The 3lt is an integrase of the HIV, the Human Immunodeficiency Virus. An integrase is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus to integrate its genetic material into the DNA of the infected cell. It is one of three enzymes of HIV, the others being the Reverse Transcriptase and the Protease.
Structural highlights
|
|
| Ligands: | , , , , , |
| NonStd Res: | |
| Related: | 1hyv, 3lpu |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, PDBe, RCSB, PDBsum, ProSAT |
Function
An integrase is an enzyme required for the integration of viral DNA into the host genome. The process of integration can be divided into two sequential reactions. In the first one, named 3'-processing, the enzyme removes di- or trinucleotides from viral DNA ends to expose 3′-hydroxyls attached to CA dinucleotides. The second step is the insertion of the processed 3′-viral DNA ends into the host chromosomal DNA by a trans-esterification reaction. This is called the strand transfer.
The HIV integrase is the enzyme responsible for the integration of the HIV's viral DNA into the host cell.Image:Ehxample.jpg
Structure
HIV-1 integrase is composed of three domains: the N-terminal (residues 1-49), the core domain (residues 50-212) and the C-terminal domain (residues 213-288).[1]
The three domain of the HIV integrase:
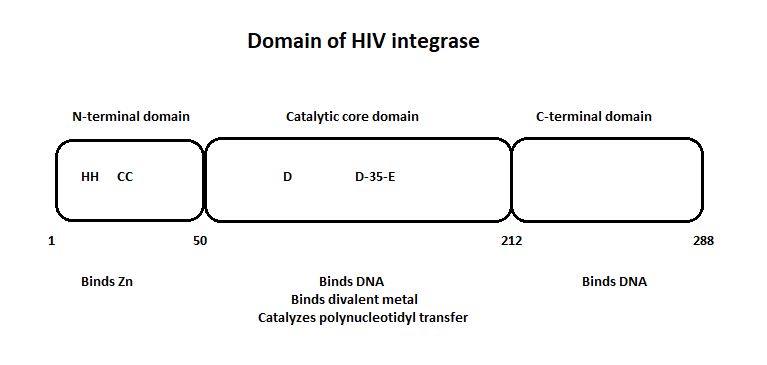 [2]
[2]
HIV Integrase sequence:
 [3]
[3]
Length:288, Mass (Da):32,199
Sequence chain view of the HIV Integrase:
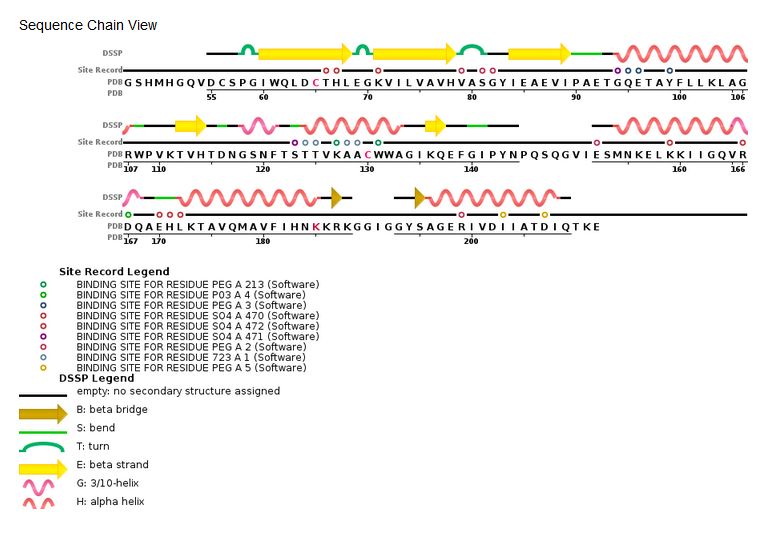 [4]
[4]
Structure and role of the core domain
The catalytic core domain contains three acidic residues, the D,D-35-E motif, comprising residues Asp64, Asp116, and Glu152. By analogy with models of catalysis by DNA polymerases, it has been proposed that coordination of divalent metal ion to these residues plays a key role in catalysis. The catalytic residues Asp64, Asp116, and Glu152of HIV-1 integrase and their counterparts in the ASV structures are in close proximity, coordinate divalent metal ion, and define the active site. However, the residues comprising the active site region exhibit considerable flexibility, suggesting that binding of DNA substrate is required to impose the precise configuration of residues that are required for catalysis.
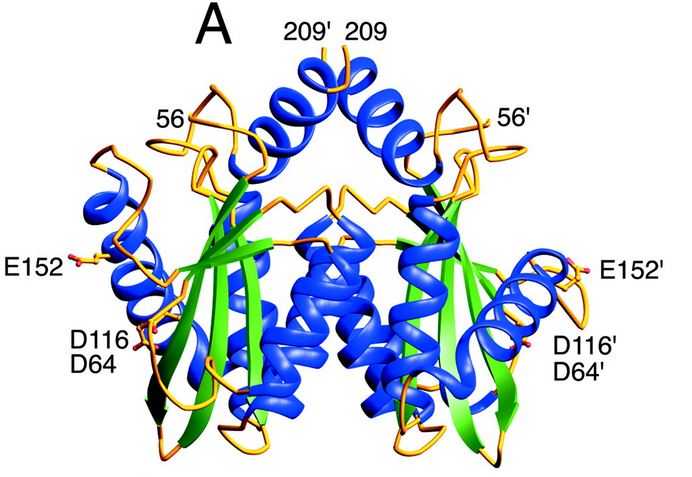 [5]
[5]
Structure and role of the N ter domain
The N-terminal domain of HIV-1 integrase contains a conserved pair of His and Cys residues, a motif similar to the zinc-coordinating residues of zinc fingers. This domain binds zinc but its structure is totally different from that of zinc fingers. It consists of a bundle of three α-helices. This domain is necessary for the oligomerization of the integrase.
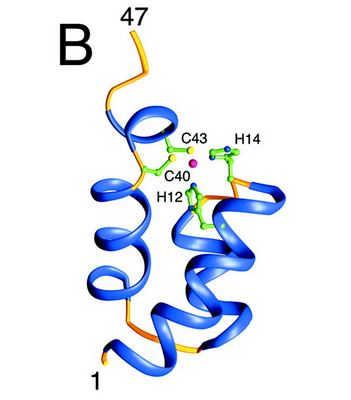 [6]
[6]
Structure and role of the C ter domain
Here is the structure of the C-ter domain :
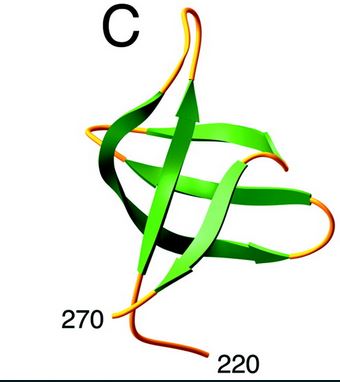 [7]
[7]
The C-terminal domain interacts in a non-specific way with DNA and would, therefore, play a stabilizing role of integrase-ADN interactions.
Interaction between the HIV integrase and LEDGF/p75
LEDGF/p75, or Lens epithelium-derived growth factor, is a cellular cofactor of HIV integrase. It promotes the viral integration of the retrovirus by tethering the preintegration complex to the chromatin. Research on the LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction [8] shows that it can be inhibited by using a molecule which will take the place of LEDGF/p75 on its binding site. Thus, the viral DNA will not be inserted into the genome of the host cell and the replication of HIV won't be possible.
Use of antiviral to inhibit the LEDGF/p75-integrase interaction
An antiviral refers to a molecule disrupting the replication cycle of one or more viruses, thus allowing to slow down but rarely to stop a viral infection. Antiviral targeting specific regions of the integrase are used to prevent the replication of HIV. For example, the 2-(quinolin-3-yl)acetic acid interacts with . More precisely, it binds to the residues E170, H171, and T174. This site is situated in the core domain of the enzyme. Once it is fixed into the core domain, the LEDGF/p75 will not be able to join and viral integration of the retrovirus will not be possible anymore.
The whole complex between the integrase and the cofactor is displayed on the Proteopedia page 2b4j.
HIV
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus. It is a retrovirus virus that damages the cells in the immune system and weakens the ability to fight everyday infections and disease. Copied into DNA, HIV is inserted into the genome of the infected cell thanks to integrases. To replicate and diffuse himself it attacks the body’s immune system, specifically the CD4 cells (T cells), which help fight off infections. As soon as HIV enters an individual, it accumulates in the cells and forms reservoirs of latent viruses in a few days or even hours. These reservoirs persist for life.
No cure currently exists, but HIV can be controlled by using antiretroviral therapy or ART. It is a combination of antiretroviral drugs to maximally suppress the HIV virus and stop the progression of HIV disease. In the mid-1990s, before the introduction of ART, people with HIV could progress to AIDS in just a few years. Today, someone diagnosed with HIV and treated before the disease is far advanced can live nearly as long as someone who does not have HIV.[9]
AIDS
AIDS is the ultimate stage of infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. The word AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. People with AIDS get an increasing number of severe illnesses, called opportunistic infections, because of there damaged immune system. Are considered to have progressed to AIDS individual whose number of CD4 cells is lower than 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood (200 cells/mm3). CD4 counts are between 500 and 1,600 cells/mm3 for someone with a healthy immune system. Developing one or more opportunistic illnesses, regardless of the CD4 count is also an indicator showing the progression to AIDS.[10]
See also
http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/2b4j :integrase ligated with the cofactor LEDGF/p75
References
https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/what-are-hiv-and-aids
https://www-nature-com.scd-rproxy.u-strasbg.fr/articles/nchembio.370
https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q76353#sequences
http://pfam.xfam.org/family/rve
http://pfam.xfam.org/protein/Q76353_9HIV1
https://www.rcsb.org/3d-view/3LPT/1
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diethylene_glycol
https://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/HIV-1_Pre-Integration_Complex
https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q76353
https://www.rcsb.org/structure/3lpt
http://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Retroviral_Integrase
http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=3lpt






