User:Estelle Blochouse/ Sandbox 1497
From Proteopedia
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
| - | Copper is one of the most important metal involed in multiple enzyme catalysed reactions as a cofactor. In living organisms its function is related to the redox property of the copper. However it is toxic at all | + | Copper is one of the most important metal involed in multiple enzyme catalysed reactions as a cofactor. In living organisms its function is related to the redox property of the copper. However it is toxic at all concentration, from the lower to the higher, and it need to be strictly controled in living organisms by molecular mechanisms.<ref>EMBL-EBI, Family: Cu-oxidase (PF00394), Summary: Multicopper oxidase, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/Cu-oxidase</ref> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Mechanism == | == Mechanism == | ||
Multicopper oxidase catalyze the oxidation of different substrates by reducing O2 into H2O without releasing activated oxygen species (H2O2)................. | Multicopper oxidase catalyze the oxidation of different substrates by reducing O2 into H2O without releasing activated oxygen species (H2O2)................. | ||
| + | |||
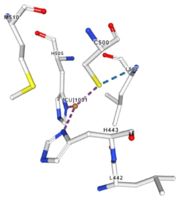
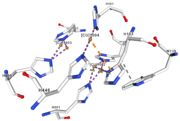
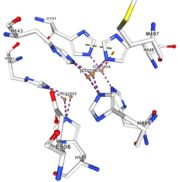
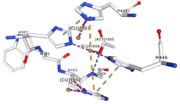
| + | Multicopper oxidase contain 3 types of copper ions involved in the transfer of electrons from the substrate to the dioxygen. The first type of copper, type 1, (Cu1001) mediate the electron transfer fron the substrate to the other copper. The three other copper are called the trinuclear copper center. It is the key element for the oxygen reduction. It contain a type 2 copper (Cu1002) and 2 type 3 copper ions, binuclear ions, (Cu1003 and Cu1004). The final electron acceptor, O2, is bound to this last type of copper and is reduced into two molecules of water.<ref> | ||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 11 January 2019
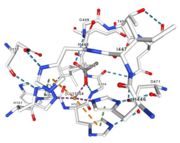
Multicopper Oxidase CueO (4e9s)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ EMBL-EBI, Family: Cu-oxidase (PF00394), Summary: Multicopper oxidase, http://pfam.xfam.org/family/Cu-oxidase
- ↑ UniProtKB
- ↑ Bento I, Martins LO, Gato Lopes G, Arménia Carrondo M, Lindley PF, title = Dioxygen reduction by multi-copper oxidases; a structural perspective, November 2005
- ↑ Messerschmidt A, Huber R, title = The blue oxidases, ascorbate oxidase, laccase and ceruloplasmin. Modelling and structural relationships, journal = Eur. J. Biochem. volume = 187, January 1990
- ↑ authors = Ouzounis C, Sander C, title = A structure-derived sequence pattern for the detection of type I copper binding domains in distantly related proteins, journal = FEBS Lett. volume = 279, February 1991
- ↑
Disease
If the amino acids 500 and 501 are mutated from CH to SR, the residual activity and loss of resistance to copper. E. Coli die.
Structural highlights
Multicopper Oxidase CueO 4e9s is a protein containing one chain with sequence from Ecoli. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance.
Ligands: [[Image:Act.jpg|thumb|middle|Figure 1: Acetate ion.<ref><span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></li> <li id="cite_note-6">[[#cite_ref-6|↑]] <span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></li> <li id="cite_note-7">[[#cite_ref-7|↑]] <span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></li> <li id="cite_note-8">[[#cite_ref-8|↑]] <span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></li> <li id="cite_note-9">[[#cite_ref-9|↑]] <span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></li> <li id="cite_note-10">[[#cite_ref-10|↑]] <span class='plainlinks'>[https://www.rcsb.org/structure/4e9s RCBS PDB]</span></li>
<li id="cite_note-11">[[#cite_ref-11|↑]] Kataoka K, Komori H, Ueki Y, Konno Y, Kamitaka Y, Kurose S, Tsujimura S, Higuchi Y, Kano K, Seo D, Sakurai T. Structure and function of the engineered multicopper oxidase CueO from Escherichia coli--deletion of the methionine-rich helical region covering the substrate-binding site. J Mol Biol. 2007 Oct 12;373(1):141-52. Epub 2007 Aug 2. PMID:[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17804014 17804014] doi:[http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.041 10.1016/j.jmb.2007.07.041]</li></ol></ref>