This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Ephrin receptor
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
EPHR domains include an ectodomain (residues 23-435) containing the LBD (residues 23-326), a second fibronectin III domain (fn3) (residues 446-539), a transmembrane domain (residues 539-563), a kinase domain (residues 596-900) and a sterile-α-motif (SAM) domain (residues 908-972). | EPHR domains include an ectodomain (residues 23-435) containing the LBD (residues 23-326), a second fibronectin III domain (fn3) (residues 446-539), a transmembrane domain (residues 539-563), a kinase domain (residues 596-900) and a sterile-α-motif (SAM) domain (residues 908-972). | ||
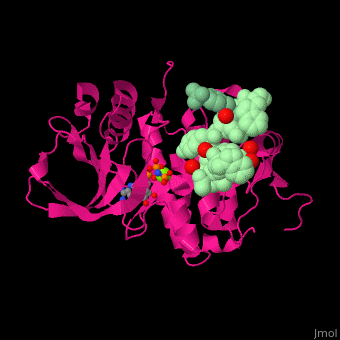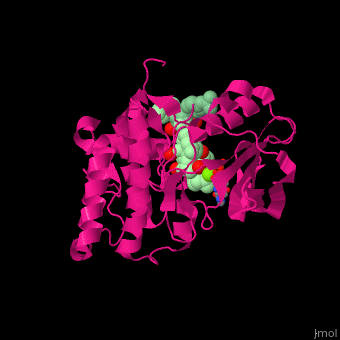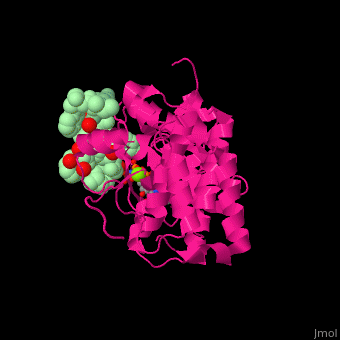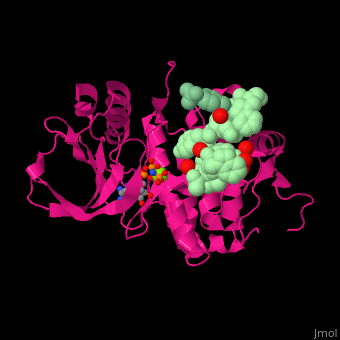
| - | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/ | + | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/8'>Ephrin A3 receptor with peptide substrate, nucleotide derivative and Mg+2 ion</scene>. Water molecules are shown as red spheres. |
| - | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/ | + | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/9'>Nucleotide derivative and Mg+2 ion binding site</scene>. |
| - | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/ | + | <scene name='45/450911/Cv/10'>Peptide substrate binding site</scene> ([[3fxx]]).<ref>PMID:19678838</ref> |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
== 3D Structures of ephrin receptors == | == 3D Structures of ephrin receptors == | ||
Revision as of 09:44, 11 March 2019
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of ephrin receptors
Updated on 11-March-2019
References
- ↑ Pitulescu ME, Adams RH. Eph/ephrin molecules--a hub for signaling and endocytosis. Genes Dev. 2010 Nov 15;24(22):2480-92. doi: 10.1101/gad.1973910. PMID:21078817 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/gad.1973910
- ↑ Genander M, Frisen J. Ephrins and Eph receptors in stem cells and cancer. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;22(5):611-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.005. PMID:20810264 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2010.08.005
- ↑ Davis TL, Walker JR, Allali-Hassani A, Parker SA, Turk BE, Dhe-Paganon S. Structural recognition of an optimized substrate for the ephrin family of receptor tyrosine kinases. FEBS J. 2009 Aug;276(16):4395-404. PMID:19678838 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07147.x