Introduction
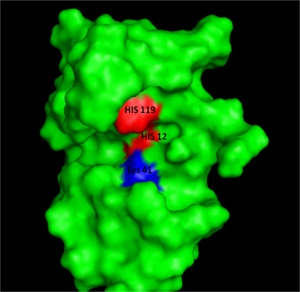
Figure I: Bovine Ribonuclease A. Colored residues are representative of amino acids important to both the acid base catalysis (Red: His12 and 119) and stabilization of the transition state (Blue: Lys41). Figure generated via
PymolRibonucleases or RNA depolymerases are enzymes that catalyze RNA degradation.[1] Ribonucleases are highly active in ruminants, such as cows, to digest large amounts of RNA produced by microorganisms in the stomach. Ruminants also have high amounts of ribonucleases to process nutrients from cellulose. One such ribonuclease, bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A or RNase A, was one of the most studied enzymes of the 20th century and was used as a model enzyme for many important findings in molecular science. [1] RNase A has been used as a foundational enzyme for the study of protein structure and function, molecular evolution, enzymatic catalysis, protein folding, protein semisynthesis, protein NMR spectroscropy, and protein oligomerization. RNase A is amenable to all of these areas due to its stability, small size, and because the three-dimensional structure is fully determined by its amino acid sequence.[1]
With its importance in molecular science, four researchers have won Nobel Prizes for their work related to RNase A. The 1972 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to three researchers for their work with RNase A on the folding of chains in RNase A and the stability of RNase A. Christian Anfinsen received the 1972 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his paper "Principles that govern the folding of protein chains." Stanford Moore and William H. Stein received the 1972 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for their paper "The chemical structures of pancreatic ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease." The 1984 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Robert Bruce Merrifield for his paper "Solid-phase synthesis" using RNase A.[1] RNase A was the first enzyme and third protein for which its amino acid sequence was correctly determined and the third enzyme and fourth protein whose three-dimensional structure was determined by X-ray diffraction analysis [1].[2][3] Disulfide bonds in RNase A were determined after developing a method using Fast Atom Bombardment Mass Spectrometry (FABMS) [2]. The methods of NMR spectroscopy [3] and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy [4] were developed with RNase A in determining protein structure and protein folding pathways. These new methods, developed with RNase A, could be used for further research to determine the protein structure and protein folding pathways of other proteins.[1]
RNase A and pancreatic ribonucleases have continued to serve as interesting enzymes for study due to the unusual biological actions of ribonuclease homologues. Onconase (ONC)[5] is a structural homologue of RNase A from the oocytes and early embryos of northern leopard frogs. Onconase shows both cytostatic (cell growth suppression) and cytotoxic (prevents cell divisions) characteristics for tumor cells and is currently in clinical trials for the treatment of non-squamous, non-small cell lung cancer.[6] Human pancreatic ribonucleases can be endowed with similar cytotoxic characteristics through specific protein engineering and are undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of late stage solid tumors.[7] Another human homologue of RNase A, angiogenin, is directly involved in neovascularization and mutations in angiogenin have been linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).[4]
Structure, Catalysis, and Substrate Binding
Structure
RNase A is made up of a single polypeptide chain of 124 residues. Of the 20 natural amino acids, RNase A possesses 19 of them, excluding tryptophan.[1] This single polypeptide chain is cross-linked internally by four disulfide linkages, which contribute to the stability of RNase A. Long four-stranded anti-parallel and three short make up the of RNase A.[1] The amino acid sequence was discovered to determine the three-dimensional structure of RNase A by Christian Anfinsen in the 1950s. Urea was used to denature RNase A, and mercaptoethanol was used to reduce and cleave the four disulfide bonds in RNase A to yield residues. Catalytic activity was lost due to denaturation. When the urea and mercaptoethanol were removed, the denatured ribonuclease refolded spontaneously into its correct tertiary structure with restoration of its catalytic activity. Disulfide bonds were also reformed in the same position. The Anfinsen experiment provided evidence that the amino acid sequence contained all the information required for the protein to fold into its native three-dimensional structure. Anfinsen received the 1972 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work with RNase A. Nevertheless, ensuing work showed some proteins require further assistance, such as molecular chaperones, to fold into their native structure.[5]
For a full list of protein structures related to RNase A, see Pancreatic Ribonucleases.
Ribonuclease A Catalysis
Acid Base Catalysis
In organic chemistry acid/base catalysis is the addition of an acid or base to accelerate a chemical reaction. RNase A also uses acid/base catatalysis to chemically change its substrates. Acidic or basic residues of the enzyme transfer protons to or from the reactant in order to stabilize the developing charges in the transition state. The transfer of protons usually creates better leaving groups, making the reaction more energetically favorable. Histidine is a very common amino acid residue involved in cataylsis, as histidine has a pKa value close to neutral, (pKa=6); therefore, histidine can both accept and donate protons at physiological pH.
Acid/base catalysis by an enzyme is dependent on the pH of the environment and the pKa's of their residues. The pKa value will increase for an acidic residue if the environment is hydrophobic or if the adjacent residues are of similar charges. In the same environmental conditions, a basic residue will decrease the pKa. This ability to alter the pKa of certain residues such as histidines, increases the diversity of reactions that an enzyme can perform [5].
Active Site Structure
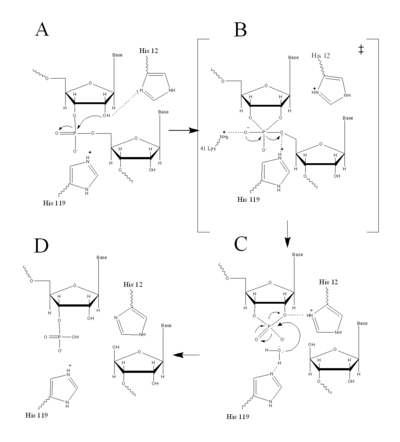
Figure II: RNase A Catalysis. (A) Initial attack of 2'hydroxyl stabilized by His12. (B) Pentavalent phosphorous intermediate. (C) 2'3' cyclic intermediate degradation. (D) Finished products: Two distinctive nucleotide sequences. Figure generated via
ChemdrawRNase A uses acid/base catlysis to speed up RNA hydrolysis. This occurs in the which is found in the cleft of RNase A and is the location of the chemical change in bound substrates. Subsites lining the active site cleft are important to the binding of single stranded RNA. Large quantities of positively charged residues, such as , recognize the negative charge on the phosphate back bone of the [6].
The active site for RNase A, although fairly nonspecific, has some specificity for sites RNA hydrolysis. , located next to the active site, will hydrogen bond to pyrimidine bases, but sterically hinder the binding of a purine on the 5' strand of OH. Thr45 significantly decreases the rate of hydrolysis of polymeric purine strands, such as poly A, by a thousand fold, as compared to polymeric pyrimidine strands.[6]
Early studies on RNase A catalysis showed that alkylation of His12 and His119 significantly decreased its catalytic activity, prompting the hypothesis that these two histidines were the acid/base catalyst. Confirmation of this hypothesis came when these histidines were replaced with alanine and the reaction rates of either mutation dropped by ten-thousand fold [6].
Acid Base Catalysis
In organic chemistry acid/base catalysis is the addition of an acid or base to accelerate a chemical reaction. RNase A also uses acid/base catatalysis to chemically change its substrates. Acidic or basic residues of the enzyme transfer protons to or from the reactant in order to stabilize the developing charges in the transition state. The transfer of protons usually creates better leaving groups, making the reaction more energetically favorable. Histidine is a very common amino acid residue involved in cataylsis, as histidine has a pKa value close to neutral, (pKa=6); therefore, histidine can both accept and donate protons at physiological pH.
Acid/base catalysis by an enzyme is dependent on the pH of the environment and the pKa's of their residues. The pKa value will increase for an acidic residue if the environment is hydrophobic or if the adjacent residues are of similar charges. In the same environmental conditions, a basic residue will decrease the pKa. This ability to alter the pKa of certain residues such as histidines, increases the diversity of reactions that an enzyme can perform [5].
Acid Base Catalysis by RNase A
RNase A catalyzes the cleavage of the Phosphodiester bonds in two steps: the formation of the pentavalent phosphate transition state and subsequent degradation of the 2’3’ cyclic phosphate intermediate using three main catalytic residues ( and ). An important part of the reaction is the ability of histidine (His 12 and His119) to both accept and donate electrons, allowing these histidine to be an acid or a base, making the reaction pH dependent [1].
RNA hydrolysis begins when abstracts a proton from the 2’ OH group on RNA; thus, assisting in the nucleophilic attack of the 2’ oxygen on the electrophilic phosphorus atom. A transition state is then formed, having a pentavalent phosphate, which is stabilized by the positively charged amino group of and the main chain amide nitrogen of Phe120. then protonates the 5' oxygen on the ribose ring and the transition state falls to form a 2’3’cyclic phosphate intermediate [1].
In a secondary and separate reaction, the 2’,3’ cyclic phosphate is hydrolyzed to a mixture of 2'phosphate and 3' hydroxyl. His12 donates a proton to the leaving group of this reaction, the 3’ oxygen of the cyclic intermediate. Simultaneously, His-119 abstracts the proton from a water molecule, activating it for nucleophilic attack. The activated water molecule attacks the cyclic phosphate causing the cleavage of the 2'3’ cyclic phosphate intermediate. The truncated nucleotide is then released with a 3’ phosphate group [1].
Ribonuclease A Substrate Binding
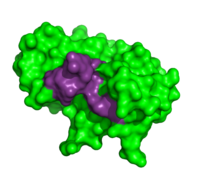
Thymidylic acid tetramer complexed with ribonuclease A
To determine the structural characteristics of RNA substrate binding to RNase A, X-ray crystallography was used to image inhibitory DNA tetramers bound to RNase A. DNA lacks the 2’OH essential to RNA cleavage, making the complex more conducive to crystallography. between RNase A and (1rta) provides information about specificity of the binding pocket subunits, B0, B1, B2 and B3. Many interactions observed in this complex occur between amino acid residues and the nucleic acid backbone. Examples of these interactions include hydrogen bonding between as well as hydrogen bonding between the O5’ oxygen of the ribose of . [7]
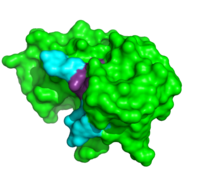
ApTpApApG complexed with ribonuclease A
Further binding pocket characterization was performed using (1rcn). This is closely positioned with the catalytic residues, and was important in determining the specificity of the binding sites of RNase A. In this complex, the B1 site is thought to exclusively bind to pyrimidine bases due to steric interactions and . When Thr45 was mutated to glycine, purines readily bound to the B1 site. [8] This interaction appears to be the driving force behind its inability to bind purines. While binding of other nucleobases to the B2 and B3 sites is possible, the imaging of this complex elucidated the preferences for adenosine bases at these two positions. In addition to its catalytic activity His119 has also been shown to be important in substrate specificity. This is due to the . When this site was mutated, the affinity for a poly(A) substrate was decreased by 104-fold. [9] It also establishes hydrogen bonding between . [10]
From the studies on RNase A complexes with deoxy nucleic acid tetramers, it has been established that this enzyme recognizes the substrate on both its phosphate backbone and on individual nucleobases. RNase A has a nonspecific B0 site, a B1 site specific to pyrimidines and a B3 and B4 site with a preference for adenosine bases. Similar to other enzymes, RNase A uses the hydrogen bonding distance between amino acids and the substrate to bind specifically to certain nucleobases. Studying the substrate recognition and specificity of enzymes such as RNase A is an important step in understanding the regulation of RNA within biological systems.
Inhibitors
(1dfj).
Due to the high rate of RNA hydrolysis by RNase A, mammalian cells have developed a protective inhibitor to prevent pancreatic ribonucleases from degrading cystolic RNA. Ribonuclease Inhibitor (RI) tightly associates to the active site of RNase A due to its . RI is a 50 kD protein that is composed of 16 repeating subunits of alpha helices and beta sheets, giving it a noticeable . The RI-RNase protein-protein interaction has the highest known affinity of any protein-protein interactions with an approximate dissociation constant (Kd) of 5.8 X 10-14 for almost all types of ribonucleases.[11] The ability to be selective for almost all types of RNases, and yet retain such a high Kd is product of its mechanism of inhibition. The interior residues of the horseshoe shaped RI are able to bind to the charged residues of the active site cleft of RNase A, such as . By studying the amphibian RNase, Onconase, the residues Lys7 and Gln11 of RNase A were shown to be the most important in this interaction. In onconase, these residues are replaced with non-charged amino acids, which help prevent the binding of RI to the protein [12]




