Motifs In Proteins
The term "motif" when used in structural biology tends to refer to one of two cases:
- A particular amino-acid sequence that characterises a biochemical function
- A set of secondary structure elements that defines a functional or structural role
There are a great number of protein sequence motifs identified, many of which have well defined structural or functional roles. One such example of this is the so-called zinc finger motif which is readily identified from the following consensus sequence pattern (where "X" represents any amino acid):
Cys - X(2-4) - Cys - X(3) - Phe - X(5) - Leu - X(2) - His - X(3) - His
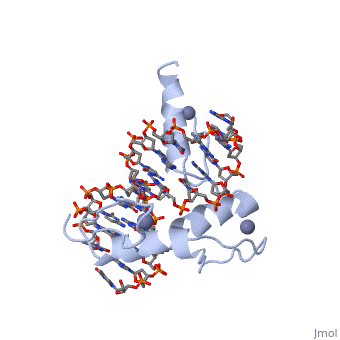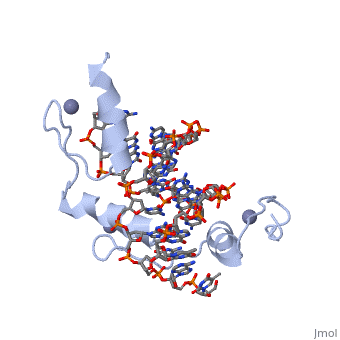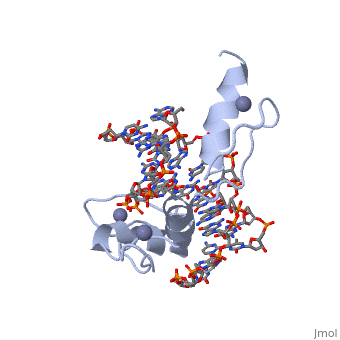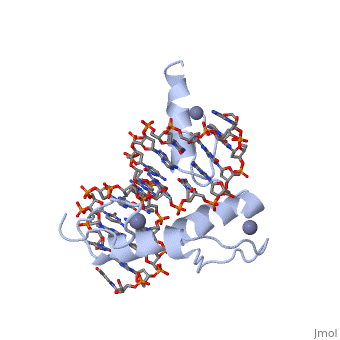
The example structure shown to is that of Zif268 protein-DNA complex from Mus musculus (PDB entry 1AAY). In this example (a C2H2 class zinc finger) the conserved and residues form ligands to a whose coordination is essential to stabilise the tertiary fold of the protein. The fold is important because it helps orientate the to bind to the .
However, there are also a number of repeated patterns and functional motifs revealed when the protein structure is examined. This page aims to introduce some of the main types of motif illustrating them on protein structures from the PDB.
Secondary structure elements
Proteins are formed from linear chains of amino acids joined together by peptide bonds. These chains then fold up to form the three dimensional shape. However, the relative rigidity of the peptide bond combined with the presence of amino acid sidechains, means that not all conformations are acceptable and there are many cases where the various atoms in the chain start to collide with one another. Two of the most stable (and therefore most commonly observed) conformations are the α-helix and the β-pleated sheet. These along with a number of small turns in the chain and random coil (folds that do not fit into a classification) are known as secondary structures.
α-helices
In the has been coloured by secondary structure (α-helices are coloured magenta and β-strands are coloured yellow). The is formed when the amino acid backbone forms a right handed spiral with 3.6 amino acids per turn. The , away from the centre of the helix, where they can interact with solvent, other protein, small molecules or macromolecules. The structure is stabilised by regular hydrogen bonds that form between the backbone carbonyl oxygens and amide hydrogens. The bonding pattern for the α-helix is characterised by the , this is known as an (i, i+4) interaction. The alpha-helix can take other less common forms including π-helices, 310-helices and their left handed forms (see table 1 for the helix parameters).
Table 1:
| Type of helix |
Bonding pattern |
Residues per turn |
Rise per residue |
Radius of helix |
| 310-helix |
(i, i+3) |
3.0 |
2.0 |
1.9 |
| α-helix |
(i, i+4) |
3.6 |
1.5 |
2.3 |
| π-helix |
(i, i+5) |
4.3 |
1.1 |
2.8 |
β-sheets
In the has been coloured by secondary structure (α-helices are coloured magenta and β-strands are coloured yellow). A single can technically be described as a flat helix with 2 residues per turn although this may not be initially obvious.
When two or more beta strands lie next to each other, forming hydrogen bonds between them, this is what is termed a . As the backbones need to come close together to interact and form a sheet, the . As the polypeptide chain is synthesised from the amino terminus to the carboxyl terminus it has a directionality (represented in the cartoon format as an arrowhead on each beta strand). β-sheets therefore occur in two varieties:
- - here the beta strands aligned next to each other run in opposite directions. As the interacting carbonyls and amides align well, the hydrogen bonds appear to be straight.
- - here the interacting strands run alongside each other and point in the same direction. In this conformation the carbonyl oxygen and the amides tend to be more staggered than in an anti-parallel sheet, therefore the hydrogen bonds tend to be angled. Also note the rare (i, i+2) bond within the lower strand.
Turns and loops
There are a number of small hydrogen bonded motifs and patterns which are observed regularly. These are described below:
- - originally defined by the one hydrogen bond common to all (an i, i+3 hydrogen bond) but some modern descriptions do not require a hydrogen bond.
- Beta Bulge Loops - often associated with beta sheets and result from an additional residue being found in one strand. This interrupts the regular hydrogen bonding and causes a distinctive bulge.
- Alpha turns - the simplest of all motifs and is characterised by one (i, i+4) hydrogen bond. It is found as part of the hydrogen bonding network of alpha helices as well as occurring on its own.
- - a common motif found at the C-termini of alpha helices which is essentially a reverse turn that breaks the alpha helix out of its cycle. It is characterised by the presence of a left handed residue and two hydrogen bonds: an i, i+3 bond and an i, i+5 bond.
- Gamma Turns - these rarer type of turns are characterised by an (i, i+2) hydrogen bond, which is rather weak because of the bent geometry involved.
These secondary structure motifs can be combined to form functional motifs, the most well known of which is the helix-turn-helix motif found in a number of DNA-binding proteins. The computational identification of these motifs is straightforward but made complicated by the fact that not all helix-turn-helix motifs bind DNA. The problem faced here is therefore one involving the distinguishing between true and false positives. The structure to the right is that of lambda repressor bound to DNA. The helix-turn-helix motif is readily identified in green.
Nests
Smaller than loops and turns are some recently discovered motifs known as "nests". These are mainchain conformations where 3 successive amide groups form a positively charged concavity capable of binding one or more negatively charged atoms (Figure 1). They are characterised by alternating enantiomeric mainchain dihedral angles from the alpha and gamma regions of the Ramachandran plot, and can be of RL (right handed - left handed) or LR type. They are most commonly found as part of previously described hydrogen bonded structural motifs but are also found at functional sites.
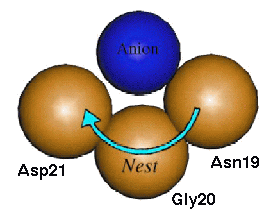
These basic units can be combined in succession to form more complex motifs and come in two categories:
- Compound nests - occur where the nests overlap so that the residues alternate between R and L forms (e.g. RL, RLR, RLRL)
- Tandem nests - where two nests sit side by side (e.g. RLLR, LRRL, RLLRRL)
In compound nests the result is a long chain with all the overlapping nests facing a similar direction. This basically forms a much wider nest that is capable of binding a larger anionic group of atoms such as the phosphate ion, and are usually functionally important motifs. Tandem nests are not as common and, due to the greater change in the direction that adjacent nests face, only seem to perform functional roles when found in conjunction with one or more compound nests.
One of the most well known functional compound nests is found in the phosphate-binding loop of Ras protein (PDB entry 5p21). The is a well described ATP- or GTP-binding loop present in a large superfamily of important proteins which includes G-proteins and kinases. The main feature of the P-loop is a long compound LRLR nest that . However, this is an example of a motif where the ligand also binds to the free main chain NH groups at the N-terminus of an alpha helix. On closer inspection it becomes evident that this interaction is in addition to the compound nest and does not interfere with it. Therefore the P-loop is actually more accurately described as a compound LRLR nest and an adjacent helical N-terminus that collectively bind to the α- and β-phosphates of the GDP substrate. The P-loop, which is retained throughout the superfamily, has a highly conserved GxxxxGKS/T consensus sequence (where the xxGK section forms the LRLR compound nest).
Templates and Active Sites
Moving away from secondary structure elements, loop and nests, another type of structural motif is that of enzyme active sites. These structural motifs are usually more difficult to detect as they can be discontinuous, often involving elements widely spaced along the sequence. One such example is that of the "catalytic triad" of the serine proteases.
Serine proteases are found in a number of organisms but common to their function is the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. These enzymes catalyse the reaction using a highly reactive serine residue to attack the carbonyl group of the backbone to be hydrolysed. The chemistry of this reaction and the regeneration of the active site, requires the presence of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. In chymotrypsin (PDB entry 1ab9) these residues are (Ser-195, His-57 and Asp-102) whereas in the bacterial subtilisin (PDB entry 1st2) the site is formed by (Ser-221, His-64 and Asp-32). These two proteins are evolutionary unrelated and this is the classic example of convergent evolution to solve the problem of peptide bond hydrolysis.
The detection of these types of motif is almost impossible by looking at the amino acid sequence: there is no evolutionary relationship to detect, the residues are ordered differently in the sequence, and the spacing between the residues also varies. These motifs can be detected relativeley easily using structural comparison, particularly template-based motif detection algorithms. Note that the global folds of subtilisin and chymotrypsin are very different so the site could not have been detected using such methods. Click to see the catalytic triad in and respectively.