Nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
=Structure= | =Structure= | ||
==General Features== | ==General Features== | ||
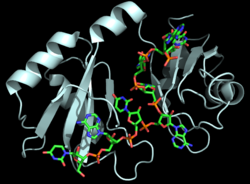
| - | Hrp1 is a single-stranded [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA-binding_protein RNA-binding protein] composed of two RNP-type [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_recognition_motif RNA-binding domains (RBDs)] arranged in tandem with a typical ßαßßαß architecture <ref name="GM3H"/>. The two RBDs have similar topolgies, both containing a central [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet antiparallel] four-stranded <scene name='78/783765/Beta_sheet/1'>ß-sheet</scene> with two [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix α-helices] running across one face <ref name="GM3H"/>. The β-strands of each βαβ domain are linked via hydrogen bonding between conserved residues, <scene name='78/783765/L166_g201/4'>Leu166 and Gly201</scene>. The two RBDs associate to form a deep and positively charged <scene name='78/781960/Hrp1-rna_interface_surface/3'>cleft</scene>, which constitutes the binding site for the RNA molecule <ref name="GM3H"/>. | + | '''Hrp1''' is a single-stranded [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA-binding_protein RNA-binding protein] composed of two RNP-type [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA_recognition_motif RNA-binding domains (RBDs)] arranged in tandem with a typical ßαßßαß architecture <ref name="GM3H"/>. The two RBDs have similar topolgies, both containing a central [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Beta_sheet antiparallel] four-stranded <scene name='78/783765/Beta_sheet/1'>ß-sheet</scene> with two [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_helix α-helices] running across one face <ref name="GM3H"/>. The β-strands of each βαβ domain are linked via hydrogen bonding between conserved residues, <scene name='78/783765/L166_g201/4'>Leu166 and Gly201</scene>. The two RBDs associate to form a deep and positively charged <scene name='78/781960/Hrp1-rna_interface_surface/3'>cleft</scene>, which constitutes the binding site for the RNA molecule <ref name="GM3H"/>. |
==Hrp1-RNA Interactions== | ==Hrp1-RNA Interactions== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==RBD-RBD Interactions and the Linker Region== | ==RBD-RBD Interactions and the Linker Region== | ||
| - | As mentioned above, Hrp1 is composed of two RBDs. The RBDs are connected by a <scene name='78/783765/Linker/3'>linker region</scene> (a short two-turn α-helix), which also contains a crucial residue for RNA binding. Ile234 in the linker region holds Ade6 in place in order to ensure proper <scene name='78/781945/Linker_rna/2'>via van der Waals contacts</scene> with the nearby Phe162. Experimental evidence from protein [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_magnetic_resonance nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)] data <ref name="GM3H"/> suggests that the two RBDs move independently prior to binding the PEE. Upon binding the PEE, the linker region adopts a short helical structure to rigidly hold the RBDs in place relative to each other. Aside from the linker helix, the only other interaction between the RBDs is <scene name='78/781945/Interaction_between_domains/8'>a single salt bridge</scene> between Lys231 and Asp271 <ref name="GM3H"/>. | + | As mentioned above, '''Hrp1''' is composed of two RBDs. The RBDs are connected by a <scene name='78/783765/Linker/3'>linker region</scene> (a short two-turn α-helix), which also contains a crucial residue for RNA binding. Ile234 in the linker region holds Ade6 in place in order to ensure proper <scene name='78/781945/Linker_rna/2'>via van der Waals contacts</scene> with the nearby Phe162. Experimental evidence from protein [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nuclear_magnetic_resonance nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)] data <ref name="GM3H"/> suggests that the two RBDs move independently prior to binding the PEE. Upon binding the PEE, the linker region adopts a short helical structure to rigidly hold the RBDs in place relative to each other. Aside from the linker helix, the only other interaction between the RBDs is <scene name='78/781945/Interaction_between_domains/8'>a single salt bridge</scene> between Lys231 and Asp271 <ref name="GM3H"/>. |
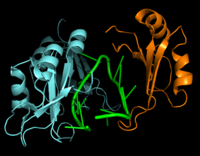
[[Image:Hrp1 RNA15 Cropped.png|200 px|left|thumb|Figure 2: Interaction between Hrp1 (blue), RNA15 (orange) and RNA (green).]] | [[Image:Hrp1 RNA15 Cropped.png|200 px|left|thumb|Figure 2: Interaction between Hrp1 (blue), RNA15 (orange) and RNA (green).]] | ||
Revision as of 09:22, 20 January 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein
Updated on 20-January-2019
References
- ↑ Wilson SM, Datar KV, Paddy MR, Swedlow JR, Swanson MS. Characterization of nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(5):1173-84. PMID:7962083
- ↑ Anderson JT, Wilson SM, Datar KV, Swanson MS. NAB2: a yeast nuclear polyadenylated RNA-binding protein essential for cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2730-41. PMID:8474438
- ↑ Loya TJ, O'Rourke TW, Reines D. Yeast Nab3 protein contains a self-assembly domain found in human heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-C (hnRNP-C) that is necessary for transcription termination. J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 25;288(4):2111-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.430678. Epub 2012, Nov 28. PMID:23192344 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.430678
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 4.19 4.20 4.21 Perez-Canadillas JM. Grabbing the message: structural basis of mRNA 3'UTR recognition by Hrp1. EMBO J. 2006 Jul 12;25(13):3167-78. Epub 2006 Jun 22. PMID:16794580
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Leeper TC, Qu X, Lu C, Moore C, Varani G. Novel protein-protein contacts facilitate mRNA 3'-processing signal recognition by Rna15 and Hrp1. J Mol Biol. 2010 Aug 20;401(3):334-49. Epub 2010 Jun 19. PMID:20600122 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2010.06.032
- ↑ Kessler MM, Henry MF, Shen E, Zhao J, Gross S, Silver PA, Moore CL. Hrp1, a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein that shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm, is required for mRNA 3'-end formation in yeast. Genes Dev. 1997 Oct 1;11(19):2545-56. PMID:9334319
- ↑ Clery A, Blatter M, Allain FH. RNA recognition motifs: boring? Not quite. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Jun;18(3):290-8. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002. PMID:18515081 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Cory A. Wuerch, Matthew Douglas Moore, Savannah Davis, Michal Harel, Jaime Prilusky