User:Estelle Blochouse/ Sandbox 1497
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
Multicopper oxidase might also be involved in the regulation of metal transport. | Multicopper oxidase might also be involved in the regulation of metal transport. | ||
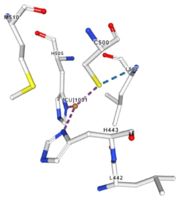
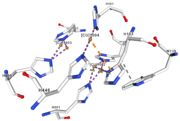
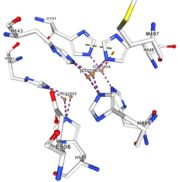
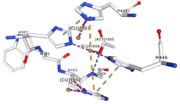
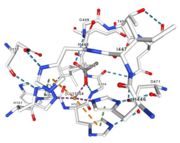
| - | Multicopper oxidases are abble to oxiise their substrate. They accept an electron in the <scene name='pdbligand=CU:COPPER+(II)+ION'>mononoclear copper center</scene> and transfer it to the trinuclear copper centre. The dioxygen bind to the trinuclear center and recieve four electron. It is transformed into two molecules of water.<ref | + | Multicopper oxidases are abble to oxiise their substrate. They accept an electron in the <scene name='pdbligand=CU:COPPER+(II)+ION'>mononoclear copper center</scene> and transfer it to the trinuclear copper centre. The dioxygen bind to the trinuclear center and recieve four electron. It is transformed into two molecules of water.<ref>authors = Bento I, Martins LO, Gato Lopes G, Arménia Carrondo M, Lindley PF, title = Dioxygen reduction by multi-copper oxidases; a structural perspective, November 2005</ref> Three copper centres exist that can be differentiate spectroscopically: Type 1 or blue (<scene name='pdbligand=CU:COPPER+(II)+ION'>mononoclear copper center</scene>), type 2 or normal (Cu1004) and type 3 or coupled binuclear (1002 and 1003).<ref>authors = Messerschmidt A, Huber R, title = The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships, journal = Eur. J. Biochem. volume = 187, January 1990</ref><ref>authors = Ouzounis C, Sander C, title = A structure-derived sequence pattern for the detection of type I copper binding domains in distantly related proteins, journal = FEBS Lett. volume = 279, February 1991</ref> |
Revision as of 14:47, 11 January 2019
Multicopper Oxidase CueO (4e9s)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ EMBL-EBI, Family: Cu-oxidase (PF00394), Summary: Multicopper oxidase, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/Cu-oxidase
- ↑ UniProtKB
- ↑ authors = Bento I, Martins LO, Gato Lopes G, Arménia Carrondo M, Lindley PF, title = Dioxygen reduction by multi-copper oxidases; a structural perspective, November 2005
- ↑ authors = Messerschmidt A, Huber R, title = The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships, journal = Eur. J. Biochem. volume = 187, January 1990
- ↑ authors = Ouzounis C, Sander C, title = A structure-derived sequence pattern for the detection of type I copper binding domains in distantly related proteins, journal = FEBS Lett. volume = 279, February 1991
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ RCSB PDB
- ↑ Kataoka K, Komori H, Ueki Y, Konno Y, Kamitaka Y, Kurose S, Tsujimura S, Higuchi Y, Kano K, Seo D, Sakurai T. Structure and function of the engineered multicopper oxidase CueO from Escherichia coli--deletion of the methionine-rich helical region covering the substrate-binding site. J Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 12;373(1):141-52. Epub 2007 Aug 2. PMID:17804014 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.041