User:Estelle Blochouse/ Sandbox 1497
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
<tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[4e9p|4e9p]], [[4e9q|4e9q]], [[4e9r|4e9r]], [[4e9t|4e9t]]</td></tr> | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[4e9p|4e9p]], [[4e9q|4e9q]], [[4e9r|4e9r]], [[4e9t|4e9t]]</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">cueO, yacK, b0123, JW0119 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=83333 ECOLI])</td></tr> | <tr id='gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Gene|Gene:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">cueO, yacK, b0123, JW0119 ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&srchmode=5&id=83333 ECOLI])</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='function'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Function:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">binding of a metal ion</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='process'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Process:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">oxidation-reduction</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='position'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Position:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">bound at the outer membrane in the periplasmic space</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='chain'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Chain:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">A</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='sequence domain'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Sequence domain:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">Cupredoxin, Multicopper oxidase type 1, type 2, type 3 and a copper-binding site</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='number of amino acids'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Number of amino acids:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">489</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='production and extraction'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Production and extraction:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">Escherichia Coli</td></tr> | ||
| + | <tr id='initial gene'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Initial gene:</b></td><td class="sblockDat">sequence from amino acid 29 to amino acid 516 from P36649</td></tr> | ||
<tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4e9s FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4e9s OCA], [http://pdbe.org/4e9s PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4e9s RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4e9s PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4e9s ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | <tr id='resources'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>Resources:</b></td><td class="sblockDat"><span class='plainlinks'>[http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-docs/fgij/fg.htm?mol=4e9s FirstGlance], [http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/ocaids?id=4e9s OCA], [http://pdbe.org/4e9s PDBe], [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore.do?structureId=4e9s RCSB], [http://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbsum/4e9s PDBsum], [http://prosat.h-its.org/prosat/prosatexe?pdbcode=4e9s ProSAT]</span></td></tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
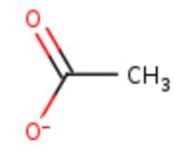
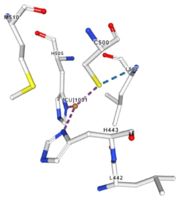
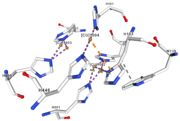
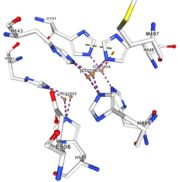
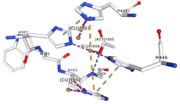
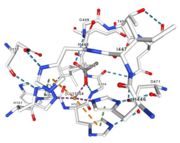
<table><tr><td colspan='2'>In the chain, 5 ligands are present: an acetate ion (C2H3O2) and 4 copper ions. <br> | <table><tr><td colspan='2'>In the chain, 5 ligands are present: an acetate ion (C2H3O2) and 4 copper ions. <br> | ||
| Line 80: | Line 89: | ||
</table><ref>PMID:17804014</ref> | </table><ref>PMID:17804014</ref> | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
Revision as of 06:59, 11 January 2019
Multicopper Oxidase CueO (4e9s)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ EMBL-EBI, Family: Cu-oxidase (PF00394), Summary: Multicopper oxidase, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/Cu-oxidase
- ↑ <ref>PMID:9556453</ref>
- ↑ <ref>PMID:9556453</ref>
- ↑ <ref>PMID:9556453</ref>
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ Kataoka K, Komori H, Ueki Y, Konno Y, Kamitaka Y, Kurose S, Tsujimura S, Higuchi Y, Kano K, Seo D, Sakurai T. Structure and function of the engineered multicopper oxidase CueO from Escherichia coli--deletion of the methionine-rich helical region covering the substrate-binding site. J Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 12;373(1):141-52. Epub 2007 Aug 2. PMID:17804014 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.041