We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
CD47
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
CD47 consists of an extracellular N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain, a transmembrane domain and a C-terminal intracellular domain. | CD47 consists of an extracellular N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain, a transmembrane domain and a C-terminal intracellular domain. | ||
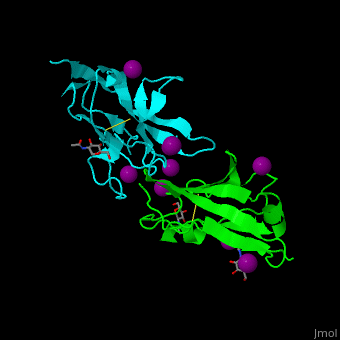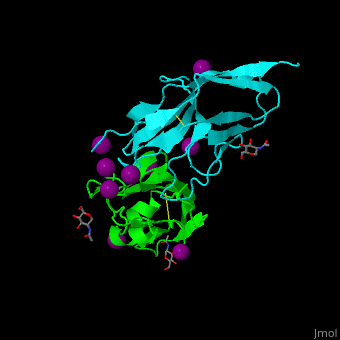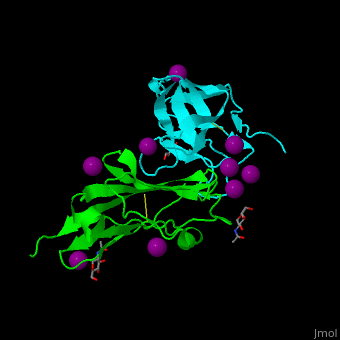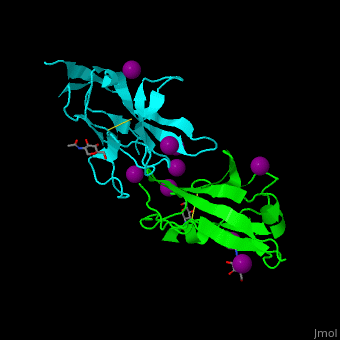
| - | *<scene name='53/538855/Cv/ | + | *<scene name='53/538855/Cv/3'>CD47 with SIRP α (cyan) and I-ions</scene> ([[2jjs]]).<ref>PMID:18657508</ref> |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:53, 10 February 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of CD47
Updated on 10-February-2019
2jjs, 2jjt, 4kjy – hCD47 extracellular domain (mutant) + SIRP α
2vsc – hCD47 extracellular domain (mutant)
4cmm - hCD47 extracellular domain (mutant) + tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type substrate
5iwl – hCD47 extracellular domain (mutant) + 5F9 diabody
5tz2, 5tzt, 5tz2 – hCD47 extracellular domain (mutant) + antibody
References
- ↑ Chao MP, Weissman IL, Majeti R. The CD47-SIRPalpha pathway in cancer immune evasion and potential therapeutic implications. Curr Opin Immunol. 2012 Apr;24(2):225-32. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2012.01.010. Epub, 2012 Feb 4. PMID:22310103 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.coi.2012.01.010
- ↑ Hatherley D, Graham SC, Turner J, Harlos K, Stuart DI, Barclay AN. Paired receptor specificity explained by structures of signal regulatory proteins alone and complexed with CD47. Mol Cell. 2008 Jul 25;31(2):266-77. PMID:18657508 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.05.026