Sandbox Reserved 1493
From Proteopedia
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
Its <scene name='80/802667/Beta_head/2'>head</scene> is composed of a '''β I domain''' which has a fold similar to the I domain of the head of the α subunit. Is has a <scene name='80/802667/Mg_in_beta_head_midas/2'>Mg2+</scene> coordinating '''metal ion dependent adhesion site (MIDAS)''' motif and a site adjacent to MIDAS ('''ADMIDAS''') which coordinates ions and plays a part in activity modulation. In the head can be found the RGD and KGD binding sites. | Its <scene name='80/802667/Beta_head/2'>head</scene> is composed of a '''β I domain''' which has a fold similar to the I domain of the head of the α subunit. Is has a <scene name='80/802667/Mg_in_beta_head_midas/2'>Mg2+</scene> coordinating '''metal ion dependent adhesion site (MIDAS)''' motif and a site adjacent to MIDAS ('''ADMIDAS''') which coordinates ions and plays a part in activity modulation. In the head can be found the RGD and KGD binding sites. | ||
| - | Its '''stalk''' is mainly composed of a plexin-sempahorin-integrin (PSI) domain and a '''hybrid domain'''. A <scene name='80/802667/Beta_head_cysteines_core/1'>cysteine-rich core</scene> ''(Cys displayed in purple, disulfide bonds in yellow)'' occupies the stalk of β3 from residues 400 to 650. Other cysteins | + | Its '''stalk''' is mainly composed of a plexin-sempahorin-integrin (PSI) domain and a '''hybrid domain'''. A <scene name='80/802667/Beta_head_cysteines_core/1'>cysteine-rich core</scene> ''(Cys displayed in purple, disulfide bonds in yellow)'' occupies the stalk of β3 from residues 400 to 650. Other cysteins link the N-terminal of the protein to the β I domain thanks to a long-range disulfide bond. <scene name='80/802667/Beta_head_cysteines/1'>Cysteines</scene> of the extracellular domain of the β subunit are thought to have a role in the activation of the headpiece. |
The cytoplasmic tail of the β3 subunit has a NPLY domain which binds proteins with phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domains. | The cytoplasmic tail of the β3 subunit has a NPLY domain which binds proteins with phosphotyrosine binding (PTB) domains. | ||
Revision as of 12:49, 14 January 2019
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 06/12/2018, through 30/06/2019 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1480 through Sandbox Reserved 1543. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Integrin αIIbβ3 Headpiece (2VDL)
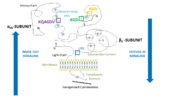
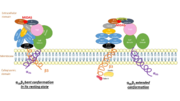
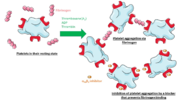
Integrin αIIbβ3 (or glycoprotein IIb/IIIa) is a complex present on the membrane of platelets that intervenes in the activation, adherence and aggregation of platelets during clotting. It is a cation-dependant heterodimeric transmembrane receptor containing a large extracellular headpiece and short intracellular tails. It is synthesized in megakaryocytes.
Its particular shape and localisation on the membrane allows both transduction of the intracellular activation signal and extracellular ligand binding. It is the dominant integrin on platelets with 70,000 to 90,000 receptors expressed on each platelet in the resting state.
The headpiece (2VDL) of integrin αIIbβ3 enables cation-facilitated ligand binding with multiple ligands (most known being fibrinogen, fibronectin, von Willebrand factors, thrombospondin and vitronectin). Binding affinity is dynamic and depends on the conformational status of the receptor.
Jmol displays residues 32-483 of αIIb and residues 27-487 of β3. In order to have a global view of the integrin, see pictures.
| |||||||||||
References
Displays of fibrinogen and eptifibatide ligands are made thanks to 2VDO and 2VDN.
Structure and function:
- doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.2210/pdb2VDL/pdb
- Barczyk M, Carracedo S, Gullberg D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):269-80. Epub 2009 Aug 20. PMID:19693543 doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0834-6
- Lefkovits J, Plow EF, Topol EJ. Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa receptors in cardiovascular medicine. N Engl J Med. 1995 Jun 8;332(23):1553-9. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199506083322306. PMID:7739710 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199506083322306
- Barczyk M, Carracedo S, Gullberg D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):269-80. Epub 2009 Aug 20. PMID:19693543 doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0834-6
- Podolnikova NP, Yakovlev S, Yakubenko VP, Wang X, Gorkun OV, Ugarova TP. The interaction of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 with fibrin occurs through multiple binding sites in the alphaIIb beta-propeller domain. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2371-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.518126. Epub 2013 , Dec 12. PMID:24338009 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.518126
- Chew DP, Moliterno DJ. A critical appraisal of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibition. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000 Dec;36(7):2028-35. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00979-7. PMID:11127436 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0735-1097(00)00979-7
- Kamata T, Tieu KK, Irie A, Springer TA, Takada Y. Amino acid residues in the alpha IIb subunit that are critical for ligand binding to integrin alpha IIbbeta 3 are clustered in the beta-propeller model. J Biol Chem. 2001 Nov 23;276(47):44275-83. Epub 2001 Sep 13. PMID:11557768 doi:10.1074/jbc.M107021200
Activity modulation:
- Hantgan RR, Stahle MC, Lord ST. Dynamic regulation of fibrinogen: integrin alphaIIbbeta3 binding. Biochemistry. 2010 Nov 2;49(43):9217-25. doi: 10.1021/bi1009858. PMID:20828133 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1021/bi1009858
- Podolnikova NP, Yakovlev S, Yakubenko VP, Wang X, Gorkun OV, Ugarova TP. The interaction of integrin alphaIIbbeta3 with fibrin occurs through multiple binding sites in the alphaIIb beta-propeller domain. J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):2371-83. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.518126. Epub 2013 , Dec 12. PMID:24338009 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.518126
- doi: https://dx.doi.org/https
- Joo SJ. Mechanisms of Platelet Activation and Integrin alphaIIbeta3. Korean Circ J. 2012 May;42(5):295-301. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2012.42.5.295. Epub 2012 , May 24. PMID:22701130 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.4070/kcj.2012.42.5.295
- Yan B, Smith JW. A redox site involved in integrin activation. J Biol Chem. 2000 Dec 22;275(51):39964-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007041200. PMID:10993900 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M007041200
Diseases and relevance:
- Estevez B, Shen B, Du X. Targeting integrin and integrin signaling in treating thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015 Jan;35(1):24-9. doi:, 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303411. Epub 2014 Sep 25. PMID:25256236 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303411
- Bledzka K, Smyth SS, Plow EF. Integrin alphaIIbbeta3: from discovery to efficacious therapeutic target. Circ Res. 2013 Apr 12;112(8):1189-200. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300570. PMID:23580774 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300570
- Wang R, Shattil SJ, Ambruso DR, Newman PJ. Truncation of the cytoplasmic domain of beta3 in a variant form of Glanzmann thrombasthenia abrogates signaling through the integrin alpha(IIb)beta3 complex. J Clin Invest. 1997 Nov 1;100(9):2393-403. doi: 10.1172/JCI119780. PMID:9351872 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI119780