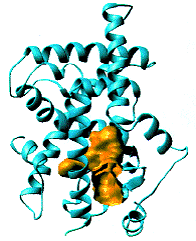This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
GLUT4
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: <StructureSection load='1suk' size='340' side='right' caption='Glucose Transporter Type 4' scene=''> '''Glucose Transporter Type 4''' (GLUT4) is an insulin-regulated membrane protein respo...) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | <StructureSection load='1suk' size='340' side='right' caption=' | + | <StructureSection load='1suk' size='340' side='right' caption='Human glucose Transporter Type 4 (PDB code [[1suk]])' scene=''> |
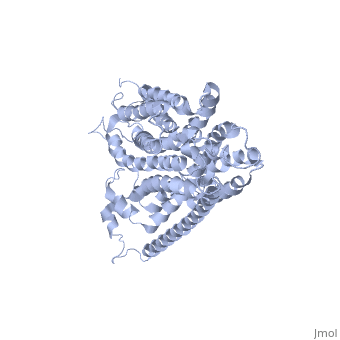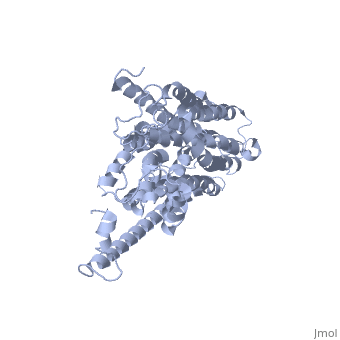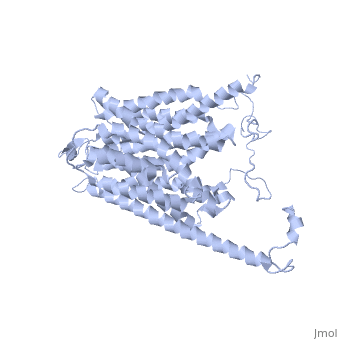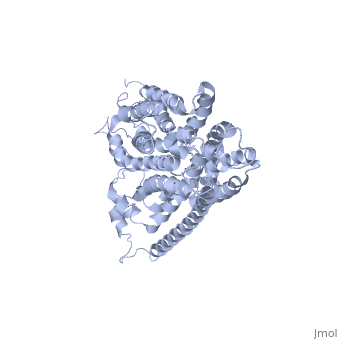
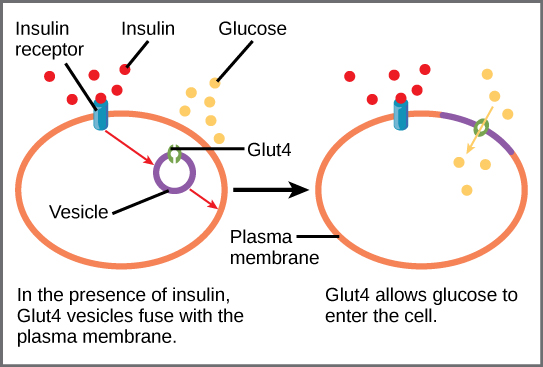
'''Glucose Transporter Type 4''' (GLUT4) is an insulin-regulated membrane protein responsible for decreasing blood glucose concentration found in both adipose tissues as well as striated muscle<ref>PMID:17403369</ref>. Activity of this protein is primarily regulated by the signal transduction pathway and several transcriptional factors found in the tissues where GLUT4 is located<ref>PMID:17487684</ref><ref>PMID:11994746</ref><ref>PMID:19448718</ref>. GLUT4 is responsible for returning blood glucose to a physiological concentration of 5-6mM after the ingestion of carbohydrates, as well as increasing the rate of glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscle following glycogen depleting exercise<ref>PMID:15822579</ref><ref>PMID:1699426</ref>. | '''Glucose Transporter Type 4''' (GLUT4) is an insulin-regulated membrane protein responsible for decreasing blood glucose concentration found in both adipose tissues as well as striated muscle<ref>PMID:17403369</ref>. Activity of this protein is primarily regulated by the signal transduction pathway and several transcriptional factors found in the tissues where GLUT4 is located<ref>PMID:17487684</ref><ref>PMID:11994746</ref><ref>PMID:19448718</ref>. GLUT4 is responsible for returning blood glucose to a physiological concentration of 5-6mM after the ingestion of carbohydrates, as well as increasing the rate of glycogen synthesis in skeletal muscle following glycogen depleting exercise<ref>PMID:15822579</ref><ref>PMID:1699426</ref>. | ||
[[Image:Glut4_3d_structure.gif]] | [[Image:Glut4_3d_structure.gif]] | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Huang S, Czech MP. The GLUT4 glucose transporter. Cell Metab. 2007 Apr;5(4):237-52. PMID:17403369 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2007.03.006
- ↑ Im SS, Kwon SK, Kim TH, Kim HI, Ahn YH. Regulation of glucose transporter type 4 isoform gene expression in muscle and adipocytes. IUBMB Life. 2007 Mar;59(3):134-45. PMID:17487684 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15216540701313788
- ↑ Bryant NJ, Govers R, James DE. Regulated transport of the glucose transporter GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Apr;3(4):267-77. PMID:11994746 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrm782
- ↑ Klip A. The many ways to regulate glucose transporter 4. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2009 Jun;34(3):481-7. doi: 10.1139/H09-047. PMID:19448718 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1139/H09-047
- ↑ Jose-Cunilleras E, Hayes KA, Toribio RE, Mathes LE, Hinchcliff KW. Expression of equine glucose transporter type 4 in skeletal muscle after glycogen-depleting exercise. Am J Vet Res. 2005 Mar;66(3):379-85. PMID:15822579
- ↑ Henriksen EJ, Bourey RE, Rodnick KJ, Koranyi L, Permutt MA, Holloszy JO. Glucose transporter protein content and glucose transport capacity in rat skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):E593-8. PMID:1699426
- ↑ Watson RT, Kanzaki M, Pessin JE. Regulated membrane trafficking of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter 4 in adipocytes. Endocr Rev. 2004 Apr;25(2):177-204. PMID:15082519 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/er.2003-0011
- ↑ Rossetti L, Stenbit AE, Chen W, Hu M, Barzilai N, Katz EB, Charron MJ. Peripheral but not hepatic insulin resistance in mice with one disrupted allele of the glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) gene. J Clin Invest. 1997 Oct 1;100(7):1831-9. PMID:9312184 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1172/JCI119711
- ↑ Zisman A, Peroni OD, Abel ED, Michael MD, Mauvais-Jarvis F, Lowell BB, Wojtaszewski JF, Hirshman MF, Virkamaki A, Goodyear LJ, Kahn CR, Kahn BB. Targeted disruption of the glucose transporter 4 selectively in muscle causes insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Nat Med. 2000 Aug;6(8):924-8. PMID:10932232 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/78693