We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Parvin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
m (Alpha-parvin moved to Parvin: requested by Editor) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<StructureSection load='2vzc' size='450' side='right' scene='Alpha-parvin/Cv/1' caption='Human C-terminal domain of α-parvin complex with MPD, glycerol and TRS (PDB code [[2vzc]])'> | <StructureSection load='2vzc' size='450' side='right' scene='Alpha-parvin/Cv/1' caption='Human C-terminal domain of α-parvin complex with MPD, glycerol and TRS (PDB code [[2vzc]])'> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
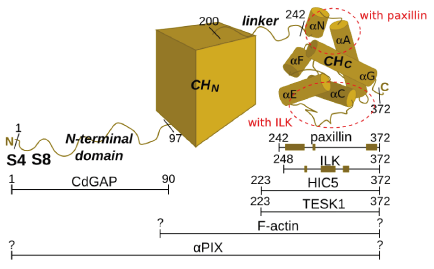
| - | + | '''Alpha-parvin'''<ref>PMID: 11171322</ref> (APAR), also known as '''actopaxin'''<ref>PMID: 11134073</ref> or '''CH domain-containing integrin-linked kinase (ILK)-binding protein''' (CH-ILK-BP)<ref>PMID: 11331308</ref> is an adapter protein known to interact with a number of focal adhesion proteins leading to focal adhesion stabilisation. Knock-out analysis confirmed it to be essential for efficient directional cell migration during embryogenesis in mice<ref>PMID: 19798050</ref>. Spatially and temporarily regulated dynamic changes in the phosphorylation status of alpha-parvin at serines 4 and 8 and consequent changes in affinities towards its binding partners (icluding CdGAP, TESK1 and possibly others, e.g. ILK) may be responsible for 1) focal adhesion turnover (disassembly of old adhesions, assembly of new ones) and 2) actin cytoskeleton reorganization, two interrelated processes contributing to cell migration.<ref>PMID: 15353548</ref><ref>PMID: 15817463</ref><ref>PMID: 16860736</ref><ref>PMID: 15872073</ref> | |
'''Beta-parvin''' (BPAR) is an actin-binding protein which contains calponin homo;ogy (CH) domains which bind actin filaments. BPAR which has a role in cytoskeleton organization and cell adhesion. BPAR inhibits integrin-linked kinase signaling and is downregulated in breast tumors<ref>PMID: 15467740</ref> | '''Beta-parvin''' (BPAR) is an actin-binding protein which contains calponin homo;ogy (CH) domains which bind actin filaments. BPAR which has a role in cytoskeleton organization and cell adhesion. BPAR inhibits integrin-linked kinase signaling and is downregulated in breast tumors<ref>PMID: 15467740</ref> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Olski TM, Noegel AA, Korenbaum E. Parvin, a 42 kDa focal adhesion protein, related to the alpha-actinin superfamily. J Cell Sci. 2001 Feb;114(Pt 3):525-38. PMID:11171322
- ↑ Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE. Actopaxin, a new focal adhesion protein that binds paxillin LD motifs and actin and regulates cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1435-48. PMID:11134073
- ↑ Tu Y, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Hua Y, Wu C. A new focal adhesion protein that interacts with integrin-linked kinase and regulates cell adhesion and spreading. J Cell Biol. 2001 Apr 30;153(3):585-98. PMID:11331308
- ↑ Montanez E, Wickstrom SA, Altstatter J, Chu H, Fassler R. Alpha-parvin controls vascular mural cell recruitment to vessel wall by regulating RhoA/ROCK signalling. EMBO J. 2009 Oct 21;28(20):3132-44. Epub 2009 Oct 1. PMID:19798050 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.295
- ↑ Clarke DM, Brown MC, LaLonde DP, Turner CE. Phosphorylation of actopaxin regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 13;166(6):901-12. Epub 2004 Sep 7. PMID:15353548 doi:10.1083/jcb.200404024
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Brown MC, Bouverat BP, Turner CE. Actopaxin interacts with TESK1 to regulate cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21680-8. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817463 doi:10.1074/jbc.M500752200
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ Yang Y, Guo L, Blattner SM, Mundel P, Kretzler M, Wu C. Formation and phosphorylation of the PINCH-1-integrin linked kinase-alpha-parvin complex are important for regulation of renal glomerular podocyte adhesion, architecture, and survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):1966-76. Epub 2005 May 4. PMID:15872073 doi:10.1681/ASN.2004121112
- ↑ Mongroo PS, Johnstone CN, Naruszewicz I, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Sung RK, Carnio L, Rustgi AK, Hannigan GE. Beta-parvin inhibits integrin-linked kinase signaling and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene. 2004 Nov 25;23(55):8959-70. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208112. PMID:15467740 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208112
- ↑ Hynes RO. The extracellular matrix: not just pretty fibrils. Science. 2009 Nov 27;326(5957):1216-9. PMID:19965464 doi:10.1126/science.1176009
- ↑ Barczyk M, Carracedo S, Gullberg D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010 Jan;339(1):269-80. Epub 2009 Aug 20. PMID:19693543 doi:10.1007/s00441-009-0834-6
- ↑ Wolfenson H, Henis YI, Geiger B, Bershadsky AD. The heel and toe of the cell's foot: a multifaceted approach for understanding the structure and dynamics of focal adhesions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Nov;66(11):1017-29. PMID:19598236 doi:10.1002/cm.20410
- ↑ Zaidel-Bar R, Itzkovitz S, Ma'ayan A, Iyengar R, Geiger B. Functional atlas of the integrin adhesome. Nat Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;9(8):858-67. PMID:17671451 doi:10.1038/ncb0807-858
- ↑ Wolfenson H, Henis YI, Geiger B, Bershadsky AD. The heel and toe of the cell's foot: a multifaceted approach for understanding the structure and dynamics of focal adhesions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 2009 Nov;66(11):1017-29. PMID:19598236 doi:10.1002/cm.20410
- ↑ Zaidel-Bar R, Geiger B. The switchable integrin adhesome. J Cell Sci. 2010 May 1;123(Pt 9):1385-8. PMID:20410370 doi:10.1242/jcs.066183
- ↑ Gardel ML, Schneider IC, Aratyn-Schaus Y, Waterman CM. Mechanical integration of actin and adhesion dynamics in cell migration. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2010 Nov 10;26:315-33. PMID:19575647 doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.011209.122036
- ↑ Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S. Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Dec;14(12):4813-25. Epub 2003 Sep 5. PMID:12960424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0308
- ↑ Olski TM, Noegel AA, Korenbaum E. Parvin, a 42 kDa focal adhesion protein, related to the alpha-actinin superfamily. J Cell Sci. 2001 Feb;114(Pt 3):525-38. PMID:11171322
- ↑ Wang X, Fukuda K, Byeon IJ, Velyvis A, Wu C, Gronenborn A, Qin J. The structure of alpha-parvin CH2-paxillin LD1 complex reveals a novel modular recognition for focal adhesion assembly. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 25;283(30):21113-9. Epub 2008 May 28. PMID:18508764 doi:10.1074/jbc.M801270200
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE. Actopaxin, a new focal adhesion protein that binds paxillin LD motifs and actin and regulates cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec 25;151(7):1435-48. PMID:11134073
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Brown MC, Bouverat BP, Turner CE. Actopaxin interacts with TESK1 to regulate cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21680-8. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817463 doi:10.1074/jbc.M500752200
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ Curtis M, Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE. Actopaxin is phosphorylated during mitosis and is a substrate for cyclin B1/cdc2 kinase. Biochem J. 2002 Apr 15;363(Pt 2):233-42. PMID:11931650
- ↑ Clarke DM, Brown MC, LaLonde DP, Turner CE. Phosphorylation of actopaxin regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 13;166(6):901-12. Epub 2004 Sep 7. PMID:15353548 doi:10.1083/jcb.200404024
- ↑ Ishibe S, Joly D, Zhu X, Cantley LG. Phosphorylation-dependent paxillin-ERK association mediates hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated epithelial morphogenesis. Mol Cell. 2003 Nov;12(5):1275-85. PMID:14636584
- ↑ Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S. Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Dec;14(12):4813-25. Epub 2003 Sep 5. PMID:12960424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0308
- ↑ Clarke DM, Brown MC, LaLonde DP, Turner CE. Phosphorylation of actopaxin regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Biol. 2004 Sep 13;166(6):901-12. Epub 2004 Sep 7. PMID:15353548 doi:10.1083/jcb.200404024
- ↑ Montanez E, Wickstrom SA, Altstatter J, Chu H, Fassler R. Alpha-parvin controls vascular mural cell recruitment to vessel wall by regulating RhoA/ROCK signalling. EMBO J. 2009 Oct 21;28(20):3132-44. Epub 2009 Oct 1. PMID:19798050 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.295
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Brown MC, Bouverat BP, Turner CE. Actopaxin interacts with TESK1 to regulate cell spreading on fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 3;280(22):21680-8. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817463 doi:10.1074/jbc.M500752200
- ↑ LaLonde DP, Grubinger M, Lamarche-Vane N, Turner CE. CdGAP associates with actopaxin to regulate integrin-dependent changes in cell morphology and motility. Curr Biol. 2006 Jul 25;16(14):1375-85. PMID:16860736 doi:S0960-9822(06)01676-9
- ↑ Yang Y, Guo L, Blattner SM, Mundel P, Kretzler M, Wu C. Formation and phosphorylation of the PINCH-1-integrin linked kinase-alpha-parvin complex are important for regulation of renal glomerular podocyte adhesion, architecture, and survival. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Jul;16(7):1966-76. Epub 2005 May 4. PMID:15872073 doi:10.1681/ASN.2004121112
- ↑ Attwell S, Mills J, Troussard A, Wu C, Dedhar S. Integration of cell attachment, cytoskeletal localization, and signaling by integrin-linked kinase (ILK), CH-ILKBP, and the tumor suppressor PTEN. Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Dec;14(12):4813-25. Epub 2003 Sep 5. PMID:12960424 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0308
- ↑ Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP. SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 May 26;95(11):5857-64. PMID:9600884
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Espinoza-Fonseca LM. Reconciling binding mechanisms of intrinsically disordered proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 May 8;382(3):479-82. Epub 2009 Mar 3. PMID:19265676 doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.02.151
- ↑ Iakoucheva LM, Radivojac P, Brown CJ, O'Connor TR, Sikes JG, Obradovic Z, Dunker AK. The importance of intrinsic disorder for protein phosphorylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004 Feb 11;32(3):1037-49. Print 2004. PMID:14960716 doi:10.1093/nar/gkh253
- ↑ Collins MO, Yu L, Campuzano I, Grant SG, Choudhary JS. Phosphoproteomic analysis of the mouse brain cytosol reveals a predominance of protein phosphorylation in regions of intrinsic sequence disorder. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2008 Jul;7(7):1331-48. Epub 2008 Apr 3. PMID:18388127 doi:10.1074/mcp.M700564-MCP200
- ↑ Friedberg F. Singlet CH domain containing human multidomain proteins: an inventory. Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Mar;37(3):1531-9. Epub 2009 May 21. PMID:19459066 doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9554-y
- ↑ Friedberg F. Duplex (or quadruplet) CH domain containing human multidomain proteins: an inventory. Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Apr;37(4):1707-16. Epub 2009 Jun 30. PMID:19565353 doi:10.1007/s11033-009-9589-0
- ↑ Stradal T, Kranewitter W, Winder SJ, Gimona M. CH domains revisited. FEBS Lett. 1998 Jul 17;431(2):134-7. PMID:9708889
- ↑ Sjoblom B, Ylanne J, Djinovic-Carugo K. Novel structural insights into F-actin-binding and novel functions of calponin homology domains. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2008 Dec;18(6):702-8. Epub 2008 Nov 13. PMID:18952167 doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2008.10.003
- ↑ Gimona M, Djinovic-Carugo K, Kranewitter WJ, Winder SJ. Functional plasticity of CH domains. FEBS Lett. 2002 Feb 20;513(1):98-106. PMID:11911887
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Wang X, Fukuda K, Byeon IJ, Velyvis A, Wu C, Gronenborn A, Qin J. The structure of alpha-parvin CH2-paxillin LD1 complex reveals a novel modular recognition for focal adhesion assembly. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jul 25;283(30):21113-9. Epub 2008 May 28. PMID:18508764 doi:10.1074/jbc.M801270200
- ↑ Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C, Qin J. The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. PMID:20005845 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Lorenz S, Vakonakis I, Lowe ED, Campbell ID, Noble ME, Hoellerer MK. Structural analysis of the interactions between paxillin LD motifs and alpha-parvin. Structure. 2008 Oct 8;16(10):1521-31. PMID:18940607 doi:10.1016/j.str.2008.08.007
- ↑ Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C, Qin J. The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. PMID:20005845 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028
- ↑ Fukuda K, Gupta S, Chen K, Wu C, Qin J. The pseudoactive site of ILK is essential for its binding to alpha-Parvin and localization to focal adhesions. Mol Cell. 2009 Dec 11;36(5):819-30. PMID:20005845 doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2009.11.028
- ↑ Wickstrom SA, Lange A, Montanez E, Fassler R. The ILK/PINCH/parvin complex: the kinase is dead, long live the pseudokinase! EMBO J. 2010 Jan 20;29(2):281-91. Epub 2009 Dec 24. PMID:20033063 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.376
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Marcin Jozef Suskiewicz, Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Jaime Prilusky