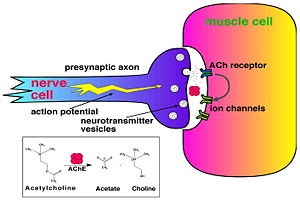
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is key enzyme in the nervous system of animals. By rapid hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine (ACh), AChE terminates neurotransmission at cholinergic synapses. It is a very fast enzyme, especially for a serine hydrolase, functioning at a rate approaching that of a diffusion-controlled reaction. AChE inhibitors are among the key drugs approved by the FDA for management of Alzheimer's disease (AD). The powerful toxicity of organophosphorus (OP) poisons is attributed primarily to their potent AChE inhibitors.
Key Enzyme in the Nervous System
Solution of the three-dimensional (3D) structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase (TcAChE) in 1991 opened up new horizons in research on an enzyme that had already been the subject of intensive investigation.[1] The unanticipated structure of this extremely rapid enzyme, in which the active site was found to be buried at the bottom of a , lined by (colored dark magenta), led to a revision of the views then held concerning substrate traffic, recognition and hydrolysis.[2] To understand how those aromatic residues behave with the enzyme, see Flexibility of aromatic residues in acetylcholinesterase. Solution of the 3D structure of acetylcholinesterase led to a series of theoretical and experimental studies, which took advantage of recent advances in theoretical techniques for treatment of proteins, such as
molecular dynamics and electrostatics and to site-directed mutagenesis, utilizing suitable expression
systems. Acetylcholinesterase hydrolysizes the neurotransmitter acetylcholine , producing group. ACh directly binds (via its nucleophilic Oγ atom) within the (ACh/TcAChE structure 2ace). The residues are also important in the ligand recognition [3]. After this binding acetylcholinesterase ACh.
Treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a disorder that attacks the central nervous system through progressive degeneration of its neurons. AD occurs in around 10% of the elderly and, as yet, there is no known cure. Patients with this disease develop dementia which becomes more severe as the disease progresses. It was suggested that symptoms of AD are caused by decrease of activity of cholinergic neocortical and hippocampal neurons. Treatment of AD by ACh precursors and cholinergic agonists was ineffective or caused severe side effects. ACh hydrolysis by AChE causes termination of cholinergic neurotransmission. Therefore, compounds which inhibit AChE might significantly increase the levels of ACh depleted in AD. Indeed, it was shown that AChE inhibitors improve the cognitive abilities of AD patients at early stages of the disease development.
Organophosphorus acid anhydride nerve agents
Organophosphorus (OP) acid anhydride nerve agents are potent inhibitors which rapidly phosphonylate AChE and then may undergo an internal dealkylation reaction (called "aging") to produce an OP-enzyme conjugate that cannot be reactivated.
As was mentioned above, AChE hydrolysizes the neurotransmitter , producing group. directly binds catalytic (via its nucleophilic Oγ atom). , O-(1,2,2-trimethylpropyl) methylphosphonofluoridate (fluorine atom is colored violet and phosphorus atom is colored darkmagenta), is one of the most toxic OPs. Soman inhibits AChE by to catalytic Ser200, . This process implicates nucleophilic attack of the Ser200 nucleophilic Oγ atom on the phosphorus atom of soman, with concomitant departure of its fluoride atom. After that AChE catalyzes the ("aging") of the soman or other OP. This causes irreversible inhibition of AChE, "aged" soman/AChE conjugate can not be reactivated. However, before “aging”, at the step of , AChE can be by nucleophiles, such as pralidoxime (2-PAM), resulting in of the phosphonyl adduct from Ser200 Oγ.
At the (2wfz) the catalytic His440 forms hydrogen bonds with Ser200 Oγ and Glu327 Oε1 via its Nε2 and Nδ1 nitrogens, respectively. The O2 atom of soman is within hydrogen bonding distance of His440 Nε2. Soman O1 mimicks carbonyl oxygen of ACh. A water molecule 1001 interacting with soman O2 is represented as a red ball. The active site residues of the nonaged soman/TcAChE are colored yellow. The O2 atom of the (2wg0) forms a salt bridge with His440 Nε2. The active site residues of the aged soman/TcAChE are colored pink. of the structures of the nonaged (2wfz) and aged (2wg0) conjugates reveals a small, but important, change within the active site - the imidazole ring of His440 is tilted back to a native-like conformation after dealkylation. The water molecule 1001, which interacts with soman O2 in the nonaged crystal structure, is not within hydrogen bonding distance of O2 in the aged crystal structure. 2-PAM binds poorly to the nonaged phosphonylated enzyme (its electron density was not found) and binds in an after soman aging to TcAChE (2wg1) [4].
Additional Resources
AChE inhibitors and substrates
Cholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase: Treatment of Alzheimer's disease
Quips › Acetylcholinesterase: A gorge-ous enzyme
Treatments:AChE Inhibitor References
Treatments:Alzheimer's Disease
Movies
Nature's Vacuum Cleaner - Binding of ACh to AChE
Movie by Richard Gillilan, Israel Silman & Joel L. Sussman
Introduction to Radiation Damage in Proteins
Movie by Richard Gillilan, Israel Silman & Joel L. Sussman
See: Specific chemical and structural damage to proteins produced by synchrotron radiation
Weik, Ravelli, Kryger, McSweeney, Raves, Harel, Gros, Silman, Kroon & Sussman
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 623-628 (2000).
Acetylcholinesterase Cleaving Acetylcholine
Movie by Alexandre Katos - USAMRICD
Sarin Inhibiting Acetylcholinesterase
Movie by Alexandre Katos - USAMRICD
2-PAM Reactivating Sarin-Inhibited Acetylcholinesterase
Movie by Alexandre Katos - USAMRICD
Acetylcholinesterase 3D structures
See Acetylcholinesterase 3D structures.