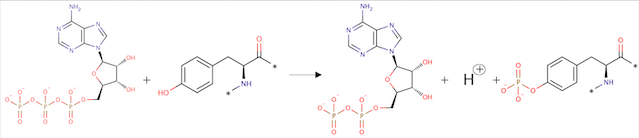
ATP + L-tyrosyl-[protein] = ADP + H+ + O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] | ATP + L-tyrosyl-[protein] = ADP + H+ + O-phospho-L-tyrosyl-[protein] | ||
Angiopoietin binding leads to receptor dimerization and activation by autophosphorylation at Tyr-992 on the kinase activation loop. | Angiopoietin binding leads to receptor dimerization and activation by autophosphorylation at Tyr-992 on the kinase activation loop. | ||
| - | [[Image:Réaction Phosphorylation.jpg]] | + | [[Image:Réaction Phosphorylation.jpg]] |
| + | ''Fig 2. Phosphorylation reaction'' | ||
===• Description of total protein=== | ===• Description of total protein=== | ||
[[Image:TIE2 Schema.jpg]] | [[Image:TIE2 Schema.jpg]] | ||
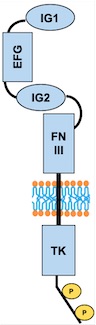
| + | ''Fig 3. Scheme of the whole TIE2 receptor'' | ||
====Important sites ==== | ====Important sites ==== | ||
AA= Amino Acid | AA= Amino Acid | ||
| Line 223: | Line 224: | ||
– '''Mutation in position 849 : Arginine → Tryptophane:''' Change from large size and basic (R) to large size and aromatic (W). Increased autophosphorylation and kinase activation; no effect on location at membrane. | – '''Mutation in position 849 : Arginine → Tryptophane:''' Change from large size and basic (R) to large size and aromatic (W). Increased autophosphorylation and kinase activation; no effect on location at membrane. | ||
Arginine at position 849 is found in six residues upstream of the invariant lysine K855 in the kinase domain (sequence preserved among the human, bovine, murine and rat TIE2 sequences). This seems to prove that a basic amino acid is essential for this position. In addition, arginine located a few amino acids before invariant lysine is involved in stabilizing the kinase domain (hydrogen binding of arginine with a proline downstream). It is therefore possible that R849 may also be involved in the stabilization of the kinase domain. Thus, the substitution of R849 by a W could modify the conformation of the kinase domain, leading to a decrease in inhibitory mechanisms and involving autophosphorylation. | Arginine at position 849 is found in six residues upstream of the invariant lysine K855 in the kinase domain (sequence preserved among the human, bovine, murine and rat TIE2 sequences). This seems to prove that a basic amino acid is essential for this position. In addition, arginine located a few amino acids before invariant lysine is involved in stabilizing the kinase domain (hydrogen binding of arginine with a proline downstream). It is therefore possible that R849 may also be involved in the stabilization of the kinase domain. Thus, the substitution of R849 by a W could modify the conformation of the kinase domain, leading to a decrease in inhibitory mechanisms and involving autophosphorylation. | ||
| - | |||
| - | '''''Diagram : Comparison of the Kinase Activities of Normal and Mutant TIE2 Receptors''''' | ||
| - | (B) Cells infected with wild-type baculovirus (wt) or virus expressing normal TIE2 (R2) or mutant TIE2 (W2). Cells expressing the mutation at position 849 (Arginine → Tryptophan) have an autophosphorylation activity 6 to 10 times higher than wild cells. | ||
[[Image:Venous Malformations Diagram.jpg]] | [[Image:Venous Malformations Diagram.jpg]] | ||
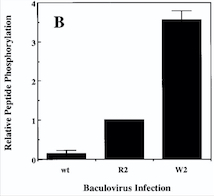
| + | ''Fig 4. Diagram : Comparison of the Kinase Activities of Normal and Mutant TIE2 Receptors. (B) Cells infected with wild-type baculovirus (wt) or virus expressing normal TIE2 (R2) or mutant TIE2 (W2). Cells expressing the mutation at position 849 (Arginine → Tryptophan) have an autophosphorylation activity 6 to 10 times higher than wild cells.'' | ||
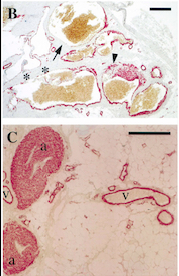
With this mutation, Venous Malformations (VMs) contain a Disproportionately high ratio of Endothelial Cells (ECs) to Smooth Muscle Cells (SMCs) | With this mutation, Venous Malformations (VMs) contain a Disproportionately high ratio of Endothelial Cells (ECs) to Smooth Muscle Cells (SMCs) | ||
| - | + | [[Image:Venous Malformations Immunohistochemistry.jpg]] | |
| + | Fig 5. Pictures of immunohistochemistry of VMs with Antibodies against Smooth Muscle Cells 𝛂-Actin | ||
B = Abnormal channels | B = Abnormal channels | ||
| Line 241: | Line 241: | ||
Antibodies directed against SMCs 𝛂-Actin from cells with VMs show that the vessels have a specific and abnormal staining (B) compared to normal vessels (C) | Antibodies directed against SMCs 𝛂-Actin from cells with VMs show that the vessels have a specific and abnormal staining (B) compared to normal vessels (C) | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Venous Malformations Immunohistochemistry.jpg]] | ||
| Line 275: | Line 273: | ||
[[Image:electro.png]] | [[Image:electro.png]] | ||
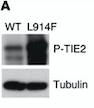
| - | Fig | + | ''Fig 6. Western blot of p-TIE2 in Human Endothelial Cells transfected with TIE2-WT (Wild type) or with mutant TIE2 (L914F). Tubulin served as loading control. The hyperphosphorylation is clearly visible.'' |
Thus, genetic and transplantation‐based models offer versatile tools to study the pathology of VMs, as well as the efficacy and safety of potential molecular therapies. | Thus, genetic and transplantation‐based models offer versatile tools to study the pathology of VMs, as well as the efficacy and safety of potential molecular therapies. | ||
| Line 282: | Line 280: | ||
[[Image:lesion area.png]] | [[Image:lesion area.png]] | ||
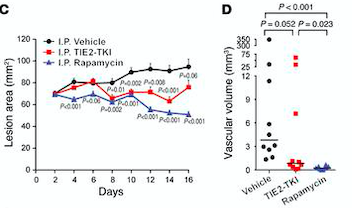
| - | Fig | + | ''Fig 7. (C) HUVECs lesional area measured every 2 days for 16 days. (D) Vascular volume at day 15 measured by analysis of color Doppler 3D image stacks. When compared with the vehicle-treated group, the lesional area was significantly smaller in the rapamycin-treated group from day 4 to day 16 and in the TIE2-TKI–treated group from day 8 to day 14.'' |
===•Cancers=== | ===•Cancers=== | ||
Revision as of 17:25, 10 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Kinase Domain of Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TIE-2 (PDB:6MWE)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hanson, R. M., Prilusky, J., Renjian, Z., Nakane, T. and Sussman, J. L. (2013), JSmol and the Next-Generation Web-Based Representation of 3D Molecular Structure as Applied to Proteopedia. Isr. J. Chem., 53:207-216. doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ijch.201300024
- ↑ Herraez A. Biomolecules in the computer: Jmol to the rescue. Biochem Mol Biol Educ. 2006 Jul;34(4):255-61. doi: 10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644. PMID:21638687 doi:10.1002/bmb.2006.494034042644