RNA
From Proteopedia
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
====Storage==== | ====Storage==== | ||
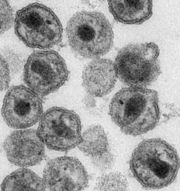
| - | + | [[Image:HIV_particles.JPG|thumb]]All known organisms use DNA as the storage molecule for genetic information. Some viruses, however use RNA instead. They are classified into double-stranded RNA viruses and plus or minus single-stranded RNA viruses depending on how they use RNA to store genetic information. For example, human immunodeficiency virus carries genetic information in the form of single stranded RNA. In the figure, the RNA is located in the dark rectangular blob inside the circular virus particles. | |
====Transcription==== | ====Transcription==== | ||
Revision as of 15:10, 11 January 2019
RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a biological macromolecule that stores and processes genetic information, catalyzes chemical reactions and regulates biological processes. Just like the other nucleic acid (DNA), it is a linear polymer (a "strand") of nucleotide building blocks. These building blocks themselves are made up of a sugar linked to a (nitrogenous) base and a phosphate. RNA utilizes a different set of bases than DNA, and it sugar (ribose) contains one additional hydroxyl group compared to that of DNA (deoxyribose). Different than DNA, which mostly occurs in pairs of complementary strands in its biological context, RNA mostly lacks a complementary strand, leading to a larger variety of 3D structures and biological functions.
RNA structure and function
| |||||||||||
Chemistry
- Base: flat, aromatic, hydrogen-bonding capability, base modifications, base pairing, base stacking
- Sugar phosphate backbone: torsion angles, sugar pucker, phosphate-phosphate distance
Transcription and Translation
The expression of genes into proteins and is a process involving two stages called transcription and translation. In the transcription stage a strand of DNA molecule serves as a template for the synthesis of an RNA molecule called messenger RNA. In the case of RNAs that code for polypetides, this messenger RNA is then translated into proteins on ribosomes.
Post-transcriptionally, specific nucleotides in RNA are often further modified. This is most frequent in [tRNA|transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNAs)]], the adapter molecules of Translation, and ribosomal ribonucleic acids (rRNAs) of the ribosome.
See Also
- Ribosome
- Translation
- DNA Replication, Transcription and Translation
- Transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA)
- Ribozyme
- Kink-turn motif
- Pseudouridine
- Non-Standard Residues
- DNA
- For additional information, see: Nucleic Acids
External Resources
- HD-RNAS: Hierarchical Database of RNA Structures is a systematic hierarchical organization classifying all RNAs available in the Protein Data Bank. This helps make it easier to navigate the availble structural data given the large numbers of redundant files and ambiguous synthetic sequences.
- Liley Database
References
- ↑ Steitz TA. The structural changes of T7 RNA polymerase from transcription initiation to elongation. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Dec;19(6):683-90. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.09.001., Epub 2009 Oct 5. PMID:19811903 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2009.09.001
- ↑ Toor N, Rajashankar K, Keating KS, Pyle AM. Structural basis for exon recognition by a group II intron. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2008 Nov;15(11):1221-2. Epub 2008 Oct 26. PMID:18953333 doi:10.1038/nsmb.1509