We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1490
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
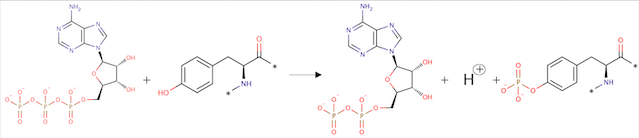
==Crystal structure of cytoplasmic kinase domain of Tie2 in complex with decipera compound DP1919== | ==Crystal structure of cytoplasmic kinase domain of Tie2 in complex with decipera compound DP1919== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='6MWE' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='6MWE' size='340' side='right' caption='Structure of the kinase domain of TIE2.' scene='' name='pp'> |
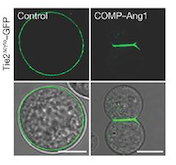
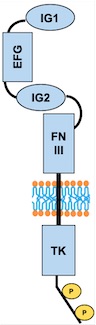
The protein we are focusing one is a protein kinase receptor to a family of ligands called angiopoietins. This receptor is a Tyrosine Kinase TIE2. We are going to analyze the kinase domain of this protein | The protein we are focusing one is a protein kinase receptor to a family of ligands called angiopoietins. This receptor is a Tyrosine Kinase TIE2. We are going to analyze the kinase domain of this protein | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
AA= Amino Acid | AA= Amino Acid | ||
| - | – Binding site : | + | – Binding site : AA 855 |
– Active site : AA 964 | – Active site : AA 964 | ||
Revision as of 12:43, 11 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Crystal structure of cytoplasmic kinase domain of Tie2 in complex with decipera compound DP1919
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Fukuhara S, Sako K, Minami T, Noda K, Kim HZ, Kodama T, Shibuya M, Takakura N, Koh GY, Mochizuki N. Differential function of Tie2 at cell-cell contacts and cell-substratum contacts regulated by angiopoietin-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008 May;10(5):513-26. doi: 10.1038/ncb1714. Epub 2008 Apr 20. PMID:18425120 doi:10.1038/ncb1714
- ↑ Yuan HT, Khankin EV, Karumanchi SA, Parikh SM. Angiopoietin 2 is a partial agonist/antagonist of Tie2 signaling in the endothelium. Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;29(8):2011-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01472-08. Epub 2009 Feb, 17. PMID:19223473 doi:10.1128/MCB.01472-08
- ↑ Yuan HT, Khankin EV, Karumanchi SA, Parikh SM. Angiopoietin 2 is a partial agonist/antagonist of Tie2 signaling in the endothelium. Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Apr;29(8):2011-22. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01472-08. Epub 2009 Feb, 17. PMID:19223473 doi:10.1128/MCB.01472-08
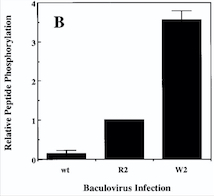
- ↑ Murray BW, Padrique ES, Pinko C, McTigue MA. Mechanistic effects of autophosphorylation on receptor tyrosine kinase catalysis: enzymatic characterization of Tie2 and phospho-Tie2. Biochemistry. 2001 Aug 28;40(34):10243-53. PMID:11513602
- ↑ Murray BW, Padrique ES, Pinko C, McTigue MA. Mechanistic effects of autophosphorylation on receptor tyrosine kinase catalysis: enzymatic characterization of Tie2 and phospho-Tie2. Biochemistry. 2001 Aug 28;40(34):10243-53. PMID:11513602
- ↑ Jones N, Chen SH, Sturk C, Master Z, Tran J, Kerbel RS, Dumont DJ. A unique autophosphorylation site on Tie2/Tek mediates Dok-R phosphotyrosine binding domain binding and function. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;23(8):2658-68. PMID:12665569
- ↑ Jones N, Chen SH, Sturk C, Master Z, Tran J, Kerbel RS, Dumont DJ. A unique autophosphorylation site on Tie2/Tek mediates Dok-R phosphotyrosine binding domain binding and function. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;23(8):2658-68. PMID:12665569
- ↑ Jones N, Chen SH, Sturk C, Master Z, Tran J, Kerbel RS, Dumont DJ. A unique autophosphorylation site on Tie2/Tek mediates Dok-R phosphotyrosine binding domain binding and function. Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Apr;23(8):2658-68. PMID:12665569
- ↑ Vikkula M, Boon LM, Carraway KL 3rd, Calvert JT, Diamonti AJ, Goumnerov B, Pasyk KA, Marchuk DA, Warman ML, Cantley LC, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR. Vascular dysmorphogenesis caused by an activating mutation in the receptor tyrosine kinase TIE2. Cell. 1996 Dec 27;87(7):1181-90. PMID:8980225
- ↑ Vikkula M, Boon LM, Carraway KL 3rd, Calvert JT, Diamonti AJ, Goumnerov B, Pasyk KA, Marchuk DA, Warman ML, Cantley LC, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR. Vascular dysmorphogenesis caused by an activating mutation in the receptor tyrosine kinase TIE2. Cell. 1996 Dec 27;87(7):1181-90. PMID:8980225
- ↑ Vikkula M, Boon LM, Carraway KL 3rd, Calvert JT, Diamonti AJ, Goumnerov B, Pasyk KA, Marchuk DA, Warman ML, Cantley LC, Mulliken JB, Olsen BR. Vascular dysmorphogenesis caused by an activating mutation in the receptor tyrosine kinase TIE2. Cell. 1996 Dec 27;87(7):1181-90. PMID:8980225
- ↑ Kangas J, Natynki M, Eklund L. Development of Molecular Therapies for Venous Malformations. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Sep;123 Suppl 5:6-19. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13027., Epub 2018 May 29. PMID:29668117 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13027
- ↑ Kangas J, Natynki M, Eklund L. Development of Molecular Therapies for Venous Malformations. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2018 Sep;123 Suppl 5:6-19. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13027., Epub 2018 May 29. PMID:29668117 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13027
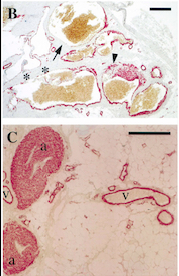
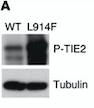
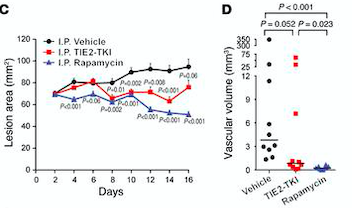
- ↑ Boscolo E, Limaye N, Huang L, Kang KT, Soblet J, Uebelhoer M, Mendola A, Natynki M, Seront E, Dupont S, Hammer J, Legrand C, Brugnara C, Eklund L, Vikkula M, Bischoff J, Boon LM. Rapamycin improves TIE2-mutated venous malformation in murine model and human subjects. J Clin Invest. 2015 Sep;125(9):3491-504. doi: 10.1172/JCI76004. Epub 2015 Aug 10. PMID:26258417 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI76004
- ↑ Boscolo E, Limaye N, Huang L, Kang KT, Soblet J, Uebelhoer M, Mendola A, Natynki M, Seront E, Dupont S, Hammer J, Legrand C, Brugnara C, Eklund L, Vikkula M, Bischoff J, Boon LM. Rapamycin improves TIE2-mutated venous malformation in murine model and human subjects. J Clin Invest. 2015 Sep;125(9):3491-504. doi: 10.1172/JCI76004. Epub 2015 Aug 10. PMID:26258417 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI76004
- ↑ Boscolo E, Limaye N, Huang L, Kang KT, Soblet J, Uebelhoer M, Mendola A, Natynki M, Seront E, Dupont S, Hammer J, Legrand C, Brugnara C, Eklund L, Vikkula M, Bischoff J, Boon LM. Rapamycin improves TIE2-mutated venous malformation in murine model and human subjects. J Clin Invest. 2015 Sep;125(9):3491-504. doi: 10.1172/JCI76004. Epub 2015 Aug 10. PMID:26258417 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI76004
- ↑ Shlamkovich T, Aharon L, Koslawsky D, Einav Y, Papo N. Targeting the Tie2-alphavbeta3 integrin axis with bi-specific reagents for the inhibition of angiogenesis. BMC Biol. 2018 Aug 17;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12915-018-0557-9. PMID:30119679 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12915-018-0557-9