We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Mark Macbeth/Sandbox5
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: =Sex lethal: RNA-binding protein= == Introduction == [[Image:Sxl function 2018-03-27 at 2.41.00 PM.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Sxl sex determination and dosage compensation pathways....) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Sex lethal: RNA-binding protein= | =Sex lethal: RNA-binding protein= | ||
| - | + | <StructureSection load='1B7F' size='350' frame='true' side='right' caption='Sex lethal (PDB: 1B7F)' scene='78/782600/Opening_image/2'> | |
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
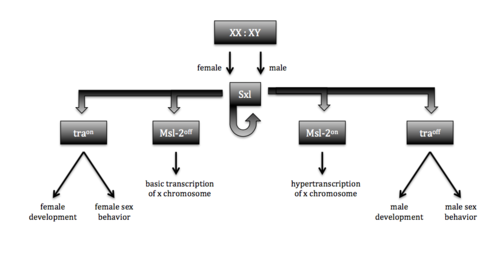
[[Image:Sxl function 2018-03-27 at 2.41.00 PM.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Sxl sex determination and dosage compensation pathways. Functionality of Sxl is determined by the number of X chromosomes. The functional protein (XX) causes a cascade that leads to female structures and behaviors, while the nonfunctional protein results in the default male structures and behaviors.]]Sex lethal (Sxl) is an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA-binding_protein RNA-binding protein] that plays a vital role in sex determination and dosage compensation in ''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drosophila_melanogaster Drosophila melanogaster]'', the common fruit fly <ref name="Black">doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720</ref>. Sxl binds specifically to the continuous single-stranded RNA sequence 5’-UGUUUUUUU <ref name="Handa">doi:10.1038/19242 | [[Image:Sxl function 2018-03-27 at 2.41.00 PM.png|500 px|right|thumb|Figure 1. Sxl sex determination and dosage compensation pathways. Functionality of Sxl is determined by the number of X chromosomes. The functional protein (XX) causes a cascade that leads to female structures and behaviors, while the nonfunctional protein results in the default male structures and behaviors.]]Sex lethal (Sxl) is an [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RNA-binding_protein RNA-binding protein] that plays a vital role in sex determination and dosage compensation in ''[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drosophila_melanogaster Drosophila melanogaster]'', the common fruit fly <ref name="Black">doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161720</ref>. Sxl binds specifically to the continuous single-stranded RNA sequence 5’-UGUUUUUUU <ref name="Handa">doi:10.1038/19242 | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| - | + | ||
===RRMs=== | ===RRMs=== | ||
[[Image:ElectroPOSITIVE.png|250 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Electropositive binding cleft. Electropositive region shown in blue and electronegative region shown in red. The electropositive binding cleft accommodates the phosphodiester backbone of the RNA molecule to which Sxl binds.]] The sex-lethal protein (Sxl) is 354 amino acid residues long. It is composed of two highly conserved regions called <scene name='78/782600/Rbd1_and_rbd2/6'>RNA recognition motifs</scene> (RRMs) that function as a monomeric unit. Each RRM is approximately 90 amino acids long with a four stranded <scene name='78/782600/B-pleated_sheets/1'>β-pleated</scene> sheet and two <scene name='78/782600/Alpha_helices/2'>α-helices</scene>. The β-pleated sheets from each RRM interact with the RNA ligand, while the α-helices interact with each other to shape the protein <ref name="Clery"/>. The RRMs interact at <scene name='78/782600/Inter-domain_interactions/6'>two places</scene>: between the side chain of Lys 197 and the main chain carbonyl of Val 238 and between the side chains of Tyr 131 and Gln 239<ref name="Handa" />. The two RRMs are connected via an interdomain linker. The linker often forms a short 3<sub>10</sub> helix from Gly205 to Thr211.The interaction between the RRMs and the ligand is facilitated by the v-shaped <scene name='78/782600/Binding_cleft/8'>binding cleft</scene> formed by the β-pleated sheet of each RRM. The v-shaped cleft is strongly electropositive which also assists in ligand binding <ref name="Handa" /> (Figure 2). The presence of two RRMs increases RNA binding specificity by allowing for an elongated and continuous binding site <ref name="Clery">DOI 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002</ref>. | [[Image:ElectroPOSITIVE.png|250 px|left|thumb|Figure 2. Electropositive binding cleft. Electropositive region shown in blue and electronegative region shown in red. The electropositive binding cleft accommodates the phosphodiester backbone of the RNA molecule to which Sxl binds.]] The sex-lethal protein (Sxl) is 354 amino acid residues long. It is composed of two highly conserved regions called <scene name='78/782600/Rbd1_and_rbd2/6'>RNA recognition motifs</scene> (RRMs) that function as a monomeric unit. Each RRM is approximately 90 amino acids long with a four stranded <scene name='78/782600/B-pleated_sheets/1'>β-pleated</scene> sheet and two <scene name='78/782600/Alpha_helices/2'>α-helices</scene>. The β-pleated sheets from each RRM interact with the RNA ligand, while the α-helices interact with each other to shape the protein <ref name="Clery"/>. The RRMs interact at <scene name='78/782600/Inter-domain_interactions/6'>two places</scene>: between the side chain of Lys 197 and the main chain carbonyl of Val 238 and between the side chains of Tyr 131 and Gln 239<ref name="Handa" />. The two RRMs are connected via an interdomain linker. The linker often forms a short 3<sub>10</sub> helix from Gly205 to Thr211.The interaction between the RRMs and the ligand is facilitated by the v-shaped <scene name='78/782600/Binding_cleft/8'>binding cleft</scene> formed by the β-pleated sheet of each RRM. The v-shaped cleft is strongly electropositive which also assists in ligand binding <ref name="Handa" /> (Figure 2). The presence of two RRMs increases RNA binding specificity by allowing for an elongated and continuous binding site <ref name="Clery">DOI 10.1016/j.sbi.2008.04.002</ref>. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stacking_(chemistry) Intermolecular stacking] between the aromatic side chains and the nucleotide bases also contributes to RNA binding. In RRM2, U3-G4-U5 stack with <scene name='78/782600/Rrm2_residues_stacking/4'>V254, Y214, and F256</scene> respectively. In RRM1, residues <scene name='78/782600/Rrm1_intermolecular_stacking/4'>Y131, R195, N130, F170</scene> are involved in favorable intermolecular stacking of aromatic rings with nucleotides U6-U11<ref name="Handa" />. | [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stacking_(chemistry) Intermolecular stacking] between the aromatic side chains and the nucleotide bases also contributes to RNA binding. In RRM2, U3-G4-U5 stack with <scene name='78/782600/Rrm2_residues_stacking/4'>V254, Y214, and F256</scene> respectively. In RRM1, residues <scene name='78/782600/Rrm1_intermolecular_stacking/4'>Y131, R195, N130, F170</scene> are involved in favorable intermolecular stacking of aromatic rings with nucleotides U6-U11<ref name="Handa" />. | ||
| - | + | ||
==Autoregulation== | ==Autoregulation== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 01:27, 19 March 2019
Sex lethal: RNA-binding protein
| |||||||||||